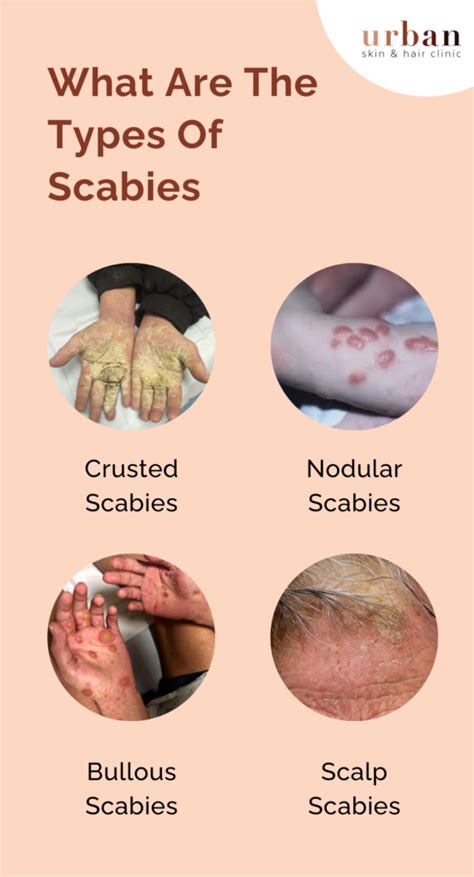
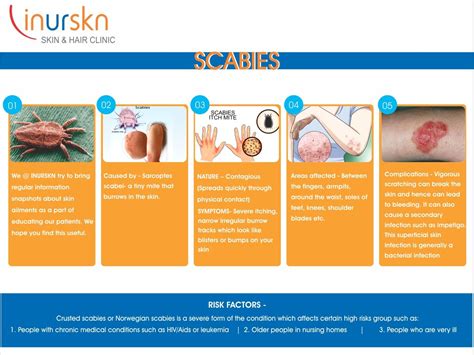
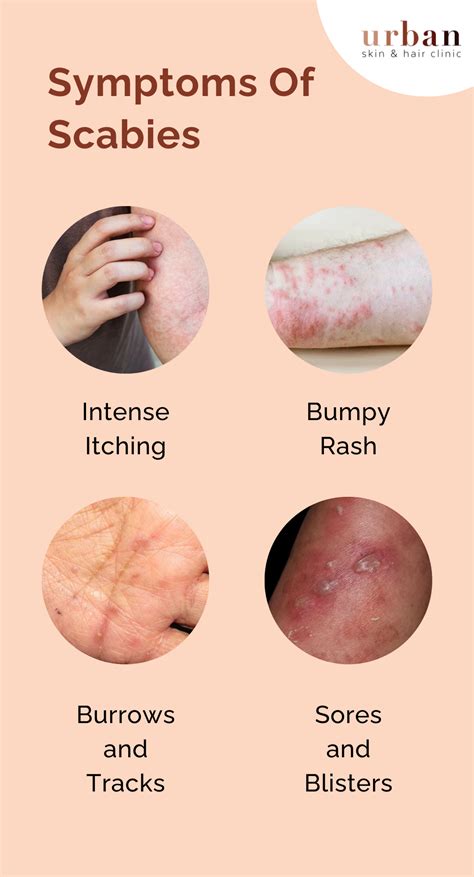
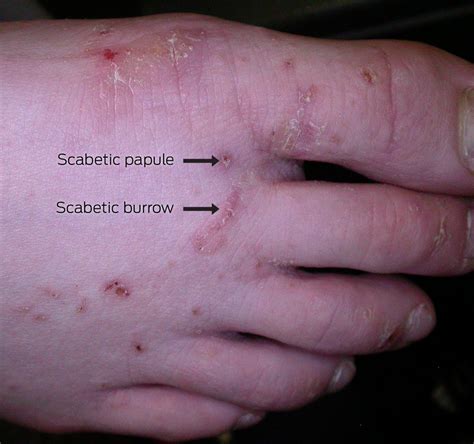
Scabies is a highly contagious skin infestation caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei. It is a significant public health problem worldwide, affecting people of all ages, races, and socioeconomic backgrounds. Scabies is characterized by intense itching, particularly at night, and a pimple-like skin rash. Understanding the causes of scabies is crucial for prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
Scabies is often misunderstood as a disease of poor hygiene, but this is not entirely accurate. While poor hygiene can contribute to the spread of scabies, it is not the primary cause. The main cause of scabies is the infestation of the skin by the scabies mite. The mite burrows into the skin, laying eggs and causing an allergic reaction that leads to the symptoms of scabies.
The scabies mite is highly contagious and can be spread through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person. This can occur through holding hands, hugging, or any other form of physical contact. Indirect contact, such as sharing clothing, towels, or bedding, can also spread the mite. Scabies can affect anyone, regardless of their age, sex, or socioeconomic status.
Introduction to Scabies Causes
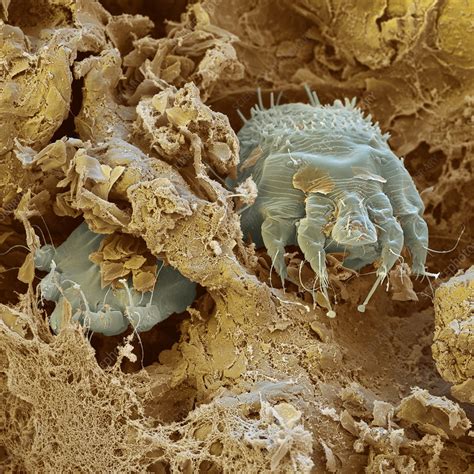
Scabies is caused by the scabies mite, which is a tiny, eight-legged parasite that burrows into the skin. The mite is about 0.3 millimeters long and is barely visible to the naked eye. It has a rounded body and long, pointed mouthparts that it uses to feed on human skin cells. The scabies mite is highly specialized and can only survive on human skin.
How Scabies Mite Infests the Skin
When the scabies mite infests the skin, it burrows into the upper layer of the skin, called the epidermis. The mite lays eggs in the burrow, which hatch into larvae after 3-4 days. The larvae then molt into nymphs, which eventually become adult mites. The entire life cycle of the scabies mite takes about 10-15 days.
Risk Factors for Scabies
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of getting scabies. These include:
* Poor hygiene: Failing to wash hands regularly, especially after touching an infected person.
* Close living quarters: Living in close proximity to others, such as in nursing homes, prisons, or refugee camps.
* Weakened immune system: Having a weakened immune system due to illness, medication, or age.
* Skin-to-skin contact: Engaging in activities that involve direct skin-to-skin contact, such as wrestling or contact sports.
* Sharing personal items: Sharing clothing, towels, or bedding with an infected person.
Seven Causes of Scabies
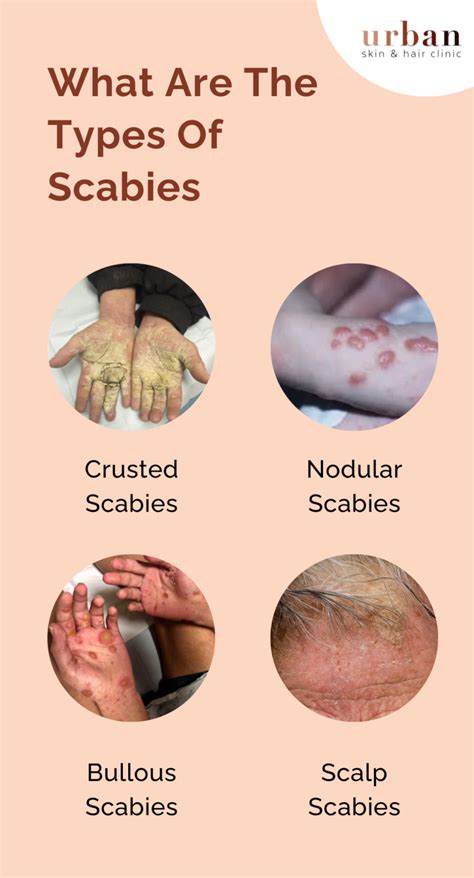
While the scabies mite is the primary cause of scabies, several other factors can contribute to the development of the disease. These include:
1. **Direct skin-to-skin contact**: This is the most common way to get scabies. Direct contact with an infected person can transfer the mite to the skin.
2. **Indirect contact**: Sharing personal items, such as clothing, towels, or bedding, can also spread the mite.
3. **Poor hygiene**: Failing to wash hands regularly, especially after touching an infected person, can increase the risk of getting scabies.
4. **Weakened immune system**: Having a weakened immune system due to illness, medication, or age can make it harder for the body to fight off the scabies mite.
5. **Malnutrition**: Poor nutrition can weaken the immune system, making it more susceptible to scabies.
6. **Crowding**: Living in close quarters with others can increase the risk of getting scabies.
7. **Genetic predisposition**: Some people may be more susceptible to scabies due to their genetic makeup.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Scabies
Diagnosing scabies can be challenging, as the symptoms are similar to those of other skin conditions. A doctor may perform a physical examination, take a skin scraping, or use a microscope to confirm the presence of the scabies mite. Treatment typically involves applying a topical cream or lotion to the entire body, from the neck down, and leaving it on for 8-14 hours. Oral medications may also be prescribed in severe cases.
Prevention of Scabies
Preventing scabies involves practicing good hygiene, avoiding direct skin-to-skin contact with infected individuals, and avoiding sharing personal items. Regular washing of hands, especially after touching an infected person, can help reduce the risk of getting scabies. Using a topical cream or lotion as a preventative measure can also help.
Practical Tips for Scabies Prevention
To prevent scabies, follow these practical tips:
* Wash your hands regularly, especially after touching an infected person.
* Avoid sharing personal items, such as clothing, towels, or bedding.
* Avoid direct skin-to-skin contact with infected individuals.
* Use a topical cream or lotion as a preventative measure.
* Wash and dry clothing, bedding, and towels in hot water and high heat.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, scabies is a highly contagious skin infestation caused by the scabies mite. Understanding the causes of scabies is crucial for prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. By practicing good hygiene, avoiding direct skin-to-skin contact with infected individuals, and avoiding sharing personal items, you can reduce the risk of getting scabies. If you suspect you have scabies, consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with scabies in the comments below. Have you or someone you know been affected by scabies? What steps did you take to prevent or treat the condition? Your input can help others better understand and manage scabies.
What is the main cause of scabies?
+
The main cause of scabies is the infestation of the skin by the scabies mite.
How is scabies spread?
+
Scabies is spread through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person, as well as through indirect contact with contaminated clothing, towels, or bedding.
What are the symptoms of scabies?
+
The symptoms of scabies include intense itching, particularly at night, and a pimple-like skin rash.
How is scabies diagnosed?
+
Scabies is diagnosed through a physical examination, skin scraping, or microscopic examination.
What is the treatment for scabies?
+
Treatment for scabies typically involves applying a topical cream or lotion to the entire body, from the neck down, and leaving it on for 8-14 hours.