Intro
Learn about prediabetes A1c levels, borderline diabetes diagnosis, and impaired glucose tolerance, understanding the risks and management of elevated blood sugar levels.
Prediabetes is a condition where an individual's blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. It is a critical stage, as it can lead to the development of type 2 diabetes if left untreated. One of the primary methods of diagnosing prediabetes is by measuring the hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels in the blood. In this article, we will delve into the world of prediabetes A1c levels, exploring what they mean, how they are measured, and what the implications are for individuals with prediabetes.
The importance of understanding prediabetes A1c levels cannot be overstated. With millions of people worldwide living with prediabetes, it is crucial to recognize the signs and symptoms of this condition. By doing so, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes, which can have severe consequences on overall health. The good news is that prediabetes is reversible, and with the right lifestyle changes and interventions, individuals can reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Understanding the concept of A1c levels is vital in the diagnosis and management of prediabetes. The A1c test measures the average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months, providing a comprehensive picture of an individual's blood sugar control. This test is essential, as it helps healthcare professionals identify individuals with prediabetes and monitor their progress over time. In the following sections, we will explore the different aspects of prediabetes A1c levels, including the normal ranges, the implications of elevated A1c levels, and the strategies for managing prediabetes.
Prediabetes A1c Levels: What Do They Mean?
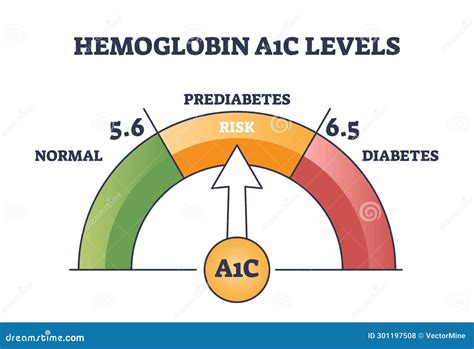
Understanding A1c Levels in Prediabetes
A1c levels in prediabetes are a crucial indicator of an individual's risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The higher the A1c level, the greater the risk. For example, an individual with an A1c level of 6.0% has a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes than someone with an A1c level of 5.8%. Understanding A1c levels is vital, as it enables healthcare professionals to develop personalized treatment plans and interventions to reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.The Importance of Early Detection

Risk Factors for Prediabetes
Certain risk factors increase an individual's likelihood of developing prediabetes. These risk factors include: * Age: 45 years or older * Family history: Having a first-degree relative with type 2 diabetes * Obesity: Being overweight or obese * Physical inactivity: Leading a sedentary lifestyle * Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanics/Latinos, and American Indians, are at higher risk * Previous history of gestational diabetes or delivering a baby over 4 kgStrategies for Managing Prediabetes

Lifestyle Changes for Prediabetes
Lifestyle changes are essential for managing prediabetes. Some of the key lifestyle changes include: * Quitting smoking * Limiting alcohol consumption * Getting enough sleep: Aiming for 7-8 hours of sleep per night * Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day * Monitoring blood sugar levels: Regularly checking blood sugar levels to track progressPrediabetes and Cardiovascular Disease
Prediabetes and Kidney Disease
Prediabetes is also a significant risk factor for kidney disease. Individuals with prediabetes are more likely to develop kidney disease, including chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease. Managing prediabetes can help reduce the risk of kidney disease. Some of the ways to reduce the risk of kidney disease include: * Monitoring kidney function: Regularly checking kidney function to track progress * Controlling blood sugar levels: Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels * Lowering blood pressure: Achieving a blood pressure of less than 120/80 mmHg * Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water throughout the dayPrediabetes and Mental Health
Prediabetes and Sleep
Prediabetes can affect sleep quality and duration. Individuals with prediabetes are more likely to experience sleep disturbances, including insomnia and sleep apnea. Managing prediabetes can help improve sleep quality and duration. Some of the ways to improve sleep quality and duration include: * Establishing a bedtime routine: Engaging in activities that promote relaxation * Creating a sleep-conducive environment: Making the bedroom a sleep haven * Avoiding caffeine and electronics before bedtime: Reducing stimulation before sleep * Getting regular physical activity: Participating in activities that promote relaxation and reduce stressConclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with prediabetes in the comments section below. Have you or someone you know been diagnosed with prediabetes? What steps have you taken to manage the condition? Share your story and help others understand the importance of managing prediabetes.
What is the normal range for A1c levels in prediabetes?
+The normal range for A1c levels in prediabetes is 5.7% to 6.4%.
What are the risk factors for developing prediabetes?
+The risk factors for developing prediabetes include age, family history, obesity, physical inactivity, and ethnicity.
How can I manage prediabetes and reduce my risk of type 2 diabetes?
+You can manage prediabetes and reduce your risk of type 2 diabetes by incorporating lifestyle changes, such as healthy eating, regular physical activity, and weight loss, and medical interventions, such as medications.
