Intro
Discover what prolactin is, a hormone regulating lactation, fertility, and growth, with related terms like prolactin levels, prolactinoma, and hyperprolactinemia, to understand its role in human health.
Prolactin is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland, a small endocrine gland located at the base of the brain. This hormone plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, particularly in lactation and reproductive processes. The importance of prolactin cannot be overstated, as it affects not only breastfeeding but also has implications for overall health and well-being. Understanding prolactin's role and its effects on the body is essential for both healthcare professionals and individuals seeking to manage their hormonal balance.
The significance of prolactin extends beyond its well-known function in milk production during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It also influences other physiological processes, including reproductive functions, immune response, and even mental health. The level of prolactin in the body can be influenced by various factors, including sleep, stress, and certain medications. Therefore, maintaining a healthy balance of prolactin is vital for preventing potential health issues related to its imbalance.
Prolactin's role in the body is multifaceted, and its effects can vary greatly depending on the context. For example, elevated levels of prolactin are necessary for lactation, but abnormally high levels can lead to conditions such as hyperprolactinemia, which may cause symptoms like infertility, erectile dysfunction, and galactorrhea (spontaneous milk production). On the other hand, low levels of prolactin can also have adverse effects, particularly in pregnant or breastfeeding women, where it may impact milk supply. The complexity of prolactin's functions underscores the need for a comprehensive understanding of its mechanisms and implications for health.
Introduction to Prolactin
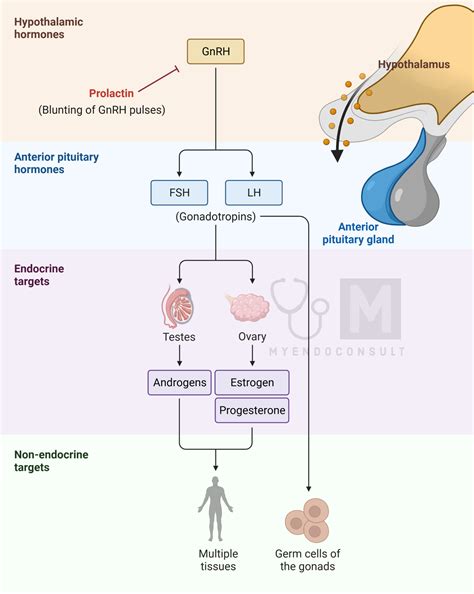
Prolactin is often referred to as the "milk hormone" due to its primary role in stimulating milk production in the breasts during pregnancy and breastfeeding. However, its influence extends beyond lactation. Prolactin is involved in over 300 bodily functions, including the regulation of the immune system, metabolism, and reproductive processes. The hormone is produced not only by the pituitary gland but also by other tissues in the body, such as the breast, uterus, and immune cells, highlighting its diverse roles.
Functions of Prolactin
The functions of prolactin can be broadly categorized into several key areas: - **Lactation:** Prolactin stimulates the growth of breast tissue during pregnancy and induces milk production after childbirth. It is essential for breastfeeding, ensuring the newborn receives necessary nutrients. - **Reproductive Functions:** Prolactin influences reproductive processes in both men and women, although its effects can vary. In women, high levels of prolactin can suppress gonadal function, leading to amenorrhea (absence of menstrual periods) and infertility. In men, elevated prolactin levels can cause hypogonadism, leading to decreased libido and erectile dysfunction. - **Immune Response:** Prolactin has immunomodulatory effects, meaning it can influence the immune system's response. It is involved in the regulation of immune cell function and cytokine production, which are crucial for fighting infections and diseases. - **Metabolic Processes:** Prolactin may also play a role in metabolic regulation, affecting factors such as energy balance, glucose metabolism, and lipid metabolism.Regulation of Prolactin Levels
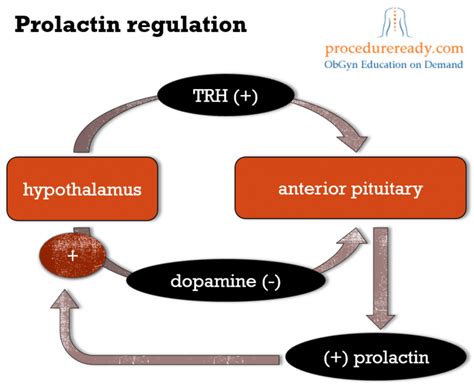
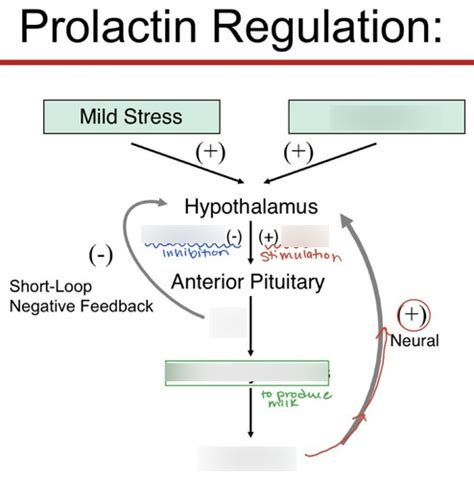
The regulation of prolactin levels is complex and involves various physiological and pathological factors. Normally, prolactin secretion is inhibited by dopamine, a neurotransmitter produced in the hypothalamus. When dopamine levels decrease or its action is blocked, prolactin secretion increases. This regulatory mechanism is crucial for maintaining normal prolactin levels.
Several factors can influence prolactin levels, including:
- Stress: Physical or psychological stress can elevate prolactin levels.
- Sleep: Prolactin levels typically increase during sleep, especially during the REM stage.
- Medications: Certain drugs, such as antipsychotics and antidepressants, can increase prolactin levels as a side effect.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy and breastfeeding are associated with high prolactin levels, while menopause can lead to decreased levels.
Implications of Abnormal Prolactin Levels
Abnormal prolactin levels, either too high or too low, can have significant health implications. Hyperprolactinemia (elevated prolactin levels) can cause: - Infertility - Galactorrhea (spontaneous milk production) - Amenorrhea (absence of menstrual periods) - Erectile dysfunction - Decreased libido - Osteoporosis (due to suppressed gonadal function)On the other hand, hypoprolactinemia (low prolactin levels) is less common but can affect milk supply in breastfeeding women and may have other metabolic implications.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Prolactin-Related Disorders

Diagnosing prolactin-related disorders typically involves measuring prolactin levels through blood tests. Imaging studies, such as MRI, may also be conducted to rule out pituitary tumors or other abnormalities that could be causing hormonal imbalances.
Treatment for prolactin-related disorders depends on the underlying cause. For hyperprolactinemia caused by pituitary tumors, treatment options may include:
- Medications: Dopamine agonists, such as bromocriptine and cabergoline, can help reduce prolactin secretion.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgical removal of the tumor may be necessary.
- Radiation Therapy: This can be an option for tumors that do not respond to medication or surgery.
For hypoprolactinemia, treatment is usually focused on addressing the underlying cause and may involve hormone replacement therapy in some cases.
Managing Prolactin Levels Naturally
While medical treatment is necessary for prolactin-related disorders, there are also natural ways to manage prolactin levels. These include: - **Dietary Changes:** Eating foods rich in vitamin B6, such as bananas and potatoes, can help regulate prolactin levels. - **Exercise:** Regular physical activity can reduce stress and help manage hormonal balance. - **Stress Reduction Techniques:** Practicing stress-reducing activities, such as yoga or meditation, can help minimize the impact of stress on prolactin levels. - **Adequate Sleep:** Ensuring sufficient sleep is crucial for maintaining normal prolactin levels and overall health.Prolactin and Mental Health

There is a significant link between prolactin and mental health. Elevated prolactin levels have been associated with various psychiatric conditions, including depression, anxiety, and psychosis. The exact mechanism of how prolactin influences mental health is complex and not fully understood, but it is believed to involve prolactin's effects on neurotransmitter systems and stress response.
Understanding the relationship between prolactin and mental health can provide insights into the development of new therapeutic strategies for treating psychiatric disorders. Moreover, recognizing the potential psychiatric effects of hyperprolactinemia is crucial for providing comprehensive care to individuals with prolactin-related disorders.
Prolactin's Role in Stress Response
Prolactin's involvement in the body's stress response is another critical aspect of its function. During stress, prolactin levels increase, which can have both protective and detrimental effects. On one hand, prolactin can help mitigate the negative impacts of stress by promoting adaptive responses. On the other hand, chronically elevated prolactin levels due to prolonged stress can contribute to various health problems, including mental health disorders.Conclusion and Future Perspectives
In conclusion, prolactin is a multifunctional hormone with a wide range of effects on the body, from lactation and reproductive processes to immune response and mental health. Understanding prolactin's mechanisms and implications for health is essential for the diagnosis and treatment of prolactin-related disorders. Future research should continue to explore the complex roles of prolactin, its regulation, and its interactions with other hormonal systems to uncover new therapeutic strategies for managing prolactin-related conditions and promoting overall well-being.
As research progresses, it is likely that new insights into prolactin's functions and dysregulation will emerge, offering potential for the development of more targeted and effective treatments. Moreover, raising awareness about the importance of prolactin and its impact on health can encourage individuals to take proactive steps in managing their hormonal balance, contributing to better health outcomes and quality of life.
What is the primary function of prolactin in the body?
+Prolactin's primary function is to stimulate milk production in the breasts during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but it also plays roles in reproductive processes, immune response, and mental health.
What causes elevated prolactin levels?
+Elevated prolactin levels can be caused by stress, certain medications, sleep, hormonal changes, and pituitary tumors, among other factors.
How can prolactin levels be managed naturally?
+Prolactin levels can be managed naturally through dietary changes, regular exercise, stress reduction techniques, and ensuring adequate sleep.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about prolactin and its effects on health. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in fostering a community that seeks to understand and manage hormonal balance for better well-being. Please feel free to comment, share this article with others who might find it informative, or explore further resources on managing prolactin levels and related health topics.
