Intro
Diagnose celiac disease with 5 key blood tests, including tissue transglutaminase and endomysial antibody tests, to detect gluten sensitivity and intestinal damage, promoting accurate diagnosis and effective treatment for autoimmune disorders.
Celiac disease is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the small intestine and is caused by a reaction to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. It is essential to diagnose celiac disease accurately to prevent long-term complications, such as malnutrition, anemia, and increased risk of other autoimmune disorders. One of the primary methods of diagnosing celiac disease is through blood tests. In this article, we will delve into the five celiac disease blood tests, their significance, and how they help in diagnosing this condition.
The importance of early diagnosis and treatment of celiac disease cannot be overstated. Untreated celiac disease can lead to severe health complications, including osteoporosis, infertility, and even certain types of cancer. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the various diagnostic tools available, including blood tests, to ensure timely and effective management of the condition. Blood tests for celiac disease have become increasingly sophisticated, allowing for more accurate diagnoses and better patient outcomes.
Celiac disease can manifest in various ways, making diagnosis challenging. Some individuals may experience classic symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fatigue, while others may have non-classical symptoms or even be asymptomatic. This variability underscores the need for reliable diagnostic methods. Blood tests have emerged as a critical component of the diagnostic process, offering a non-invasive and relatively quick way to assess the presence of certain antibodies associated with celiac disease.
Introduction to Celiac Disease Blood Tests

Celiac disease blood tests are designed to detect the presence of specific antibodies in the blood that are associated with the immune system's reaction to gluten. These tests are crucial for identifying individuals who may have celiac disease, especially those who are asymptomatic or have non-classical symptoms. The five primary blood tests for celiac disease are:
- Tissue Transglutaminase Antibody (tTGA) test
- Endomysial Antibody (EMA) test
- Gliadin Antibody test
- Deamidated Gliadin Peptide (DGP) test
- Total IgA test
Understanding Each Blood Test
Each of these blood tests plays a vital role in the diagnostic process, and understanding their specific functions and limitations is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.Tissue Transglutaminase Antibody (tTGA) Test
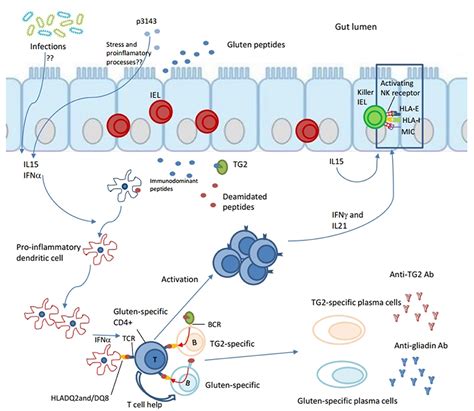
The tTGA test is one of the most commonly used blood tests for celiac disease. It measures the levels of IgA and IgG antibodies against tissue transglutaminase, an enzyme found in the small intestine. Elevated levels of these antibodies are indicative of an immune response to gluten, suggesting celiac disease. The tTGA test is highly sensitive and specific, making it a valuable tool for diagnosis.
Interpreting tTGA Test Results
Interpreting the results of the tTGA test requires careful consideration of the clinical context. A positive result, especially in the presence of symptoms and intestinal damage, strongly supports a diagnosis of celiac disease. However, a negative result does not entirely rule out the condition, especially in individuals with IgA deficiency, a condition where the body does not produce enough IgA antibodies.Endomysial Antibody (EMA) Test
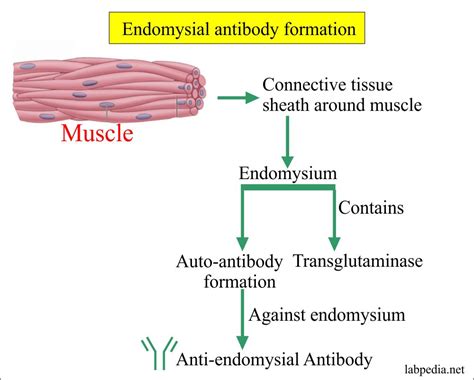
The EMA test detects the presence of IgA antibodies against endomysium, a component of muscle tissue. This test is highly specific for celiac disease and is often used to confirm the diagnosis, especially when the tTGA test is positive. The EMA test is considered more specific than the tTGA test but may be less sensitive.
Significance of EMA Test in Diagnosis
The EMA test plays a crucial role in confirming the diagnosis of celiac disease, particularly in cases where the tTGA test is positive but clinical symptoms are mild or absent. It is also useful in monitoring the response to a gluten-free diet, as antibody levels should decrease with successful treatment.Gliadin Antibody Test
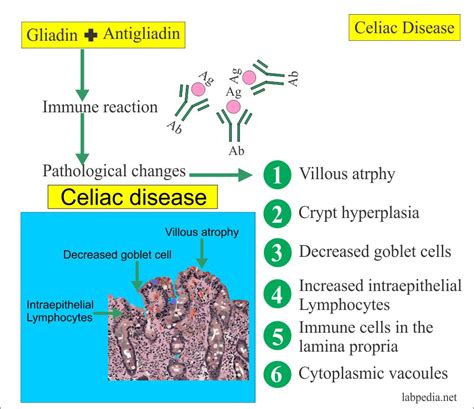
The gliadin antibody test measures the levels of IgA and IgG antibodies against gliadin, a protein found in wheat. While this test can be positive in individuals with celiac disease, it is less specific than the tTGA and EMA tests. It is often used in conjunction with other tests to support a diagnosis.
Limitations and Applications of Gliadin Antibody Test
The gliadin antibody test has limitations due to its lower specificity for celiac disease. However, it can be useful in certain situations, such as in children or in individuals with suspected non-celiac gluten sensitivity.Deamidated Gliadin Peptide (DGP) Test
The DGP test detects antibodies against deamidated gliadin peptides, which are more specific to celiac disease than native gliadin. This test is particularly useful in individuals with IgA deficiency, as it can detect IgG antibodies, providing a more accurate diagnosis.
DGP Test and Its Role in Diagnosing Celiac Disease
The DGP test offers an alternative for diagnosing celiac disease, especially in cases where other tests may not be conclusive. Its ability to detect both IgA and IgG antibodies makes it a valuable tool in the diagnostic arsenal.Total IgA Test
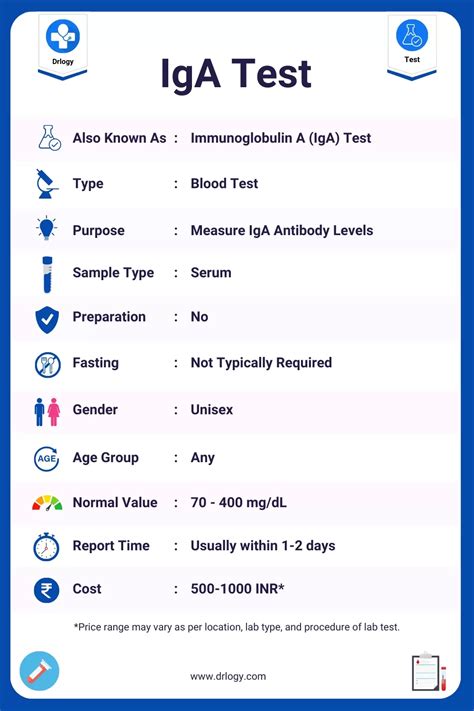
The total IgA test measures the overall level of IgA antibodies in the blood. This test is essential because some individuals with celiac disease may have selective IgA deficiency, where they do not produce enough IgA antibodies. In such cases, relying solely on IgA-based tests could lead to false-negative results.
Importance of Total IgA Test in Celiac Disease Diagnosis
The total IgA test is crucial for identifying individuals with selective IgA deficiency. By knowing the total IgA level, healthcare providers can interpret the results of other celiac disease blood tests more accurately and decide on the appropriate diagnostic pathway.What are the common symptoms of celiac disease?
+Common symptoms of celiac disease include diarrhea, abdominal pain, fatigue, weight loss, and nausea. However, some individuals may be asymptomatic or have non-classical symptoms.
How accurate are blood tests for diagnosing celiac disease?
+Blood tests for celiac disease are highly sensitive and specific, especially when used in combination. However, accuracy can be affected by factors such as the presence of IgA deficiency or the timing of the test in relation to gluten exposure.
What is the next step after a positive blood test for celiac disease?
+A positive blood test is typically followed by an intestinal biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and assess the degree of intestinal damage. A gluten-free diet is often recommended, and follow-up tests may be conducted to monitor the response to treatment.
In conclusion, the five celiac disease blood tests - tTGA, EMA, gliadin antibody, DGP, and total IgA tests - are invaluable tools in the diagnosis of celiac disease. Each test has its unique characteristics and applications, and understanding their roles is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management of the condition. By recognizing the importance of these blood tests and their appropriate use, healthcare providers can offer better care to individuals with celiac disease, improving their quality of life and preventing long-term complications.
We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about celiac disease and its diagnosis in the comments section below. Sharing knowledge and personal stories can help raise awareness about this condition and support those who are affected. Additionally, consider sharing this article with others who may benefit from understanding more about celiac disease blood tests and their significance in diagnosing and managing this autoimmune disorder.
