Intro
Understand Na in blood test results, including normal sodium levels, hypernatremia, and hyponatremia. Learn how to interpret electrolyte imbalance and its causes, symptoms, and treatments for optimal health management.
The importance of understanding blood test results cannot be overstated, as they provide valuable insights into our overall health and wellbeing. Among the various components that make up blood, sodium (Na) plays a crucial role in maintaining proper bodily functions. Sodium levels in the blood are closely monitored through blood tests, and any deviations from the normal range can indicate underlying health issues. In this article, we will delve into the world of sodium in blood test results, exploring its significance, normal ranges, and what abnormal levels might signify.
Sodium is an essential electrolyte that helps regulate the amount of water in the body, supports nerve and muscle function, and maintains proper blood pressure. The human body tightly controls sodium levels, and even slight imbalances can have significant consequences. Blood tests are a common diagnostic tool used to assess sodium levels, among other parameters. By examining sodium levels in the blood, healthcare professionals can diagnose and monitor a range of conditions, from mild dehydration to life-threatening disorders.
The relevance of sodium in blood test results extends beyond its role in maintaining proper bodily functions. Abnormal sodium levels can be indicative of underlying health issues, such as kidney disease, heart failure, or hormonal imbalances. Furthermore, certain medications and medical treatments can also affect sodium levels, making it essential to closely monitor these levels in patients undergoing treatment. As we explore the intricacies of sodium in blood test results, we will discuss the normal ranges, causes of abnormal levels, and the implications of these findings on our health and wellbeing.
Understanding Sodium Levels in Blood Test Results

To comprehend the significance of sodium levels in blood test results, it is essential to understand the normal ranges and how these levels are measured. The normal range for sodium in the blood is typically between 135 and 145 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L). Levels within this range indicate that the body is maintaining proper sodium balance. However, sodium levels can fluctuate due to various factors, such as changes in diet, certain medical conditions, or the use of diuretics.
Normal Ranges and Measurement
Sodium levels are usually measured through a blood test, which involves drawing a sample of blood from a vein in the arm. The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where the sodium level is measured using specialized equipment. The results are typically reported in milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). Understanding the normal ranges and measurement units is crucial for interpreting blood test results and identifying potential health issues.Causes of Abnormal Sodium Levels

Abnormal sodium levels can be caused by a range of factors, including dehydration, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions. Dehydration, for instance, can lead to elevated sodium levels, as the body loses water and electrolytes. On the other hand, conditions such as heart failure, liver disease, or kidney disease can cause sodium levels to drop. Additionally, certain medications, such as diuretics, can also affect sodium levels by increasing urine production and leading to a loss of electrolytes.
Dehydration and Sodium Levels
Dehydration is a common cause of abnormal sodium levels, particularly in individuals who engage in strenuous physical activity or live in hot climates. When the body loses water and electrolytes, sodium levels can become elevated, leading to a condition known as hypernatremia. Mild dehydration can often be treated with oral rehydration solutions, while severe cases may require hospitalization and intravenous fluids.Implications of Abnormal Sodium Levels
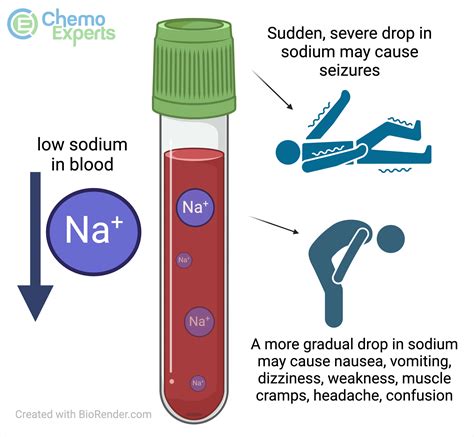
Abnormal sodium levels can have significant implications for our health and wellbeing. Hypernatremia, or elevated sodium levels, can cause symptoms such as thirst, headaches, and fatigue. In severe cases, it can lead to seizures, coma, or even death. On the other hand, hyponatremia, or low sodium levels, can cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and muscle weakness. If left untreated, hyponatremia can lead to more severe complications, including respiratory arrest and brain damage.
Treatment and Management
Treatment and management of abnormal sodium levels depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In cases of dehydration, treatment typically involves replenishing fluids and electrolytes. For individuals with underlying medical conditions, treatment may involve addressing the underlying condition, such as managing heart failure or kidney disease. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help regulate sodium levels and prevent further complications.Prevention and Maintenance
Preventing and maintaining normal sodium levels is crucial for overall health and wellbeing. This can be achieved by staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, and avoiding excessive sodium intake. Individuals with underlying medical conditions should work closely with their healthcare provider to manage their condition and prevent complications. Additionally, regular blood tests can help monitor sodium levels and detect any potential issues early on.
Dietary Considerations
Dietary considerations play a significant role in maintaining normal sodium levels. A balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help regulate sodium levels. It is also essential to limit sodium intake from processed and packaged foods, which are often high in sodium. By making informed dietary choices, individuals can help maintain normal sodium levels and reduce the risk of complications.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, understanding sodium levels in blood test results is essential for maintaining proper bodily functions and overall health. By recognizing the normal ranges, causes of abnormal levels, and implications of these findings, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and manage sodium-related disorders. As research continues to uncover the complexities of sodium balance, it is crucial to stay informed and adapt to new developments in the field. By working together with healthcare professionals and making informed lifestyle choices, individuals can maintain optimal sodium levels and reduce the risk of complications.
What is the normal range for sodium levels in the blood?
+The normal range for sodium levels in the blood is typically between 135 and 145 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L).
What causes abnormal sodium levels in the blood?
+Abnormal sodium levels can be caused by dehydration, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions such as kidney disease, heart failure, or hormonal imbalances.
How can I prevent and maintain normal sodium levels?
+Preventing and maintaining normal sodium levels can be achieved by staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, avoiding excessive sodium intake, and working closely with a healthcare provider to manage underlying medical conditions.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of sodium levels in blood test results. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below. Share this article with friends and family to help raise awareness about the importance of sodium balance and its implications for our health and wellbeing. Take the first step towards maintaining optimal sodium levels and reducing the risk of complications – consult with a healthcare professional today!
