Intro
Discover 5 ways to address high CO2 blood test results, including symptoms, causes, and treatment options, to manage respiratory acidosis and hypercapnia, and improve overall health and wellness.
High CO2 blood test results can be a cause for concern, but understanding the implications and taking corrective action can help mitigate potential health risks. A high CO2 level in the blood, also known as hypercapnia, occurs when the body retains more carbon dioxide than it should. This can be due to various factors, including respiratory problems, metabolic disorders, or other underlying health conditions. It is essential to address high CO2 levels to prevent complications and ensure overall well-being.
The importance of maintaining healthy CO2 levels cannot be overstated. When CO2 levels are elevated, it can lead to respiratory acidosis, a condition where the blood becomes too acidic. This can cause symptoms such as headaches, confusion, and fatigue. In severe cases, high CO2 levels can lead to more serious complications, including respiratory failure, organ damage, and even death. Therefore, it is crucial to identify the underlying causes of high CO2 levels and take corrective action to restore balance to the body.
Understanding the causes of high CO2 levels is vital to developing effective treatment strategies. Some common causes of high CO2 levels include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia, and other respiratory infections. Metabolic disorders, such as diabetes and kidney disease, can also contribute to elevated CO2 levels. Additionally, certain medications, such as sedatives and opioids, can slow down breathing rates, leading to increased CO2 retention. By identifying the underlying cause of high CO2 levels, individuals can take targeted steps to address the issue and improve their overall health.
Understanding CO2 Blood Tests

Types of CO2 Blood Tests
CO2 blood tests can be categorized into three main types: arterial, venous, and capillary. Arterial blood gas (ABG) tests involve taking a blood sample from an artery, usually in the wrist or groin area. This test provides a comprehensive picture of the body's acid-base balance and oxygenation status. Venous blood gas (VBG) tests, on the other hand, involve taking a blood sample from a vein. This test is less invasive than an ABG test but still provides valuable information about CO2 levels and acid-base balance. Capillary blood gas (CBG) tests involve taking a blood sample from a capillary, usually in the finger or earlobe. This test is quick and easy to perform but may not provide as much information as ABG or VBG tests.Causes of High CO2 Levels
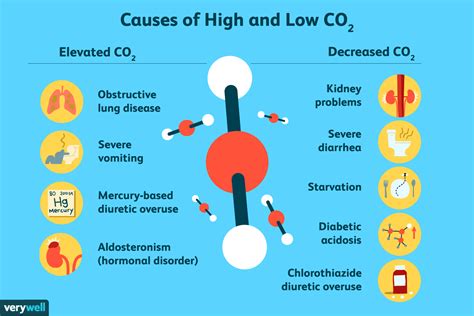
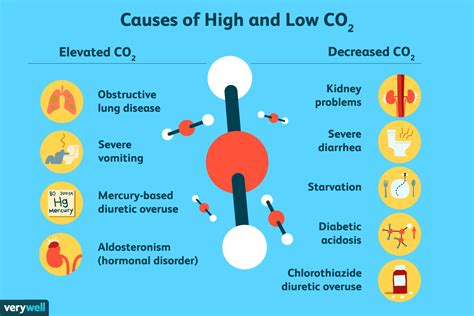
Respiratory Causes of High CO2 Levels
Respiratory problems are a common cause of high CO2 levels. Conditions such as COPD, pneumonia, and asthma can damage the lungs and impair gas exchange, leading to elevated CO2 levels. Other respiratory causes of high CO2 levels include chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and cystic fibrosis. In addition to these conditions, certain medications, such as sedatives and opioids, can slow down breathing rates and lead to increased CO2 retention.Treatment Options for High CO2 Levels
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce CO2 Levels
Lifestyle changes can play an essential role in reducing CO2 levels and improving overall health. Quitting smoking, for example, can help improve lung function and reduce the risk of respiratory problems. Exercising regularly can also help improve respiratory function and increase oxygenation of the body. Maintaining a healthy weight can also help reduce the risk of metabolic disorders and improve overall health. Other lifestyle changes, such as reducing stress, getting enough sleep, and eating a healthy diet, can also help improve respiratory function and reduce CO2 levels.Complications of High CO2 Levels
Long-Term Effects of High CO2 Levels
The long-term effects of high CO2 levels can be devastating. Chronic respiratory problems, such as COPD, can lead to permanent damage to the lungs and impair gas exchange. Metabolic disorders, such as diabetes and kidney disease, can also lead to long-term complications, including organ damage and increased risk of infection. In addition to these complications, high CO2 levels can also lead to cognitive impairment, mood disorders, and other neurological problems.Prevention Strategies for High CO2 Levels

Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and treatment of high CO2 levels are crucial to preventing long-term complications and improving overall health. Regular health check-ups, including CO2 blood tests, can help identify potential respiratory or metabolic problems early on. Prompt treatment, including lifestyle changes and medical interventions, can help reduce CO2 levels and improve respiratory function. In addition to these interventions, public health awareness campaigns and education programs can also help raise awareness about the risks of high CO2 levels and promote healthy behaviors.What are the symptoms of high CO2 levels?
+The symptoms of high CO2 levels can include headaches, confusion, fatigue, and shortness of breath. In severe cases, high CO2 levels can lead to respiratory failure, organ damage, and even death.
How are high CO2 levels diagnosed?
+High CO2 levels are typically diagnosed using CO2 blood tests, such as arterial blood gas (ABG) tests, venous blood gas (VBG) tests, or capillary blood gas (CBG) tests. These tests measure the levels of carbon dioxide in the blood and can help identify potential respiratory or metabolic problems.
What are the treatment options for high CO2 levels?
+Treatment for high CO2 levels depends on the underlying cause of the condition. In cases where respiratory problems are the cause, treatment may involve oxygen therapy, bronchodilators, or other medications to help improve breathing and gas exchange. In cases where metabolic disorders are the cause, treatment may involve dietary changes, medications, or other interventions to help regulate acid-base balance.
Can high CO2 levels be prevented?
+Yes, high CO2 levels can be prevented by making lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight. Medical interventions, such as oxygen therapy and medications, can also help improve breathing and gas exchange. Environmental modifications, such as reducing exposure to air pollution and improving indoor air quality, can also help reduce the risk of respiratory problems and high CO2 levels.
What are the long-term effects of high CO2 levels?
+The long-term effects of high CO2 levels can be devastating. Chronic respiratory problems, such as COPD, can lead to permanent damage to the lungs and impair gas exchange. Metabolic disorders, such as diabetes and kidney disease, can also lead to long-term complications, including organ damage and increased risk of infection.
In conclusion, high CO2 levels can have serious consequences for overall health, but understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help individuals take control of their health. By making lifestyle changes, seeking medical attention when necessary, and staying informed about the risks of high CO2 levels, individuals can reduce their risk of developing respiratory and metabolic problems. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with high CO2 levels in the comments section below and to take proactive steps to protect their health.
