Intro
Discover what is effusion, a geological process involving lava flow, volcanic eruption, and magma movement, related to volcanic activity, land formation, and geology concepts.
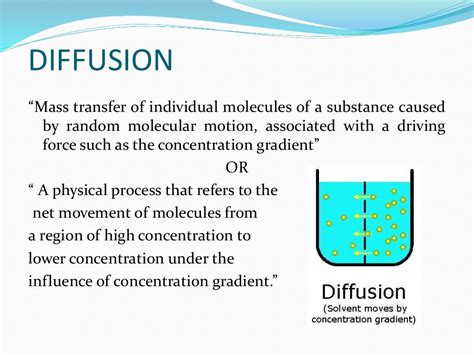
The process of effusion is a vital concept in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and biology. Effusion refers to the flow of particles, such as molecules or ions, through a small opening or pore in a container or membrane. This process is essential in understanding the behavior of gases, the separation of mixtures, and the functioning of biological systems. The importance of effusion lies in its ability to separate particles based on their size, shape, and molecular weight, making it a crucial concept in fields like chemistry and biotechnology.
The concept of effusion has been studied extensively in chemistry, where it is used to separate gases and understand their properties. The rate of effusion is influenced by factors such as the size of the opening, the pressure of the gas, and the molecular weight of the particles. By understanding the principles of effusion, scientists can design more efficient separation techniques and develop new technologies for gas purification and analysis. Furthermore, the study of effusion has led to significant advancements in fields like materials science, where it is used to develop new materials with specific properties.
The process of effusion is not limited to chemistry and physics; it also plays a crucial role in biological systems. In living organisms, effusion occurs in cell membranes, where it regulates the flow of molecules in and out of cells. This process is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis, regulating the concentration of ions and nutrients, and facilitating the removal of waste products. The study of effusion in biological systems has led to a deeper understanding of cellular function and has significant implications for fields like medicine and biotechnology.
Introduction to Effusion

The concept of effusion is closely related to the kinetic theory of gases, which describes the behavior of gas molecules in terms of their random motion. According to this theory, gas molecules are in constant motion, colliding with each other and the walls of their container. The rate of effusion is influenced by the velocity of the gas molecules, which is determined by their temperature and molecular weight. By understanding the principles of effusion, scientists can design more efficient separation techniques and develop new technologies for gas purification and analysis.
Key Principles of Effusion
The process of effusion is governed by several key principles, including: * The size of the opening: The rate of effusion is influenced by the size of the opening, with smaller openings resulting in slower rates of effusion. * The pressure of the gas: The rate of effusion is also influenced by the pressure of the gas, with higher pressures resulting in faster rates of effusion. * The molecular weight of the particles: The rate of effusion is influenced by the molecular weight of the particles, with lighter particles effusing more rapidly than heavier particles.Types of Effusion
There are several types of effusion, including:
- Graham's law of effusion: This law states that the rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molecular weight.
- Knudsen effusion: This type of effusion occurs when the mean free path of the gas molecules is comparable to the size of the opening.
- Molecular effusion: This type of effusion occurs when the gas molecules interact with each other and the walls of the container.
Applications of Effusion
The process of effusion has numerous applications in various fields, including: * Gas separation: Effusion is used to separate gases based on their molecular weight and size. * Materials science: Effusion is used to develop new materials with specific properties, such as porous materials and membranes. * Biotechnology: Effusion is used to separate biomolecules, such as proteins and DNA, based on their size and shape.Effusion in Biological Systems
In biological systems, effusion plays a crucial role in regulating the flow of molecules in and out of cells. The cell membrane is a semi-permeable barrier that allows certain molecules to pass through while restricting others. The process of effusion is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis, regulating the concentration of ions and nutrients, and facilitating the removal of waste products.
Cell Membrane Structure and Function
The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, with embedded proteins that regulate the flow of molecules. The structure and function of the cell membrane are essential for understanding the process of effusion in biological systems. The cell membrane is selectively permeable, allowing certain molecules to pass through while restricting others. This selectivity is achieved through the presence of specific transport proteins that facilitate the movement of molecules across the membrane.Effusion in Chemistry

In chemistry, effusion is used to separate gases and understand their properties. The rate of effusion is influenced by factors such as the size of the opening, the pressure of the gas, and the molecular weight of the particles. By understanding the principles of effusion, scientists can design more efficient separation techniques and develop new technologies for gas purification and analysis.
Gas Separation Techniques
There are several gas separation techniques that utilize the process of effusion, including: * Distillation: This technique involves the separation of gases based on their boiling points. * Chromatography: This technique involves the separation of gases based on their affinity for a stationary phase. * Membrane separation: This technique involves the separation of gases based on their size and shape.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, the process of effusion is a vital concept in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and biology. The importance of effusion lies in its ability to separate particles based on their size, shape, and molecular weight, making it a crucial concept in fields like chemistry and biotechnology. Future research directions include the development of new technologies for gas purification and analysis, as well as a deeper understanding of the role of effusion in biological systems.
What is effusion?
+Effusion is the flow of particles, such as molecules or ions, through a small opening or pore in a container or membrane.
What are the key principles of effusion?
+The key principles of effusion include the size of the opening, the pressure of the gas, and the molecular weight of the particles.
What are the applications of effusion?
+The applications of effusion include gas separation, materials science, and biotechnology.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the process of effusion and its importance in various fields. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with others who may be interested in learning more about effusion.
