Intro
Discover what statin medications are, their uses, and benefits in lowering cholesterol levels, reducing heart disease risk, and managing cardiovascular health with statin therapy and medication options.
Statin medications have become a cornerstone in the management and prevention of cardiovascular diseases, particularly in reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. These drugs work by lowering the levels of "bad" cholesterol, known as low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, in the blood. High levels of LDL cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis, which can increase the risk of cardiovascular events.
The importance of statins in modern medicine cannot be overstated. They have been extensively studied, and their benefits in reducing cardiovascular risk have been well-documented. Statins are prescribed to millions of people worldwide, making them one of the most commonly used classes of medications. Their widespread use is a testament to their efficacy and safety profile, although like all medications, they can have side effects and may not be suitable for everyone.
Understanding how statins work and their role in managing cholesterol levels is crucial for individuals looking to reduce their cardiovascular risk. Statins inhibit an enzyme in the liver called HMG-CoA reductase, which plays a central role in the production of cholesterol. By blocking this enzyme, statins reduce the liver's ability to produce cholesterol, leading to lower levels of LDL cholesterol in the blood. This mechanism not only reduces the risk of forming new plaques but can also help stabilize existing plaques, making them less likely to rupture and cause a heart attack or stroke.
Benefits of Statins
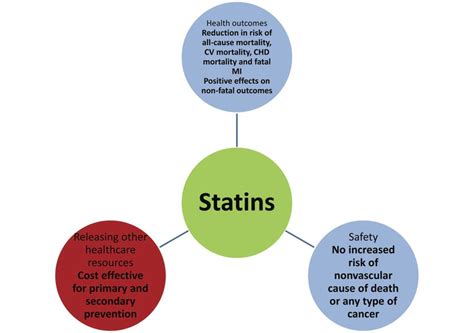
The benefits of statins are multifaceted, extending beyond just the reduction of LDL cholesterol levels. They have anti-inflammatory properties, can improve the function of the inner lining of blood vessels, and may even have effects on reducing the risk of certain types of cancer, although these latter benefits are still under investigation. For individuals at high risk of cardiovascular events, statins can be lifesaving, significantly reducing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and the need for coronary artery bypass grafting or other interventions.
Who Should Take Statins?
The decision to start statin therapy is based on an individual's overall risk of developing cardiovascular disease. This assessment considers factors such as age, gender, family history of cardiovascular disease, levels of LDL and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, blood pressure, and whether the individual has diabetes or has already experienced a cardiovascular event. Guidelines often recommend statin therapy for individuals with elevated cardiovascular risk, including those with established cardiovascular disease, diabetes, or very high levels of LDL cholesterol.Types of Statins
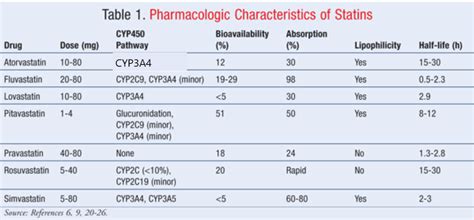
There are several types of statins available, each with its own pharmacological profile. These include atorvastatin, simvastatin, rosuvastatin, pravastatin, and fluvastatin, among others. The choice of statin can depend on the individual's specific needs, including the degree of LDL reduction required, potential side effects, and interactions with other medications. Some statins are more potent than others, and certain statins may be preferred in patients with specific conditions, such as diabetes or kidney disease.
Side Effects of Statins
While statins are generally well-tolerated, they can cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects include muscle pain, liver enzyme elevations, and increased risk of diabetes. Rare but serious side effects can include muscle breakdown (rhabdomyolysis) and liver failure. It's essential for individuals taking statins to be aware of these potential side effects and to discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider. Regular monitoring of liver enzymes and muscle symptoms can help identify any issues early.Statin Intolerance
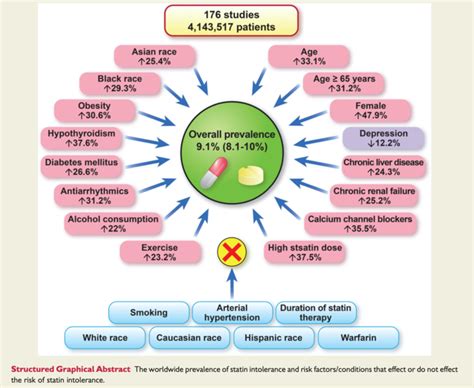
Some individuals may experience intolerance to statins, characterized by significant side effects that make continued use of the medication unbearable. In such cases, alternative strategies may be employed, including the use of other cholesterol-lowering medications, lifestyle modifications, or the use of statins at lower doses or less frequently. Recent studies have also explored the use of PCSK9 inhibitors, which can significantly lower LDL cholesterol levels in individuals who cannot tolerate statins or have familial hypercholesterolemia.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to statin therapy, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing cholesterol levels and reducing cardiovascular risk. These include adopting a healthy diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol intake. For some individuals, these lifestyle changes alone may be sufficient to manage their cholesterol levels and reduce their cardiovascular risk, potentially avoiding the need for medication.Future Directions

The field of cholesterol management and cardiovascular disease prevention is continually evolving. Ongoing research is exploring new targets for therapy, including the development of medications that can raise HDL cholesterol levels or improve the function of HDL. Additionally, genetic studies are helping to identify individuals at higher risk of cardiovascular disease, allowing for earlier and more targeted interventions. The use of precision medicine, tailored to an individual's specific genetic and environmental risk factors, holds promise for improving outcomes in cardiovascular disease.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, statins have revolutionized the management of cardiovascular disease by providing a highly effective means of reducing LDL cholesterol levels and cardiovascular risk. While they are not without side effects and may not be suitable for everyone, their benefits have been extensively documented, and they remain a cornerstone of preventive cardiology. As research continues to uncover new pathways and targets for therapy, the future of cardiovascular disease management looks promising. Individuals concerned about their cardiovascular health should consult with their healthcare provider to discuss the potential benefits and risks of statin therapy and to explore all available options for managing their cholesterol levels and reducing their risk of heart disease.What are statins used for?
+Statins are used to lower the levels of "bad" cholesterol (LDL) in the blood, reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
How do statins work?
+Statins work by inhibiting an enzyme in the liver called HMG-CoA reductase, which is involved in the production of cholesterol, thereby reducing the liver's ability to produce cholesterol.
What are the common side effects of statins?
+Common side effects of statins include muscle pain, liver enzyme elevations, and an increased risk of diabetes. Rare but serious side effects can include muscle breakdown and liver failure.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with statin therapy in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can work towards a better understanding of cardiovascular health and the role of statins in managing cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of heart disease.
