Intro
Identify Achilles heel tear symptoms, including pain, swelling, and limited mobility, and learn about treatment options for this common injury, such as physical therapy and surgery, to alleviate discomfort and promote healing.
The Achilles tendon is a vital part of the human body, connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone and playing a crucial role in movements such as walking, running, and jumping. However, this tendon can be prone to injuries, particularly tears, which can be debilitating and require immediate medical attention. An Achilles heel tear, also known as an Achilles tendon rupture, occurs when the tendon partially or completely tears, leading to severe pain and limited mobility. Understanding the symptoms of an Achilles heel tear is essential for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
The importance of recognizing Achilles heel tear symptoms cannot be overstated. Delayed diagnosis and treatment can lead to further complications, such as chronic pain, limited mobility, and increased risk of re-rupture. Moreover, an untreated Achilles tendon rupture can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, making everyday activities a challenge. Therefore, it is crucial to be aware of the warning signs and seek medical help immediately if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Achilles heel tears can occur suddenly, often without warning, and may be caused by a variety of factors, including overuse, trauma, or underlying medical conditions. The symptoms of an Achilles heel tear can vary in severity and may include a sudden, sharp pain in the back of the ankle, swelling, and bruising. In some cases, a popping or snapping sound may be heard at the time of injury, followed by difficulty walking or standing on the affected leg. As the condition progresses, symptoms may worsen, leading to chronic pain, stiffness, and limited mobility.
Achilles Heel Tear Causes and Risk Factors
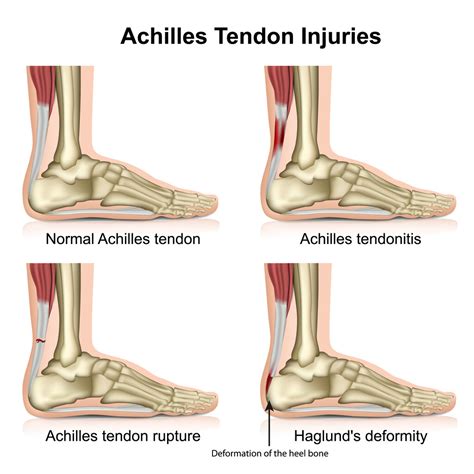
Common Causes of Achilles Heel Tears
Some common causes of Achilles heel tears include: * Sudden contraction of the calf muscles * Overstretching or sudden stretching of the tendon * Direct blow to the tendon * Poor foot mechanics or biomechanics * Inadequate warm-up or cool-down exercises * Previous injuries or tendonitisAchilles Heel Tear Symptoms and Diagnosis
Diagnosing an Achilles heel tear typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests, such as an X-ray or MRI. A healthcare professional will assess the affected area, looking for signs of swelling, bruising, or tenderness, and may perform a series of tests to evaluate the tendon's integrity.
Imaging Tests for Achilles Heel Tears
Imaging tests, such as X-rays and MRIs, can help confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes of symptoms. These tests can provide valuable information about the extent of the injury and guide treatment decisions.Achilles Heel Tear Treatment and Management
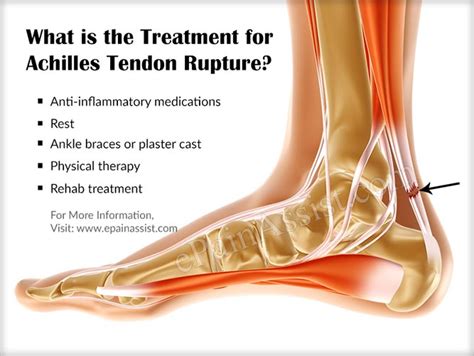
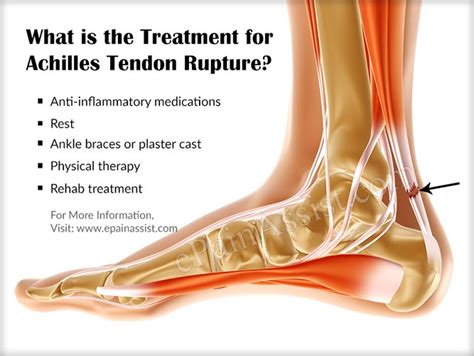
Conservative Treatment Options
Conservative treatment options for Achilles heel tears include: * Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) to reduce pain and inflammation * Physical therapy to improve range of motion and strength * Bracing or orthotics to support the affected area * Pain management, such as medication or injectionsSurgical Treatment Options
Surgical treatment options for Achilles heel tears include: * Open repair, which involves making an incision to repair the tendon * Percutaneous repair, which involves making small incisions to repair the tendon * Minimally invasive repair, which involves using a small camera and instruments to repair the tendonAchilles Heel Tear Prevention and Recovery
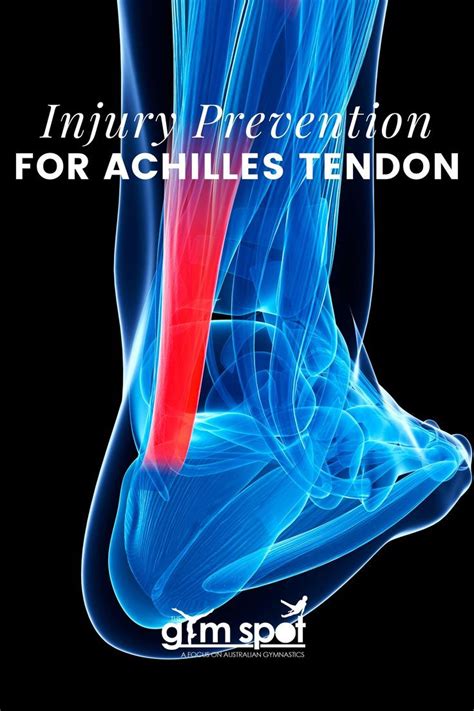
Recovery from an Achilles heel tear can be a lengthy and challenging process, requiring patience, dedication, and proper care. Individuals can promote recovery by:
- Following a rehabilitation program, including physical therapy and exercises
- Using bracing or orthotics to support the affected area
- Managing pain and inflammation
- Gradually returning to activity and sports
Rehabilitation Programs for Achilles Heel Tears
Rehabilitation programs for Achilles heel tears typically involve a combination of physical therapy, exercises, and bracing or orthotics. These programs can help promote recovery, improve range of motion and strength, and reduce the risk of re-rupture.What are the symptoms of an Achilles heel tear?
+The symptoms of an Achilles heel tear can include sudden, severe pain in the back of the ankle, swelling, bruising, or redness around the affected area, difficulty walking or standing on the affected leg, weakness or stiffness in the calf muscles, limited mobility or range of motion, and a popping or snapping sound at the time of injury.
How is an Achilles heel tear diagnosed?
+An Achilles heel tear is typically diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests, such as an X-ray or MRI. A healthcare professional will assess the affected area, looking for signs of swelling, bruising, or tenderness, and may perform a series of tests to evaluate the tendon's integrity.
What are the treatment options for an Achilles heel tear?
+Treatment options for an Achilles heel tear depend on the severity of the injury and may involve a combination of conservative and surgical approaches. Conservative treatment options, such as physical therapy, bracing, and pain management, can be effective for mild to moderate tears. However, more severe tears may require surgical intervention to repair the tendon.
How can I prevent an Achilles heel tear?
+Preventing an Achilles heel tear requires a combination of proper training, equipment, and techniques. Individuals can reduce their risk of developing an Achilles tendon rupture by warming up and cooling down properly, stretching and strengthening the calf muscles, using proper foot mechanics and biomechanics, avoiding overuse and trauma, and wearing proper footwear and orthotics.
What is the recovery time for an Achilles heel tear?
+Recovery time for an Achilles heel tear can vary depending on the severity of the injury and the effectiveness of treatment. Generally, recovery can take several months to a year or more, requiring patience, dedication, and proper care. Individuals can promote recovery by following a rehabilitation program, including physical therapy and exercises, using bracing or orthotics to support the affected area, managing pain and inflammation, and gradually returning to activity and sports.
In conclusion, recognizing the symptoms of an Achilles heel tear is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment. By understanding the causes, risk factors, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this condition. If you suspect you have an Achilles heel tear, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately to avoid further complications and promote optimal recovery. We encourage you to share your experiences, ask questions, and seek advice from healthcare professionals to ensure the best possible outcomes.
