Intro
Discover what is Strep B, a bacterial infection causing Group B strep disease, with symptoms, risks, and prevention methods explained, including strep B testing and treatment options for pregnant women and newborns.
Strep B, also known as Group B streptococcus, is a type of bacterial infection that can be found in the digestive and urinary tracts of adults. While it is commonly harmless in healthy individuals, Strep B can pose a significant risk to newborn babies, particularly during childbirth. The bacteria can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery, potentially leading to severe health complications. It is essential for pregnant women to be aware of the risks associated with Strep B and take necessary precautions to minimize the transmission of the bacteria to their newborns.
The importance of understanding Strep B cannot be overstated, as it affects thousands of pregnant women and their babies every year. In fact, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 1 in 4 pregnant women in the United States carry Strep B bacteria. This highlights the need for expectant mothers to be informed about the risks and take proactive steps to ensure a healthy delivery. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention methods of Strep B, pregnant women can reduce the risk of transmission and protect their newborns from potential harm.
Strep B is a significant concern for pregnant women, as it can lead to severe health complications in newborns, including sepsis, pneumonia, and meningitis. These conditions can be life-threatening if left untreated, emphasizing the importance of prompt medical attention. Moreover, Strep B can also increase the risk of stillbirth, preterm labor, and low birth weight, making it crucial for expectant mothers to be aware of the risks and take necessary precautions. By understanding the causes and symptoms of Strep B, pregnant women can work closely with their healthcare providers to minimize the risk of transmission and ensure a healthy delivery.
What is Strep B Infection?

Strep B infection, also known as Group B streptococcal infection, is a type of bacterial infection caused by the Strep B bacteria. The infection can affect anyone, but it is most commonly found in pregnant women. The bacteria can be present in the digestive and urinary tracts of adults, and it is usually harmless. However, during childbirth, the bacteria can be transmitted from mother to child, potentially leading to severe health complications. Strep B infection can cause a range of symptoms, including fever, chills, and flu-like symptoms, and it can be diagnosed through a series of tests, including blood cultures and PCR (polymerase chain reaction) tests.
Causes and Risk Factors of Strep B Infection
The causes and risk factors of Strep B infection are not fully understood, but research suggests that the bacteria can be transmitted through close contact with an infected person. Pregnant women who carry the Strep B bacteria are at a higher risk of transmitting the infection to their newborns during childbirth. Other risk factors include a history of Strep B infection, a family history of the infection, and certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and kidney disease. Understanding the causes and risk factors of Strep B infection is essential for pregnant women, as it can help them take proactive steps to minimize the risk of transmission and protect their newborns from potential harm.Symptoms of Strep B Infection

The symptoms of Strep B infection can vary depending on the severity of the infection and the individual's overall health. Common symptoms include fever, chills, and flu-like symptoms, such as coughing and sneezing. In severe cases, Strep B infection can cause sepsis, pneumonia, and meningitis, which can be life-threatening if left untreated. Newborns who contract Strep B infection may exhibit symptoms such as difficulty breathing, lethargy, and refusal to feed. It is essential for pregnant women to be aware of the symptoms of Strep B infection and seek medical attention promptly if they experience any of these symptoms.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Strep B Infection
The diagnosis of Strep B infection typically involves a series of tests, including blood cultures and PCR (polymerase chain reaction) tests. These tests can detect the presence of the Strep B bacteria in the blood and other bodily fluids. Treatment for Strep B infection usually involves antibiotics, which can help to clear the infection and prevent transmission to the newborn. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to ensure close monitoring and treatment. Pregnant women who test positive for Strep B infection may be given antibiotics during labor to reduce the risk of transmission to their newborns.Prevention and Management of Strep B Infection
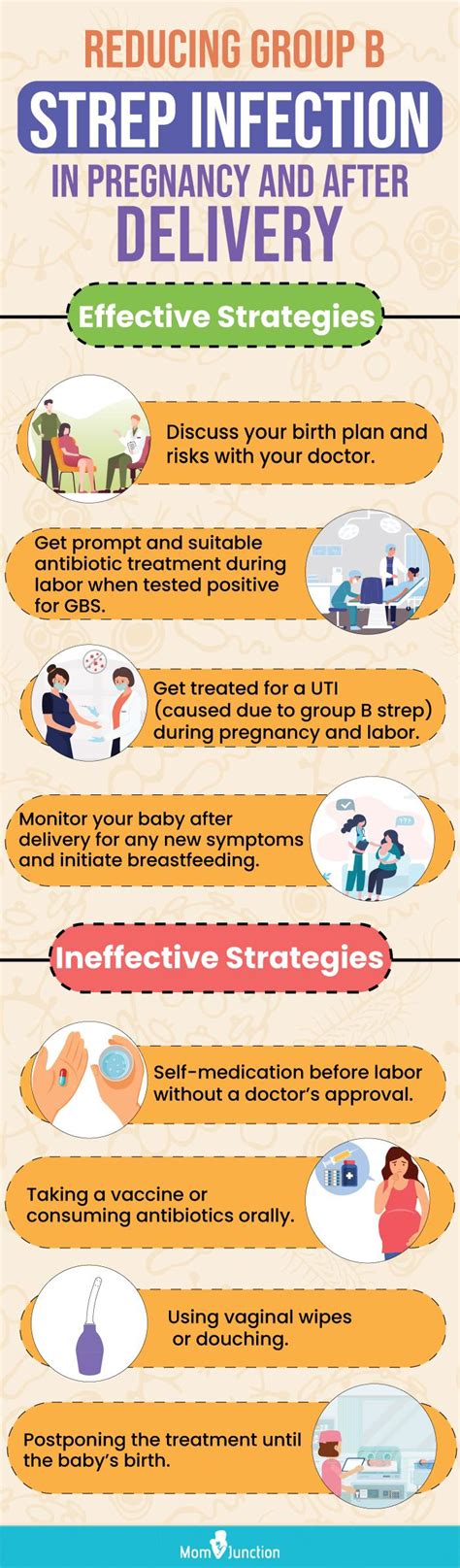
Prevention and management of Strep B infection are crucial for pregnant women, as they can help to minimize the risk of transmission and protect their newborns from potential harm. The following are some ways to prevent and manage Strep B infection:
- Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly and avoiding close contact with people who are sick
- Getting tested for Strep B infection between 35 and 37 weeks of pregnancy
- Taking antibiotics during labor if Strep B infection is detected
- Avoiding unnecessary medical interventions during labor, such as breaking the water or using a fetal monitor
- Considering a cesarean delivery if Strep B infection is severe or if there are other complications during labor
Complications of Strep B Infection
The complications of Strep B infection can be severe and life-threatening, particularly for newborns. Some of the potential complications include: * Sepsis: a life-threatening condition that occurs when the infection spreads to the bloodstream * Pneumonia: a lung infection that can cause difficulty breathing and other respiratory problems * Meningitis: a brain infection that can cause seizures, coma, and death * Stillbirth: the death of a baby before birth * Preterm labor: labor that occurs before 37 weeks of pregnancy * Low birth weight: a birth weight that is less than 5.5 poundsStrep B Infection and Pregnancy
Strep B infection is a significant concern for pregnant women, as it can increase the risk of complications during pregnancy and childbirth. Pregnant women who carry the Strep B bacteria are at a higher risk of transmitting the infection to their newborns during delivery. The risk of transmission is highest during vaginal delivery, particularly if the mother's water breaks or if she has a fever during labor. Pregnant women who test positive for Strep B infection may be given antibiotics during labor to reduce the risk of transmission to their newborns.
Strep B Infection and Newborns
Newborns who contract Strep B infection are at a higher risk of developing severe health complications, including sepsis, pneumonia, and meningitis. These conditions can be life-threatening if left untreated, emphasizing the importance of prompt medical attention. Newborns who are at a higher risk of Strep B infection include: * Premature babies: babies born before 37 weeks of pregnancy * Low birth weight babies: babies born weighing less than 5.5 pounds * Babies born to mothers who have a fever during labor * Babies born to mothers who have a history of Strep B infectionTreatment Options for Strep B Infection
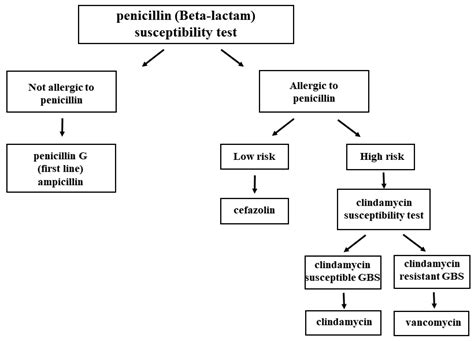
The treatment options for Strep B infection depend on the severity of the infection and the individual's overall health. The following are some of the common treatment options for Strep B infection:
- Antibiotics: antibiotics are usually prescribed to clear the infection and prevent transmission to the newborn
- Hospitalization: hospitalization may be necessary to ensure close monitoring and treatment, particularly if the infection is severe or if there are other complications
- Supportive care: supportive care, such as oxygen therapy and hydration, may be necessary to manage symptoms and prevent complications
Home Remedies for Strep B Infection
While there are no guaranteed home remedies for Strep B infection, the following may help to manage symptoms and prevent complications: * Rest and hydration: getting plenty of rest and staying hydrated can help to manage symptoms and prevent complications * Warm compresses: applying warm compresses to the affected area may help to reduce pain and discomfort * Over-the-counter pain relievers: over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, may help to manage pain and reduce feverConclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, Strep B infection is a significant concern for pregnant women and their newborns. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention methods of Strep B infection is essential for minimizing the risk of transmission and protecting newborns from potential harm. Pregnant women who are at a higher risk of Strep B infection should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a plan for managing the infection and preventing transmission to their newborns. By taking proactive steps to prevent and manage Strep B infection, pregnant women can help to ensure a healthy delivery and a healthy start for their newborns.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with Strep B infection in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. We are committed to providing you with the most up-to-date and accurate information on Strep B infection and other health topics.
What is Strep B infection?
+Strep B infection, also known as Group B streptococcal infection, is a type of bacterial infection caused by the Strep B bacteria.
How is Strep B infection transmitted?
+Strep B infection can be transmitted from mother to child during childbirth, particularly if the mother's water breaks or if she has a fever during labor.
What are the symptoms of Strep B infection?
+The symptoms of Strep B infection can vary depending on the severity of the infection and the individual's overall health, but common symptoms include fever, chills, and flu-like symptoms.
How is Strep B infection treated?
+Strep B infection is usually treated with antibiotics, which can help to clear the infection and prevent transmission to the newborn.
Can Strep B infection be prevented?
+While Strep B infection cannot be completely prevented, pregnant women can take proactive steps to minimize the risk of transmission, such as practicing good hygiene and getting tested for Strep B infection between 35 and 37 weeks of pregnancy.
