Intro
Identify dehydration symptoms with our guide to 10 signs, including dry mouth, fatigue, and dark urine, to prevent severe dehydration and heat stroke, and learn dehydration treatment and prevention methods.
Dehydration is a common and potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including excessive sweating, diarrhea, vomiting, and certain medical conditions. Despite its prevalence, many people are unaware of the signs and symptoms of dehydration, which can lead to delayed treatment and serious complications. In this article, we will explore the 10 signs of dehydration, its causes, and its consequences, as well as provide tips on how to prevent and treat this condition.
Dehydration can affect anyone, regardless of age, sex, or physical condition. It is particularly common in older adults, young children, and people with certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or kidney disease. Even mild dehydration can cause significant discomfort and impair daily activities, while severe dehydration can lead to organ failure, seizures, and even death. Therefore, it is essential to recognize the signs and symptoms of dehydration and take prompt action to prevent and treat it.
The importance of recognizing the signs of dehydration cannot be overstated. Early detection and treatment can help prevent serious complications and improve outcomes. Moreover, dehydration can have a significant impact on daily life, causing fatigue, headaches, and difficulty concentrating. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and consequences of dehydration, individuals can take steps to prevent it and maintain optimal health. In the following sections, we will delve into the 10 signs of dehydration, its causes, and its consequences, as well as provide tips on how to prevent and treat this condition.
Introduction to Dehydration
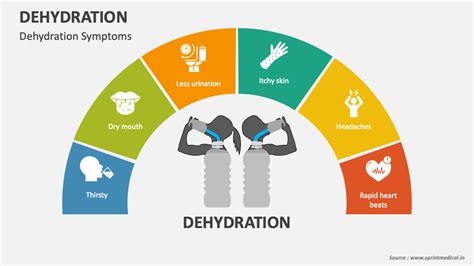
Causes of Dehydration
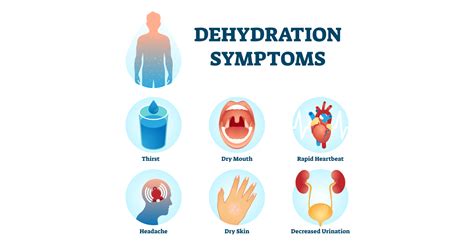
Types of Dehydration
There are three types of dehydration, including: * Mild dehydration: This is the most common type of dehydration and can be treated with oral rehydration therapy. * Moderate dehydration: This type of dehydration requires medical attention and may require intravenous fluids. * Severe dehydration: This is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.10 Signs of Dehydration
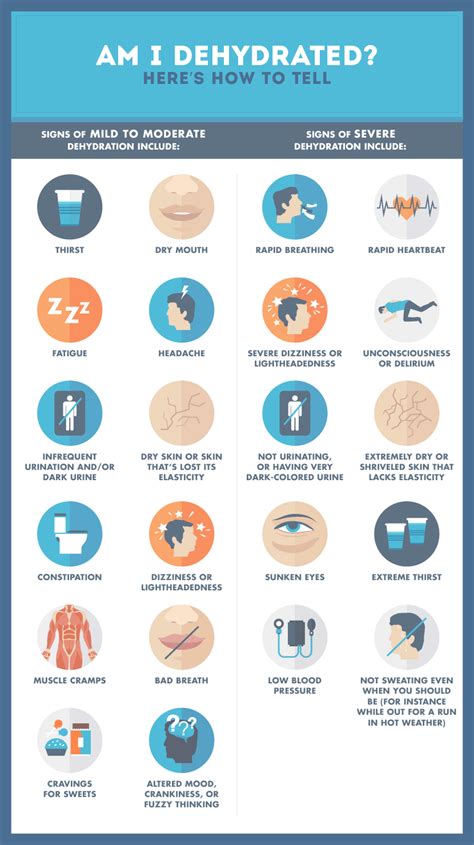
Consequences of Dehydration
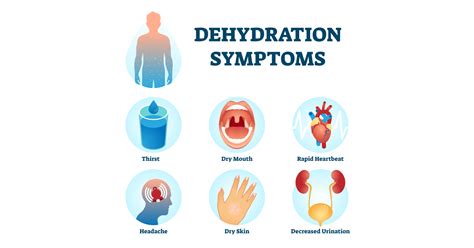
Preventing Dehydration
Preventing dehydration is crucial, especially in hot weather or during intense physical activity. The following tips can help prevent dehydration: * Drink plenty of water and other fluids. * Avoid excessive sweating by staying cool and wearing lightweight clothing. * Avoid caffeine and alcohol, which can increase urine production and lead to dehydration. * Eat foods that are high in water content, such as fruits and vegetables.Treatment of Dehydration

Oral Rehydration Therapy
Oral rehydration therapy involves drinking plenty of water and other fluids to replace lost fluids and electrolytes. The following tips can help: * Drink small, frequent amounts of fluid to avoid overwhelming the stomach. * Use an oral rehydration solution, such as Pedialyte or Gatorade, to replace lost electrolytes. * Avoid caffeinated beverages, which can increase urine production and worsen dehydration.What are the most common causes of dehydration?
+The most common causes of dehydration include excessive sweating, diarrhea, vomiting, and certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and kidney disease.
How can I prevent dehydration?
+Preventing dehydration involves drinking plenty of water and other fluids, avoiding excessive sweating, and eating foods that are high in water content, such as fruits and vegetables.
What are the symptoms of severe dehydration?
+The symptoms of severe dehydration include confusion, disorientation, seizures, and loss of consciousness. Severe dehydration requires immediate medical attention and can be life-threatening if left untreated.
How can I treat mild dehydration?
+Mild dehydration can be treated with oral rehydration therapy, which involves drinking plenty of water and other fluids to replace lost fluids and electrolytes.
What are the consequences of untreated dehydration?
+Untreated dehydration can have serious consequences, including organ failure, seizures, and even death. It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if symptoms of dehydration occur.
In
Final Thoughts

