Intro
Discover Seroquel uses, side effects, and interactions. Learn about its role in treating schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder, while understanding potential risks and benefits, including weight gain and withdrawal symptoms.
Seroquel, also known as quetiapine, is an atypical antipsychotic medication that has been widely used to treat various mental health conditions. The importance of understanding the uses and side effects of Seroquel cannot be overstated, as it can have a significant impact on the lives of individuals who take it. In this article, we will delve into the world of Seroquel, exploring its uses, benefits, and potential side effects, as well as providing valuable insights and information for those who are considering taking this medication.
The use of Seroquel has become increasingly common in recent years, and it is now prescribed for a range of conditions, including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder. The medication works by altering the levels of certain chemicals in the brain, such as dopamine and serotonin, which are thought to be involved in the development of these conditions. By taking Seroquel, individuals can experience a significant reduction in symptoms, such as hallucinations, delusions, and mood swings, which can greatly improve their quality of life.
However, like all medications, Seroquel is not without its side effects. Some individuals may experience mild side effects, such as drowsiness, dizziness, and weight gain, while others may experience more severe side effects, such as increased risk of stroke, high blood sugar, and suicidal thoughts. It is essential to be aware of these potential side effects and to discuss them with a healthcare professional before starting treatment. By understanding the potential risks and benefits of Seroquel, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment and take steps to minimize the risk of side effects.
Seroquel Uses
Some of the specific uses of Seroquel include:
- Treating schizophrenia: Seroquel is used to treat the symptoms of schizophrenia, such as hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking.
- Treating bipolar disorder: Seroquel is used to treat the symptoms of bipolar disorder, such as mood swings, irritability, and anxiety.
- Treating major depressive disorder: Seroquel is used to treat the symptoms of major depressive disorder, such as low mood, loss of interest in activities, and changes in appetite.
- Treating anxiety disorders: Seroquel is sometimes used to treat anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder.
How Seroquel Works
Seroquel works by altering the levels of certain chemicals in the brain, such as dopamine and serotonin. These chemicals are thought to be involved in the development of mental health conditions, such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. By altering the levels of these chemicals, Seroquel can help to reduce symptoms and improve mood.The exact mechanism of action of Seroquel is not fully understood, but it is thought to involve the following:
- Blocking dopamine receptors: Seroquel blocks dopamine receptors in the brain, which can help to reduce symptoms of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
- Increasing serotonin levels: Seroquel increases the levels of serotonin in the brain, which can help to improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression.
- Blocking histamine receptors: Seroquel blocks histamine receptors in the brain, which can help to reduce symptoms of anxiety and insomnia.
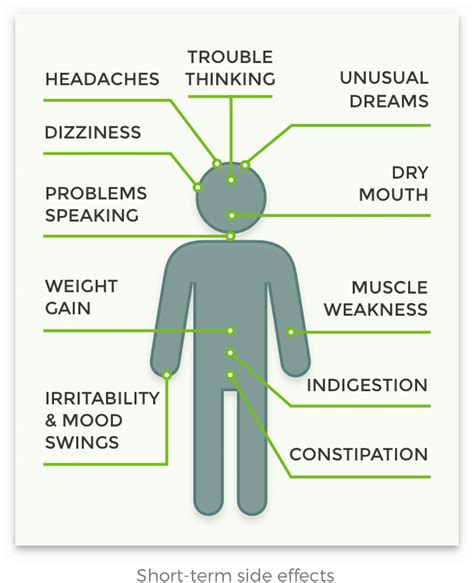
Seroquel Side Effects
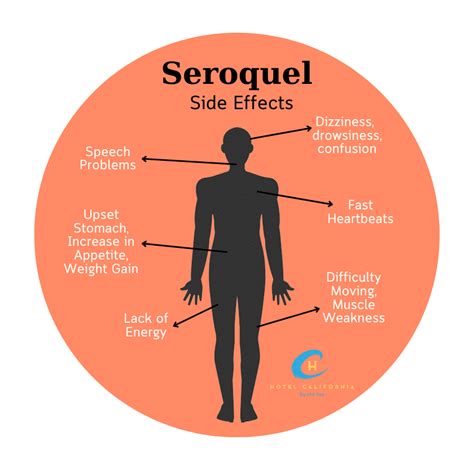
Some common side effects of Seroquel include:
- Drowsiness: Seroquel can cause drowsiness and sedation, especially when first starting treatment.
- Dizziness: Seroquel can cause dizziness and lightheadedness, especially when standing up or changing positions.
- Weight gain: Seroquel can cause weight gain, especially in the first few months of treatment.
- Dry mouth: Seroquel can cause dry mouth and increased thirst.
- Constipation: Seroquel can cause constipation and difficulty passing stools.
Severe Side Effects
In rare cases, Seroquel can cause severe side effects, such as: * Increased risk of stroke: Seroquel can increase the risk of stroke, especially in older adults. * High blood sugar: Seroquel can cause high blood sugar and increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. * Suicidal thoughts: Seroquel can increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors, especially in children and adolescents. * Neuroleptic malignant syndrome: Seroquel can cause a rare but life-threatening condition called neuroleptic malignant syndrome, which is characterized by fever, muscle stiffness, and changes in mental status.Seroquel Dosage
Some general guidelines for Seroquel dosage include:
- Schizophrenia: The recommended dosage of Seroquel for schizophrenia is 150-300 mg per day, taken in two or three divided doses.
- Bipolar disorder: The recommended dosage of Seroquel for bipolar disorder is 300-600 mg per day, taken in two or three divided doses.
- Major depressive disorder: The recommended dosage of Seroquel for major depressive disorder is 150-300 mg per day, taken in two or three divided doses.
Titration and Adjustment
The dosage of Seroquel may need to be adjusted over time to achieve the best results. This is called titration and adjustment.Some general guidelines for titration and adjustment include:
- Starting with a low dose: The dosage of Seroquel should be started at a low level and gradually increased as needed and tolerated.
- Gradually increasing the dose: The dosage of Seroquel should be increased gradually, over a period of several days or weeks, to minimize the risk of side effects.
- Monitoring for side effects: The individual should be monitored closely for side effects, such as drowsiness and dizziness, and the dosage adjusted as needed.
Seroquel Interactions
Some potential interactions with Seroquel include:
- Antidepressants: Seroquel can interact with antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and increase the risk of side effects, such as serotonin syndrome.
- Anti-anxiety medications: Seroquel can interact with anti-anxiety medications, such as benzodiazepines, and increase the risk of side effects, such as drowsiness and dizziness.
- Blood thinners: Seroquel can interact with blood thinners, such as warfarin, and increase the risk of bleeding.
Avoiding Interactions
To minimize the risk of interactions, it is essential to: * Inform the healthcare provider about all medications, including prescription and over-the-counter medications, as well as herbal supplements. * Avoid taking Seroquel with other medications that can interact with it. * Monitor for side effects, such as drowsiness and dizziness, and adjust the dosage as needed.Seroquel Warnings and Precautions
Some warnings and precautions include:
- Increased risk of stroke: Seroquel can increase the risk of stroke, especially in older adults.
- High blood sugar: Seroquel can cause high blood sugar and increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Suicidal thoughts: Seroquel can increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors, especially in children and adolescents.
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome: Seroquel can cause a rare but life-threatening condition called neuroleptic malignant syndrome, which is characterized by fever, muscle stiffness, and changes in mental status.
Special Populations
Seroquel can be used in special populations, such as children and adolescents, as well as older adults, but it is essential to be aware of the potential risks and benefits.Some special considerations include:
- Children and adolescents: Seroquel can be used in children and adolescents, but it is essential to monitor for side effects, such as suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
- Older adults: Seroquel can be used in older adults, but it is essential to monitor for side effects, such as increased risk of stroke and high blood sugar.
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women: Seroquel can be used in pregnant and breastfeeding women, but it is essential to monitor for side effects, such as birth defects and infant withdrawal symptoms.
What is Seroquel used for?
+Seroquel is used to treat mental health conditions, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder.
What are the common side effects of Seroquel?
+Common side effects of Seroquel include drowsiness, dizziness, weight gain, dry mouth, and constipation.
Can Seroquel be used in children and adolescents?
+Yes, Seroquel can be used in children and adolescents, but it is essential to monitor for side effects, such as suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
Can Seroquel be used in older adults?
+Yes, Seroquel can be used in older adults, but it is essential to monitor for side effects, such as increased risk of stroke and high blood sugar.
Can Seroquel be used in pregnant and breastfeeding women?
+Yes, Seroquel can be used in pregnant and breastfeeding women, but it is essential to monitor for side effects, such as birth defects and infant withdrawal symptoms.
In conclusion, Seroquel is a widely used medication for treating mental health conditions, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder. While it can be effective in reducing symptoms and improving mood, it is essential to be aware of the potential side effects and interactions. By understanding the uses, benefits, and risks of Seroquel, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment and take steps to minimize the risk of side effects. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments section below, and to consult with a healthcare professional before starting treatment with Seroquel.
