Intro
Discover the normal glucose numbers range and maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Learn about ideal glucose levels, blood glucose monitoring, and managing diabetes with target glucose ranges and optimal glucose control.
Maintaining normal glucose numbers is crucial for overall health, as it helps prevent conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and other complications. Glucose, a simple sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. The body regulates glucose levels through insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. When glucose levels are within the normal range, the body functions optimally, and the risk of developing glucose-related disorders is minimized. Understanding normal glucose numbers and how to maintain them is essential for individuals of all ages.
The importance of monitoring glucose levels cannot be overstated, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. By keeping track of glucose levels, individuals can make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication, which helps maintain normal glucose numbers. Moreover, research has shown that tight glucose control can significantly reduce the risk of long-term complications associated with diabetes, such as kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems. With the increasing prevalence of diabetes worldwide, it is essential to educate individuals about the importance of maintaining normal glucose numbers and provide them with the necessary tools and resources to do so.
Effective glucose management involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and stress management. A diet rich in whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, can help regulate glucose levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, or cycling, can also improve insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to more efficiently use insulin to regulate glucose levels. Additionally, stress management techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises, can help reduce stress, which can contribute to elevated glucose levels. By incorporating these lifestyle modifications into daily routine, individuals can maintain normal glucose numbers and reduce their risk of developing glucose-related disorders.
Understanding Normal Glucose Numbers

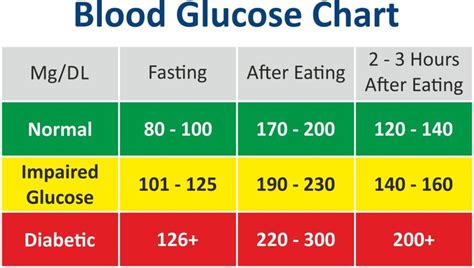
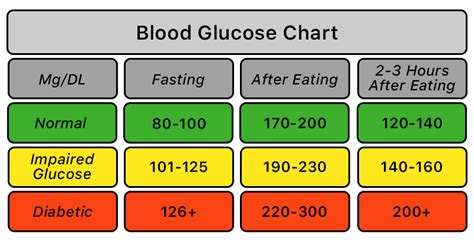
Normal glucose numbers vary throughout the day, depending on factors such as diet, physical activity, and sleep. Fasting glucose levels, which are measured after an overnight fast, are typically between 70 and 99 mg/dL. Postprandial glucose levels, which are measured after eating, can rise to 140 mg/dL or higher, but should return to normal within 2 hours. Individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition should aim to maintain glucose levels within the following ranges:
- Fasting glucose: 70-99 mg/dL
- Postprandial glucose: Less than 140 mg/dL
- Average glucose: 80-120 mg/dL
Factors That Affect Glucose Levels
Several factors can affect glucose levels, including: * Diet: Consuming high-carbohydrate or high-sugar foods can cause glucose levels to rise. * Physical activity: Regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity and lower glucose levels. * Sleep: Poor sleep quality or duration can disrupt glucose regulation. * Stress: Chronic stress can raise glucose levels and worsen insulin resistance. * Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can affect glucose levels.Maintaining Normal Glucose Numbers
Maintaining normal glucose numbers requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, and, if necessary, medication. The following strategies can help individuals maintain normal glucose numbers:
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help regulate glucose levels.
- Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to help regulate glucose levels.
- Manage stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Lifestyle Modifications for Glucose Management
Lifestyle modifications play a critical role in maintaining normal glucose numbers. The following lifestyle modifications can help individuals manage glucose levels: * Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce glucose levels. * Smoking cessation: Smoking can worsen insulin resistance and increase glucose levels. * Limiting alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can disrupt glucose regulation and worsen insulin resistance. * Getting enough physical activity: Regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity and lower glucose levels.Monitoring Glucose Levels
Monitoring glucose levels is essential for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. The following methods can be used to monitor glucose levels:
- Fasting glucose tests: Measure glucose levels after an overnight fast.
- Postprandial glucose tests: Measure glucose levels after eating.
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): Measures glucose levels throughout the day using a small sensor inserted under the skin.
- Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) tests: Measure average glucose levels over the past 2-3 months.
Interpreting Glucose Test Results
Interpreting glucose test results requires understanding the different ranges and what they indicate. The following ranges are used to interpret glucose test results: * Normal: Less than 100 mg/dL (fasting) or less than 140 mg/dL (postprandial) * Impaired glucose tolerance: 100-125 mg/dL (fasting) or 140-199 mg/dL (postprandial) * Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher (fasting) or 200 mg/dL or higher (postprandial)Treating Abnormal Glucose Levels
Treating abnormal glucose levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring. The following treatments can be used to manage abnormal glucose levels:
- Lifestyle modifications: Focus on diet, physical activity, weight management, and stress reduction.
- Medications: Oral medications, such as metformin, or injectable medications, such as insulin, can help regulate glucose levels.
- Insulin therapy: Insulin injections or an insulin pump can help regulate glucose levels.
Medications for Glucose Management
Medications play a critical role in managing abnormal glucose levels. The following medications can be used to treat abnormal glucose levels: * Metformin: An oral medication that improves insulin sensitivity and reduces glucose production in the liver. * Sulfonylureas: Oral medications that stimulate insulin release from the pancreas. * Meglitinides: Oral medications that stimulate insulin release from the pancreas. * Thiazolidinediones: Oral medications that improve insulin sensitivity.Complications of Abnormal Glucose Levels

Abnormal glucose levels can lead to several complications, including:
- Heart disease: High glucose levels can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease.
- Kidney disease: High glucose levels can damage the kidneys and increase the risk of kidney failure.
- Nerve damage: High glucose levels can damage nerves and increase the risk of numbness, tingling, and pain.
- Vision problems: High glucose levels can damage the eyes and increase the risk of blindness.
Preventing Complications of Abnormal Glucose Levels
Preventing complications of abnormal glucose levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, and medication. The following strategies can help prevent complications: * Maintain normal glucose levels: Focus on diet, physical activity, weight management, and stress reduction. * Monitor glucose levels regularly: Use glucose tests to monitor glucose levels and adjust treatment as needed. * Manage blood pressure and cholesterol: High blood pressure and cholesterol can increase the risk of complications.What is the normal range for glucose levels?
+Normal glucose levels vary throughout the day, but generally fall between 70 and 99 mg/dL for fasting glucose and less than 140 mg/dL for postprandial glucose.
How can I maintain normal glucose levels?
+Maintaining normal glucose levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet, regular physical activity, weight management, and stress reduction, as well as regular monitoring and medication, if necessary.
What are the complications of abnormal glucose levels?
+Abnormal glucose levels can lead to several complications, including heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems.
In conclusion, maintaining normal glucose numbers is crucial for overall health and well-being. By understanding the importance of glucose management, incorporating lifestyle modifications, and using medication, if necessary, individuals can reduce their risk of developing glucose-related disorders and maintain optimal health. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with glucose management in the comments below and to share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
