Intro
Learn about 3 types of burns, including first, second, and third-degree burns, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options, understanding burn care and prevention.
Burns are a common type of injury that can occur due to various reasons such as fire, hot liquids, or electrical accidents. They can be classified into different types based on their severity and depth. Understanding the different types of burns is essential to provide proper treatment and care. In this article, we will discuss the three main types of burns, their characteristics, and treatment options.
Burns can be devastating and life-altering, causing significant pain, scarring, and emotional distress. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), burns are a major public health problem, with an estimated 180,000 deaths occurring annually due to burn injuries. In the United States alone, it is estimated that over 450,000 people are treated in emergency departments for burn injuries each year. The severity of burns can vary greatly, ranging from minor first-degree burns to life-threatening third-degree burns.
The treatment and management of burns depend on the type and severity of the injury. It is essential to understand the different types of burns to provide proper care and prevent further complications. The three main types of burns are first-degree, second-degree, and third-degree burns. Each type has distinct characteristics, and understanding these differences is crucial for effective treatment and management.
First-Degree Burns
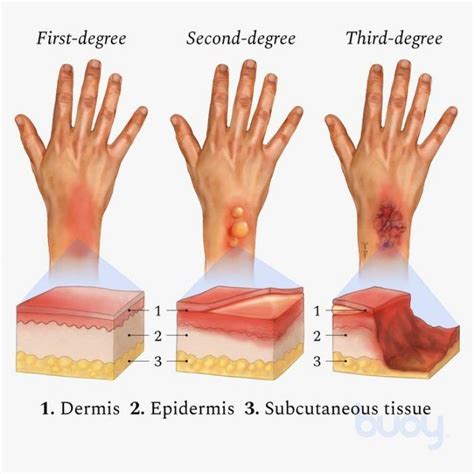
Causes and Symptoms of First-Degree Burns
First-degree burns can be caused by various factors, including exposure to heat, sunburn, or chemical irritants. The symptoms of first-degree burns include: * Redness and swelling of the affected area * Pain or discomfort * Dry, peeling skin * Mild inflammationSecond-Degree Burns
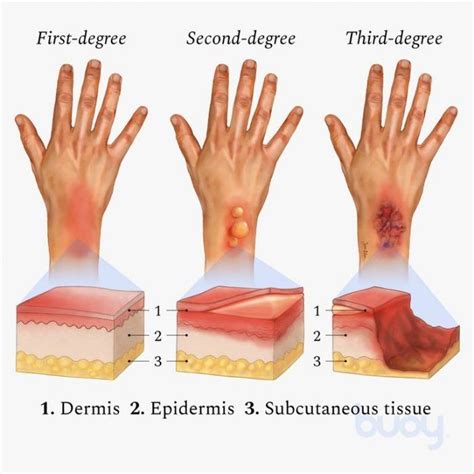
Treatment Options for Second-Degree Burns
The treatment of second-degree burns depends on the severity of the injury. Some common treatment options include: * Wound cleaning and dressing * Applying topical antibiotics to prevent infection * Using pain relievers to manage pain and discomfort * Elevating the affected area to reduce swellingThird-Degree Burns
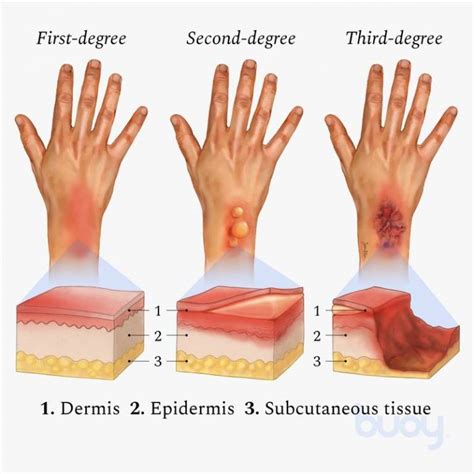
Complications and Management of Third-Degree Burns
Third-degree burns can lead to various complications, including infection, scarring, and contractures. The management of third-degree burns involves: * Surgical excision of dead tissue * Wound closure using skin grafts or flaps * Rehabilitation to restore range of motion and function * Pain management to reduce discomfort and promote healingPrevention and Safety Measures
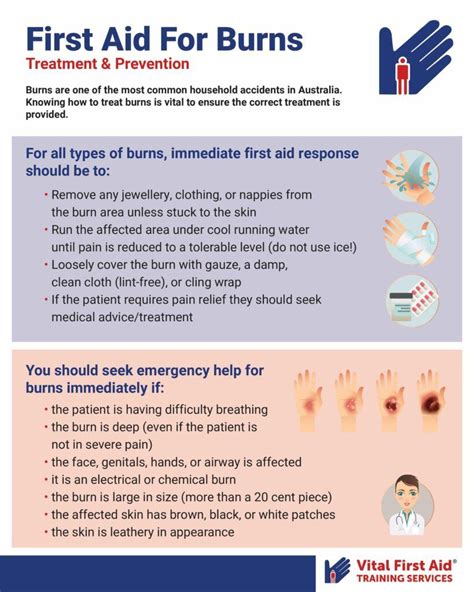
Importance of Burn Awareness and Education
Burn awareness and education are essential to preventing burn injuries and promoting proper treatment and care. Some key aspects of burn awareness include: * Understanding the different types of burns and their characteristics * Recognizing the signs and symptoms of burn injuries * Knowing how to provide basic first aid and wound care * Promoting burn prevention and safety measures in the communityRehabilitation and Recovery

Challenges and Opportunities in Burn Rehabilitation
Burn rehabilitation can be challenging, with individuals facing physical, emotional, and psychological barriers to recovery. Some common challenges include: * Chronic pain and discomfort * Scarring and disfigurement * Emotional trauma and anxiety * Social isolation and stigmaConclusion and Future Directions

What are the most common causes of burns?
+The most common causes of burns include fire, hot liquids, electrical accidents, and chemical irritants.
How can I prevent burn injuries?
+To prevent burn injuries, be cautious when handling hot objects or liquids, use protective gear, install smoke alarms and fire extinguishers, and teach children about fire safety and burn prevention.
What are the different types of burns?
+The three main types of burns are first-degree, second-degree, and third-degree burns, which vary in severity and depth of injury.
How can I treat minor burn injuries at home?
+To treat minor burn injuries at home, apply cool water, use topical creams, and take pain relievers as needed. However, seek medical attention if the burn is severe or covers a large area.
What are the complications of burn injuries?
+The complications of burn injuries include infection, scarring, contractures, and emotional trauma. Prompt medical attention and proper wound care can help prevent these complications.
