Intro
Learn key facts about the Tetanus vaccine, including its effectiveness, booster shots, and prevention of lockjaw, tetanus infection, and neurological disorders, ensuring immunity and public health safety.
Tetanus, also known as lockjaw, is a serious bacterial infection that can lead to severe muscle stiffness, spasms, and even death. The tetanus vaccine is a crucial tool in preventing this disease, and it is essential to understand its importance and how it works. In this article, we will delve into the world of tetanus vaccination, exploring its history, benefits, and key facts that everyone should know.
The tetanus vaccine has been a cornerstone of public health for decades, saving countless lives and preventing untold suffering. Despite its importance, many people remain unaware of the crucial role it plays in protecting us from this debilitating disease. As we navigate the complexities of vaccination, it is vital to separate fact from fiction and to understand the science behind this life-saving intervention. Whether you are a parent, a healthcare professional, or simply someone interested in staying healthy, this article aims to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the tetanus vaccine and its significance in modern medicine.
Tetanus is a disease that can affect anyone, regardless of age or background. It is caused by the bacterium Clostridium tetani, which is found in soil, dust, and the gastrointestinal tracts of animals. When the bacteria enter the body, typically through a wound or cut, they produce toxins that can lead to muscle stiffness, spasms, and rigidity. In severe cases, tetanus can cause respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, and even death. The tetanus vaccine is the most effective way to prevent this disease, and it is essential to understand how it works and why it is so crucial for public health.
History of Tetanus Vaccine
Key Milestones in Tetanus Vaccine Development
The development of the tetanus vaccine has been a gradual process, with several key milestones along the way. Some of the most significant developments include: * The introduction of the first tetanus vaccine in the 1920s * The development of a more effective vaccine in the 1950s, using a combination of toxoid and aluminum salts * The introduction of a vaccine that combined tetanus toxoid with diphtheria and pertussis toxoids, known as the DTP vaccine * The development of a tetanus vaccine that can be used in adults, known as the Td vaccineHow Tetanus Vaccine Works
Benefits of Tetanus Vaccine
The benefits of the tetanus vaccine are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant advantages include: * Prevention of tetanus infection: The vaccine is highly effective in preventing tetanus infection, which can be a life-threatening disease. * Reduction in mortality rates: The tetanus vaccine has been shown to reduce mortality rates from tetanus by up to 90%. * Protection against other diseases: The tetanus vaccine can also provide protection against other diseases, such as diphtheria and pertussis, when given in combination with other vaccines.Types of Tetanus Vaccine
Who Should Get the Tetanus Vaccine
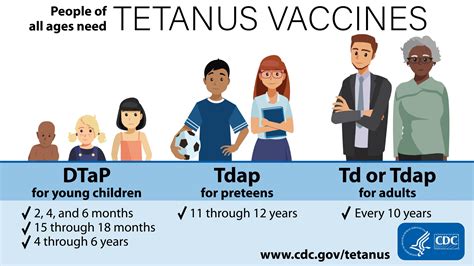
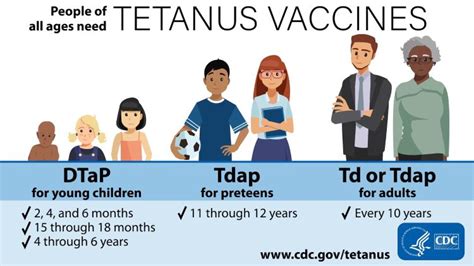
The tetanus vaccine is recommended for everyone, regardless of age or background. Some of the groups that are at highest risk of tetanus infection include: * Children: Children under the age of 7 are at highest risk of tetanus infection and should receive the DTP vaccine as part of their routine vaccination schedule. * Adults: Adults who have not received a tetanus vaccine in the past 10 years should receive a booster dose to maintain immunity. * Pregnant women: Pregnant women should receive a tetanus vaccine during pregnancy to protect themselves and their newborns from tetanus infection.Side Effects of Tetanus Vaccine

Contraindications of Tetanus Vaccine
There are some contraindications to the tetanus vaccine, including: * Severe allergic reactions to previous doses of the vaccine * History of neurological disorders, such as seizures or Guillain-Barré syndrome * Pregnancy or breastfeeding, although the vaccine can be given in these situations if the benefits outweigh the risks.Conclusion and Future Directions

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with the tetanus vaccine in the comments section below. Have you or a loved one received the tetanus vaccine? What do you think are the most important benefits and challenges of vaccination? Let's work together to promote awareness and understanding of the tetanus vaccine and to protect public health.
What is the tetanus vaccine and how does it work?
+The tetanus vaccine is a vaccine that protects against tetanus infection, a serious and potentially life-threatening disease. It works by stimulating the body's immune system to produce antibodies against the toxin produced by Clostridium tetani.
Who should get the tetanus vaccine?
+The tetanus vaccine is recommended for everyone, regardless of age or background. Children under the age of 7 are at highest risk of tetanus infection and should receive the DTP vaccine as part of their routine vaccination schedule. Adults who have not received a tetanus vaccine in the past 10 years should receive a booster dose to maintain immunity.
What are the side effects of the tetanus vaccine?
+Like all vaccines, the tetanus vaccine can cause side effects, although these are typically mild and temporary. Some of the most common side effects include pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site, fatigue or tiredness, headache or muscle aches, and nausea or vomiting.
