Intro
Discover Clindamycin uses and benefits, a broad-spectrum antibiotic treating bacterial infections, acne, and skin conditions, with applications in dental, respiratory, and bone infections, offering effective relief and prevention.
Clindamycin is a medication that has been widely used for several decades to treat various bacterial infections. It is a lincosamide antibiotic, which works by stopping the growth of bacteria. Clindamycin is effective against a range of bacteria, including those that are resistant to other antibiotics. In this article, we will explore the uses and benefits of clindamycin, as well as its potential side effects and interactions.
Clindamycin has been used to treat a variety of infections, including skin and soft tissue infections, respiratory tract infections, and infections of the female reproductive organs. It is also used to treat infections caused by anaerobic bacteria, which are bacteria that do not require oxygen to grow. Clindamycin is often prescribed to patients who are allergic to penicillin or other antibiotics, as it is generally well-tolerated and effective.
The benefits of clindamycin include its ability to treat a wide range of bacterial infections, its effectiveness against resistant bacteria, and its relatively low risk of side effects. Clindamycin is also available in a variety of formulations, including capsules, tablets, and topical creams, which makes it easy to use and administer. Additionally, clindamycin has been shown to be effective in treating infections in patients with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy.
What is Clindamycin Used For?

How Does Clindamycin Work?
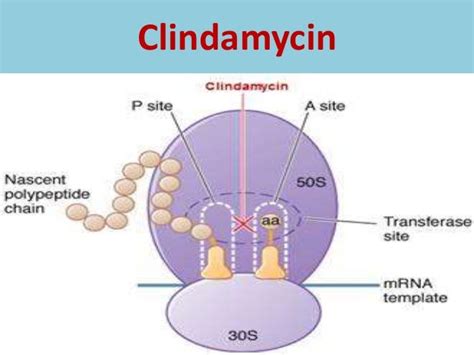
Clindamycin works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria by binding to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome, which is responsible for protein synthesis. This prevents the bacteria from producing essential proteins, ultimately leading to the death of the bacteria. Clindamycin is effective against a range of bacteria, including Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, as well as anaerobic bacteria.Benefits of Clindamycin

Side Effects of Clindamycin
While clindamycin is generally well-tolerated, it can cause some side effects, including: * Diarrhea * Nausea and vomiting * Abdominal pain * Rash * Itching * Yeast infectionsInteractions with Other Medications
Precautions and Warnings
Clindamycin should be used with caution in patients with: * Allergies to clindamycin or other lincosamide antibiotics * Liver or kidney disease * Pregnancy or breastfeeding * Compromised immune systemsAdministration and Dosage
Forms of Clindamycin
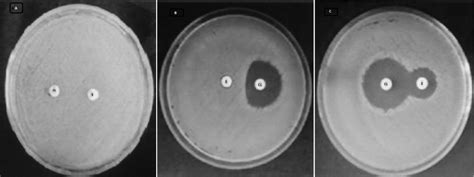
Clindamycin is available in a variety of formulations, including: * Capsules * Tablets * Topical creams * InjectablesResistance and Misuse
Environmental Impact
The production and disposal of clindamycin can have an environmental impact, including: * Contamination of water and soil * Harm to aquatic life * Contribution to antibiotic resistanceConclusion and Future Directions
What is clindamycin used for?
+Clindamycin is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including skin and soft tissue infections, respiratory tract infections, and infections of the female reproductive organs.
How does clindamycin work?
+Clindamycin works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria by binding to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome, which is responsible for protein synthesis.
What are the side effects of clindamycin?
+The side effects of clindamycin include diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, rash, itching, and yeast infections.
Can clindamycin be used in patients with compromised immune systems?
+Yes, clindamycin can be used in patients with compromised immune systems, including those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy.
How can I minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance when using clindamycin?
+To minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance, use clindamycin only as directed by a healthcare provider, complete the full course of treatment, and avoid sharing antibiotics with others.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of clindamycin uses and benefits. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with clindamycin, please comment below. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please share it with others who may benefit from this information.
