Intro
Amlodipine uses include treating hypertension, angina, and coronary artery disease, with benefits like lowered blood pressure and improved heart health, also aiding in preventing cardiovascular events.
Amlodipine is a medication that has been widely used for several decades to treat various cardiovascular conditions. It belongs to a class of drugs known as calcium channel blockers, which work by relaxing blood vessels and increasing blood flow to the heart. This medication has been a cornerstone in the management of hypertension, angina, and other cardiovascular diseases. In this article, we will delve into the uses of amlodipine, its benefits, and its working mechanisms, as well as provide practical examples and statistical data to support its effectiveness.
Amlodipine is primarily prescribed to treat high blood pressure, also known as hypertension. High blood pressure can lead to serious health complications, such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease, if left uncontrolled. By taking amlodipine, patients can lower their blood pressure and reduce the risk of these complications. Additionally, amlodipine is used to treat angina, a condition characterized by chest pain or discomfort caused by reduced blood flow to the heart. It works by increasing blood flow to the heart, reducing the frequency and severity of angina attacks.
The importance of amlodipine lies in its ability to improve cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of serious health complications. According to the American Heart Association, high blood pressure affects over 100 million adults in the United States, and it is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke. By controlling high blood pressure and managing angina, amlodipine plays a critical role in preventing these complications and improving overall health outcomes. Furthermore, amlodipine has been shown to be effective in reducing the risk of heart failure, a condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs.
Amlodipine Mechanism of Action

Benefits of Amlodipine
The benefits of amlodipine are numerous and well-documented. Some of the key benefits include: * Lowering blood pressure and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease * Reducing the frequency and severity of angina attacks * Improving blood flow to the heart and reducing the risk of heart failure * Having anti-inflammatory properties, which can help to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease * Being generally well-tolerated and having a low risk of side effectsAmlodipine Uses in Different Conditions

Amlodipine Dosage and Administration
The dosage and administration of amlodipine vary depending on the condition being treated and the individual patient's needs. Typically, amlodipine is taken orally, once a day, with or without food. The usual starting dose is 5 mg, which can be increased to 10 mg after 7-14 days if necessary. It is essential to take amlodipine exactly as prescribed by a healthcare provider and not to stop taking it without consulting a doctor.Amlodipine Side Effects and Interactions

Amlodipine Precautions and Warnings
Amlodipine is generally well-tolerated, but there are some precautions and warnings to be aware of: * Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Amlodipine should be used with caution in pregnant or breastfeeding women, as it may pass into breast milk and affect the baby. * Children: Amlodipine is not recommended for children under the age of 6, as its safety and effectiveness have not been established. * Liver or kidney disease: Amlodipine should be used with caution in patients with liver or kidney disease, as it may affect the liver or kidneys.Amlodipine and Lifestyle Changes
Amlodipine and Other Medications
Amlodipine can be used in combination with other medications to treat various conditions. Some examples include: * Beta blockers: Amlodipine can be used with beta blockers to treat high blood pressure and angina. * Diuretics: Amlodipine can be used with diuretics to treat high blood pressure and edema. * ACE inhibitors: Amlodipine can be used with ACE inhibitors to treat high blood pressure and heart failure.Amlodipine and Patient Education

Amlodipine and Future Directions
The future of amlodipine is promising, with ongoing research and development aimed at improving its efficacy and safety. Some potential future directions include: * Developing new formulations of amlodipine, such as extended-release or combination products * Investigating the use of amlodipine in new indications, such as heart failure or pulmonary hypertension * Developing personalized treatment approaches, such as genetic testing to predict response to amlodipineAmlodipine and Real-World Experience

Amlodipine and Comparative Effectiveness
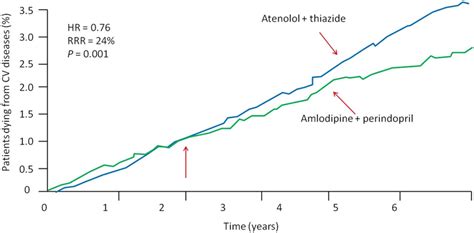
Amlodipine has been compared to other medications in several studies, with results showing it to be effective and well-tolerated. Some examples include: * A study comparing amlodipine to atenolol found that amlodipine was more effective in reducing blood pressure and improving cardiovascular outcomes. * A study comparing amlodipine to lisinopril found that amlodipine was more effective in reducing blood pressure and improving symptoms in patients with heart failure.Amlodipine and Pharmacoeconomics

Amlodipine and Regulatory Affairs
Amlodipine is regulated by various government agencies, including the US FDA and the European Medicines Agency. Some examples of regulatory affairs related to amlodipine include: * Approval of new formulations or indications * Changes to labeling or warnings * Post-marketing surveillance and adverse event reportingWhat is amlodipine used for?
+Amlodipine is used to treat high blood pressure, angina, and other cardiovascular conditions.
How does amlodipine work?
+Amlodipine works by blocking calcium channels in the blood vessels, causing them to relax and widen.
What are the common side effects of amlodipine?
+Common side effects of amlodipine include dizziness, headache, fatigue, nausea, and swelling of the legs, ankles, or feet.
Can amlodipine be used in combination with other medications?
+Yes, amlodipine can be used in combination with other medications, such as beta blockers, diuretics, and ACE inhibitors.
Is amlodipine safe for pregnant or breastfeeding women?
+Amlodipine should be used with caution in pregnant or breastfeeding women, as it may pass into breast milk and affect the baby.
In conclusion, amlodipine is a valuable medication for the treatment of various cardiovascular conditions, including hypertension, angina, and heart failure. Its mechanism of action, benefits, and side effects make it a popular choice among healthcare providers. By understanding how amlodipine works and its potential interactions with other medications, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment and work with their healthcare providers to achieve optimal outcomes. We invite readers to share their experiences with amlodipine, ask questions, or provide feedback on this article.
