Intro
Discover the Rhino virus, a common cold-causing rhinovirus, and learn about its symptoms, transmission, and treatment options, including prevention methods and remedies for rhino virus infection.
The rhinovirus is a type of virus that is commonly associated with the common cold. It is a member of the picornavirus family and is one of the most frequent causes of upper respiratory tract infections in humans. Rhinoviruses are highly contagious and can spread easily from person to person through contact with contaminated surfaces, airborne transmission, or close contact with an infected individual.
Rhinoviruses are incredibly diverse, with over 150 different strains identified to date. This diversity is one of the reasons why it's so challenging to develop a vaccine that can protect against all rhinovirus infections. Each strain can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and can affect people of all ages. However, young children, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to severe rhinovirus infections.
The symptoms of a rhinovirus infection can vary depending on the strain and the individual's overall health. Common symptoms include a runny nose, sneezing, coughing, sore throat, and fatigue. In some cases, rhinovirus infections can lead to more severe complications, such as bronchiolitis, pneumonia, or exacerbations of underlying respiratory conditions like asthma. Understanding the rhinovirus and its effects on human health is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Rhinovirus Structure and Genetics
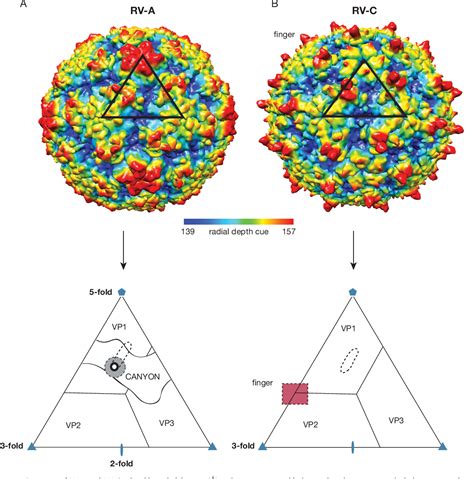
The rhinovirus is a small, single-stranded RNA virus that is approximately 20-30 nanometers in diameter. Its genetic material is composed of a single strand of RNA that is surrounded by a protein capsid. The capsid is made up of four proteins, which are arranged in a specific pattern to form the viral particle. The genetic material of the rhinovirus is highly variable, with different strains having distinct genetic sequences. This variability is one of the key factors that makes it challenging to develop a universal vaccine against rhinovirus infections.
Rhinovirus Replication Cycle
The replication cycle of the rhinovirus involves several key steps. First, the virus attaches to the surface of a host cell, typically a respiratory epithelial cell. The virus then penetrates the cell membrane and releases its genetic material into the cytoplasm. The viral RNA is translated into proteins, which are necessary for the replication of the viral genome. The new viral particles are then assembled and released from the host cell, allowing the infection to spread to other cells.Rhinovirus Transmission and Prevention

Rhinoviruses are highly contagious and can spread easily from person to person. The primary modes of transmission include contact with contaminated surfaces, airborne transmission, and close contact with an infected individual. To prevent the spread of rhinovirus infections, it's essential to practice good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, and avoiding touching your eyes, nose, and mouth.
Rhinovirus Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for rhinovirus infections, there are several treatment options available to help manage symptoms and prevent complications. Over-the-counter medications, such as pain relievers and decongestants, can help alleviate symptoms like headache, fever, and congestion. In some cases, prescription medications, such as antiviral drugs, may be necessary to treat more severe infections. It's also essential to get plenty of rest, stay hydrated, and use a humidifier to help relieve congestion.Rhinovirus and Asthma
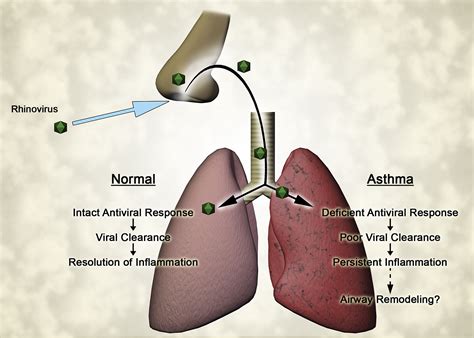
Rhinovirus infections are a common trigger for asthma exacerbations. The virus can cause inflammation and airway constriction, leading to symptoms like wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. People with asthma are more susceptible to severe rhinovirus infections, and it's essential to take steps to prevent and manage symptoms. This can include using controller medications, such as inhaled corticosteroids, and developing an asthma action plan to help manage symptoms and prevent exacerbations.
Rhinovirus and Other Respiratory Conditions
Rhinovirus infections can also exacerbate other respiratory conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and cystic fibrosis. The virus can cause inflammation and airway constriction, leading to symptoms like wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. In some cases, rhinovirus infections can lead to more severe complications, such as pneumonia or respiratory failure. It's essential to take steps to prevent and manage symptoms, such as getting vaccinated against flu and pneumonia, and using controller medications to manage underlying conditions.Rhinovirus Research and Development
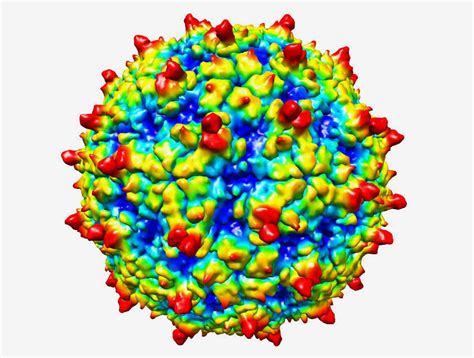
Researchers are working to develop new treatments and prevention strategies for rhinovirus infections. This includes the development of antiviral drugs, vaccines, and other therapies. One of the challenges in developing effective treatments is the high degree of genetic variability among rhinovirus strains. However, advances in fields like genomics and proteomics are helping researchers to better understand the virus and develop more effective treatments.
Rhinovirus and the Future of Respiratory Health
The rhinovirus is a significant public health concern, and it's essential to continue researching and developing new treatments and prevention strategies. By understanding the virus and its effects on human health, we can develop more effective ways to prevent and manage symptoms, and reduce the risk of complications. This includes developing vaccines, antiviral drugs, and other therapies, as well as promoting good hygiene and prevention practices.What is the most common cause of rhinovirus infections?
+Rhinovirus infections are most commonly caused by contact with contaminated surfaces, airborne transmission, or close contact with an infected individual.
How can I prevent the spread of rhinovirus infections?
+To prevent the spread of rhinovirus infections, practice good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, and avoiding touching your eyes, nose, and mouth.
What are the most common symptoms of a rhinovirus infection?
+The most common symptoms of a rhinovirus infection include a runny nose, sneezing, coughing, sore throat, and fatigue.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the rhinovirus and its effects on human health. By understanding the virus and its transmission, we can take steps to prevent and manage symptoms, and reduce the risk of complications. We encourage you to share this article with others, and to take steps to protect yourself and your loved ones from rhinovirus infections. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to reach out. Together, we can work towards a healthier future for everyone.
