Intro
Learn about the A1c blood test, a crucial diabetes diagnostic tool, measuring average blood sugar levels, glycated hemoglobin, and glucose control, to manage diabetes, monitor blood glucose, and prevent complications.
The A1c blood test is a crucial diagnostic tool used to measure the average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months. It is a vital component in the management and diagnosis of diabetes, a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding the A1c test and its significance can help individuals with diabetes make informed decisions about their health and treatment. In this article, we will delve into the world of A1c testing, exploring its importance, working mechanisms, and the steps involved in the testing process.
The importance of A1c testing cannot be overstated. It provides a comprehensive picture of an individual's blood glucose control, enabling healthcare providers to assess the effectiveness of treatment plans and make necessary adjustments. The test is also used to diagnose diabetes, prediabetes, and gestational diabetes. Moreover, A1c testing helps identify individuals who are at risk of developing diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. By monitoring A1c levels, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and prevent long-term damage.
A1c testing is a relatively simple and painless procedure that involves a blood draw. The test measures the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that has been glycated, or bound to glucose. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to the body's tissues. When glucose is present in the blood, it binds to hemoglobin, forming glycated hemoglobin. The higher the blood glucose levels, the more hemoglobin is glycated. By measuring the percentage of glycated hemoglobin, healthcare providers can determine an individual's average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months.
A1c Test Overview
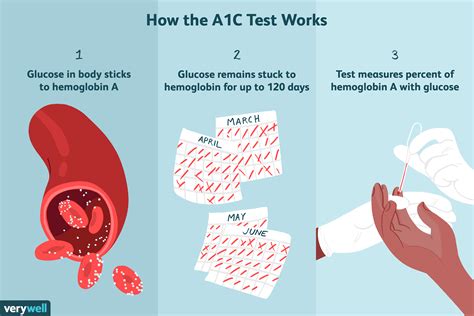
Understanding A1c Results
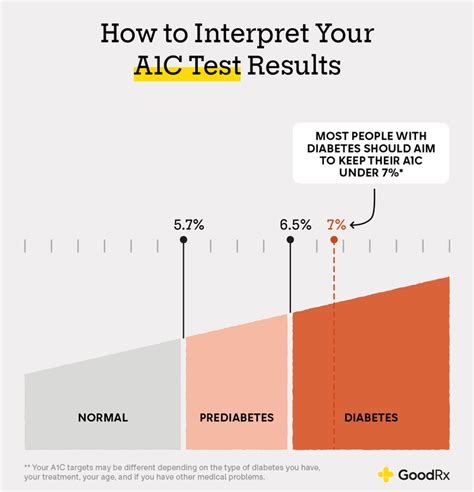
The A1c test results are interpreted based on the percentage of glycated hemoglobin in the blood. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends the following A1c targets: * Less than 5.7%: Normal * 5.7% to 6.4%: Prediabetes * 6.5% or higher: Diabetes It is essential to note that A1c results can be influenced by various factors, such as age, ethnicity, and certain medical conditions. Healthcare providers take these factors into account when interpreting A1c results and developing treatment plans.A1c Testing for Diabetes Diagnosis
A1c Testing for Prediabetes
Prediabetes is a condition in which blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. A1c testing is used to diagnose prediabetes, and the results are interpreted based on the percentage of glycated hemoglobin in the blood. The ADA recommends the following A1c targets for prediabetes: * 5.7% to 6.4%: Prediabetes Individuals with prediabetes are at risk of developing type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. A1c testing helps identify individuals with prediabetes, enabling them to take proactive steps to manage their condition and prevent long-term damage.A1c Testing for Gestational Diabetes
A1c Testing for Monitoring Diabetes
A1c testing is not only used for diagnosis but also for monitoring diabetes. The test is used to assess the effectiveness of treatment plans and make necessary adjustments. The ADA recommends A1c testing at least twice a year for individuals with diabetes, and more frequently for those who are not meeting their treatment targets. By monitoring A1c levels, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and prevent long-term damage.A1c Test Preparation

A1c Test Risks and Side Effects
The A1c test is a relatively safe procedure, but it can cause some side effects. The most common side effects include: * Pain or bruising at the injection site * Dizziness or lightheadedness * Fainting * Infection It is essential to note that these side effects are rare and usually mild. However, individuals should inform their healthcare provider if they experience any unusual symptoms or side effects.A1c Test Results Interpretation

A1c Test Results and Treatment
A1c test results play a critical role in developing treatment plans for diabetes. The results help healthcare providers assess the effectiveness of treatment plans and make necessary adjustments. The ADA recommends the following treatment targets: * A1c levels less than 7% for most adults * A1c levels less than 7.5% for adults with a history of severe hypoglycemia or limited life expectancy * A1c levels less than 8% for adults with significant comorbidities or extensive insulin use By monitoring A1c levels, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and prevent long-term damage.A1c Testing and Insurance Coverage
A1c Testing and Cost
The cost of A1c testing varies depending on the location, insurance coverage, and the type of test. On average, the cost of an A1c test can range from $20 to $100. However, with insurance coverage, the out-of-pocket cost is usually minimal. It is essential to note that the cost of A1c testing is a small fraction of the overall cost of diabetes care, and the benefits of regular testing far outweigh the costs.What is the A1c test used for?
+The A1c test is used to measure the average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months. It is a vital component in the management and diagnosis of diabetes.
How is the A1c test performed?
+The A1c test is performed by drawing a blood sample from a vein in the arm. The sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis, and the results are usually available within a few days.
What are the benefits of regular A1c testing?
+Regular A1c testing helps individuals with diabetes monitor their condition, assess the effectiveness of treatment plans, and make necessary adjustments. It also helps identify individuals who are at risk of developing diabetes-related complications.
How often should I get an A1c test?
+The American Diabetes Association recommends A1c testing at least twice a year for individuals with diabetes, and more frequently for those who are not meeting their treatment targets.
Can I take the A1c test at home?
+No, the A1c test is typically performed in a healthcare setting, such as a doctor's office or laboratory. However, there are some at-home A1c testing kits available, but they may not be as accurate as the tests performed in a laboratory.
In summary, the A1c test is a vital component in the management and diagnosis of diabetes. It provides a comprehensive picture of an individual's blood glucose control, enabling healthcare providers to assess the effectiveness of treatment plans and make necessary adjustments. By understanding the A1c test and its significance, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and prevent long-term damage. We encourage readers to share their experiences with A1c testing, ask questions, and seek guidance from healthcare professionals to better manage their diabetes.
