Intro
Understand 5 A1c levels, from normal to diabetic ranges, and learn how HbA1c tests diagnose and monitor blood sugar control, prediabetes, and diabetes management.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, particularly for individuals with diabetes. One of the key metrics used to measure blood sugar control is the HbA1c test, which reflects average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months. Understanding the significance of HbA1c levels and their implications for health can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their diabetes management. The importance of monitoring and controlling HbA1c levels cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the risk of developing diabetes-related complications.
Effective management of HbA1c levels requires a comprehensive approach, incorporating lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, and regular monitoring. By grasping the concepts underlying HbA1c levels and their impact on health, individuals can better navigate the complexities of diabetes care. Moreover, recognizing the factors that influence HbA1c levels, such as diet, physical activity, and stress, can help individuals develop personalized strategies for maintaining optimal blood sugar control.
The relationship between HbA1c levels and health outcomes is well-established, with higher levels associated with an increased risk of diabetes-related complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Conversely, maintaining HbA1c levels within the target range can significantly reduce the risk of these complications, improving overall quality of life. As such, it is essential to understand the factors that influence HbA1c levels and to develop effective strategies for maintaining optimal blood sugar control.
Understanding HbA1c Levels
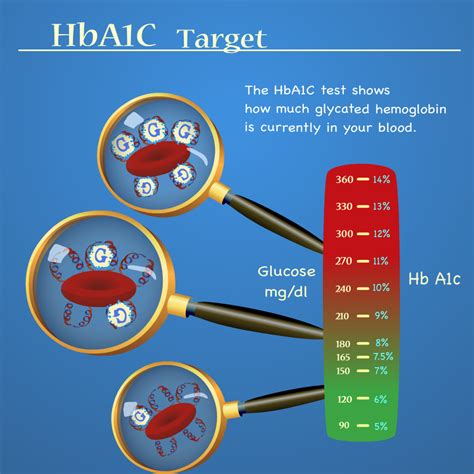
Interpreting HbA1c Results
Interpreting HbA1c results requires a comprehensive understanding of the target range and the factors that influence blood sugar control. The American Diabetes Association recommends the following HbA1c targets: * Less than 5.7% for individuals without diabetes * Less than 7% for individuals with diabetes * Less than 8% for individuals with a history of severe hypoglycemia or limited life expectancy Understanding these targets and the implications of HbA1c results can help individuals develop effective strategies for maintaining optimal blood sugar control.Factors Influencing HbA1c Levels

Strategies for Maintaining Optimal HbA1c Levels
Maintaining optimal HbA1c levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, and regular monitoring. Some strategies for maintaining optimal HbA1c levels include: * Developing a personalized meal plan that takes into account individual nutritional needs and preferences * Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or jogging, to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels * Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga, to minimize the impact of stress on blood sugar control * Prioritizing sleep quality and duration to maintain optimal blood sugar controlMonitoring and Controlling HbA1c Levels
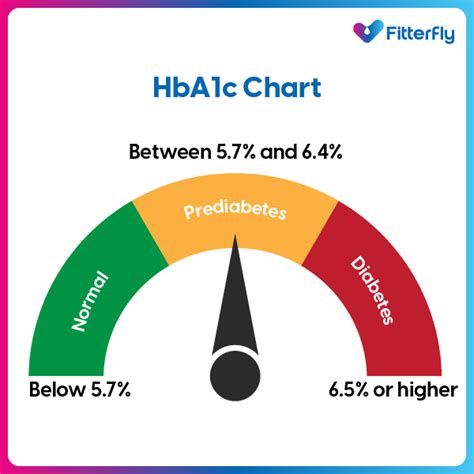
Benefits of Maintaining Optimal HbA1c Levels
Maintaining optimal HbA1c levels can have numerous benefits, including: * Reduced risk of diabetes-related complications, such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage * Improved overall quality of life * Enhanced physical and mental well-being * Increased life expectancyCommon Mistakes in HbA1c Level Management
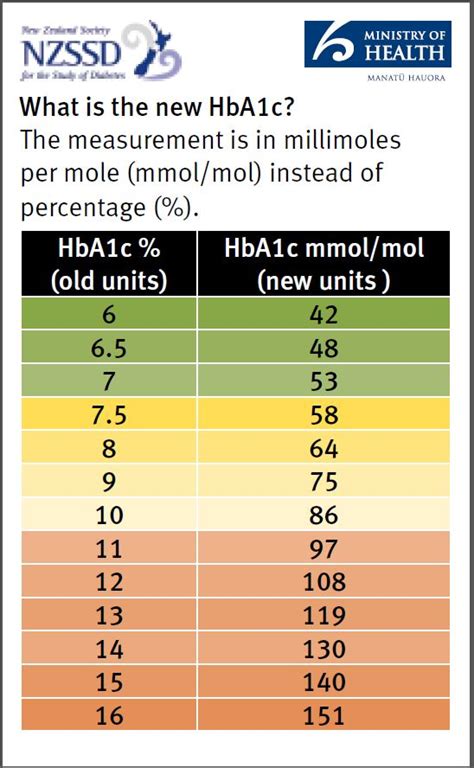
Overcoming Challenges in HbA1c Level Management
Overcoming challenges in HbA1c level management requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, and regular monitoring. Some strategies for overcoming challenges in HbA1c level management include: * Developing a personalized treatment plan that takes into account individual needs and preferences * Working with a healthcare provider to address challenges and develop effective solutions * Prioritizing self-care and stress management to minimize the impact of stress on blood sugar control * Staying informed about the latest developments in diabetes care and managementFuture Directions in HbA1c Level Management

Implications for Clinical Practice
The implications of HbA1c level management for clinical practice are significant, with healthcare providers playing a critical role in supporting individuals with diabetes to maintain optimal blood sugar control. Some strategies for healthcare providers to support HbA1c level management include: * Developing personalized treatment plans that take into account individual needs and preferences * Providing ongoing education and support to individuals with diabetes * Encouraging regular monitoring and controlling of HbA1c levels * Staying informed about the latest developments in diabetes care and managementConclusion and Recommendations

We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences on HbA1c level management in the comments section below. Additionally, we encourage readers to share this article with others who may benefit from the information and to explore other resources on diabetes care and management. By working together, we can improve outcomes for individuals with diabetes and promote better health and well-being for all.
What is the normal range for HbA1c levels?
+The normal range for HbA1c levels is less than 5.7% for individuals without diabetes and less than 7% for individuals with diabetes.
How often should I get my HbA1c levels checked?
+HbA1c levels should be checked at least twice a year, or more frequently if you have a history of poor blood sugar control or are experiencing symptoms of diabetes-related complications.
What can I do to lower my HbA1c levels?
+To lower your HbA1c levels, focus on maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and adhering to your medication regimen as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
