Intro
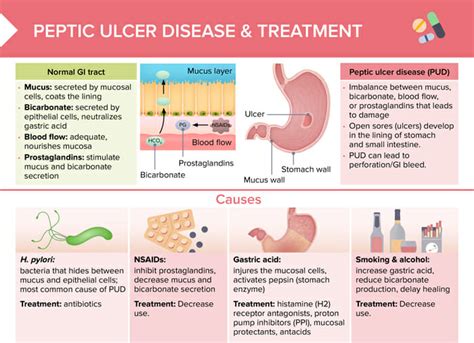
Peptic ulcers are a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. These painful sores can develop in the lining of the stomach or the first part of the small intestine, causing discomfort, bloating, and other symptoms. The importance of understanding peptic ulcers cannot be overstated, as left untreated, they can lead to serious complications, such as bleeding, perforation, and narrowing of the stomach or intestine. In this article, we will delve into the world of peptic ulcers, exploring their causes, symptoms, and most importantly, the various treatments available to alleviate this condition.
Peptic ulcers are often associated with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacterial infections, which can weaken the protective lining of the stomach and small intestine, making them more susceptible to acid damage. Other factors, such as long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), stress, and a family history of ulcers, can also contribute to the development of peptic ulcers. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of peptic ulcers, such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and weight loss, is crucial for seeking medical attention and preventing further complications.
The diagnosis of peptic ulcers typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as endoscopy, blood tests, and stool tests. Once diagnosed, the primary goal of treatment is to heal the ulcer, prevent recurrence, and manage symptoms. This can be achieved through a variety of treatments, including medications, lifestyle modifications, and alternative therapies. In the following sections, we will explore the different treatment options available for peptic ulcers, highlighting their benefits, risks, and effectiveness.
Medications for Peptic Ulcers
Benefits and Risks of Medications
While medications can effectively manage peptic ulcers, they can also have benefits and risks. For example, antacids can provide quick relief from symptoms, but long-term use can lead to side effects such as constipation and diarrhea. H2 blockers and PPIs can reduce acid production, but they can also increase the risk of osteoporosis and vitamin B12 deficiency. Antibiotics can eliminate H. pylori bacteria, but they can also cause side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting.Lifestyle Modifications for Peptic Ulcers

Benefits of Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications can have numerous benefits for individuals with peptic ulcers. For example, quitting smoking can reduce the risk of complications, such as bleeding and perforation. Avoiding NSAIDs can reduce the risk of recurrence, while managing stress can improve overall quality of life. Eating a balanced diet can provide essential nutrients for healing, and avoiding trigger foods can reduce symptoms.Alternative Therapies for Peptic Ulcers
Benefits and Risks of Alternative Therapies
While alternative therapies can be effective in managing peptic ulcers, they can also have benefits and risks. For example, acupuncture can provide pain relief and improve digestion, but it can also cause side effects such as bruising and dizziness. Herbal supplements can soothe the stomach lining, but they can also interact with medications and cause side effects such as allergic reactions. Probiotics can maintain a healthy gut microbiome, but they can also cause side effects such as bloating and gas.Surgical Treatments for Peptic Ulcers
Benefits and Risks of Surgical Treatments
While surgical treatments can be effective in treating peptic ulcers, they can also have benefits and risks. For example, endoscopy can provide a diagnosis and treatment, but it can also cause side effects such as bleeding and perforation. Laparotomy can repair or remove the affected area, but it can also cause side effects such as infection and adhesions. Vagotomy can reduce stomach acid production, but it can also cause side effects such as diarrhea and weight loss.Prevention of Peptic Ulcers
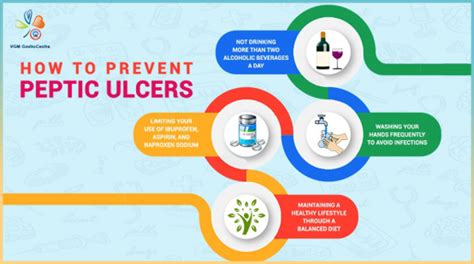
Benefits of Prevention
Preventing peptic ulcers can have numerous benefits, including reducing the risk of complications, improving overall quality of life, and reducing healthcare costs. By practicing good hygiene, avoiding NSAIDs, managing stress, and eating a balanced diet, individuals can reduce their risk of developing peptic ulcers and improve their overall health and well-being.What are the symptoms of peptic ulcers?
+The symptoms of peptic ulcers can include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and bloating. In severe cases, peptic ulcers can cause bleeding, perforation, or obstruction of the stomach or intestine.
How are peptic ulcers diagnosed?
+Peptic ulcers are typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as endoscopy, blood tests, and stool tests.
What are the treatment options for peptic ulcers?
+The treatment options for peptic ulcers can include medications, lifestyle modifications, alternative therapies, and surgical treatments. The most effective treatment approach often involves a combination of these options.
Can peptic ulcers be prevented?
+Yes, peptic ulcers can be prevented by practicing good hygiene, avoiding NSAIDs, managing stress, and eating a balanced diet. These measures can help reduce the risk of H. pylori infection and other factors that contribute to the development of peptic ulcers.
What are the complications of peptic ulcers?
+The complications of peptic ulcers can include bleeding, perforation, obstruction of the stomach or intestine, and narrowing of the stomach or intestine. In severe cases, peptic ulcers can lead to life-threatening complications, such as sepsis and organ failure.
In conclusion, peptic ulcers are a common health issue that can be effectively managed through a combination of medications, lifestyle modifications, alternative therapies, and surgical treatments. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for peptic ulcers, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk of developing this condition and improve their overall health and well-being. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with peptic ulcers in the comments section below, and to share this article with anyone who may benefit from this information.
