The presence of albumin in urine, also known as albuminuria, is a significant indicator of kidney health. Albumin is a type of protein that is normally found in the blood, and it plays a crucial role in maintaining blood volume and preventing fluids from leaking out of blood vessels. However, when albumin is detected in urine, it can be a sign of kidney damage or disease. In this article, we will delve into the world of albumin urine levels, exploring what they mean, how they are measured, and what the implications are for our health.
Albuminuria is a common complication of various diseases, including diabetes, hypertension, and kidney disease. It is estimated that over 100 million people worldwide have albuminuria, and this number is expected to rise due to the increasing prevalence of these underlying conditions. The good news is that early detection and treatment of albuminuria can help prevent further kidney damage and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Therefore, it is essential to understand the significance of albumin urine levels and how they can impact our overall health.
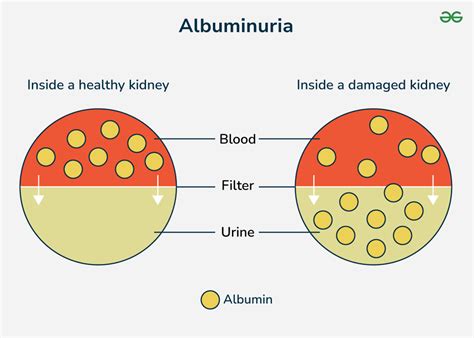
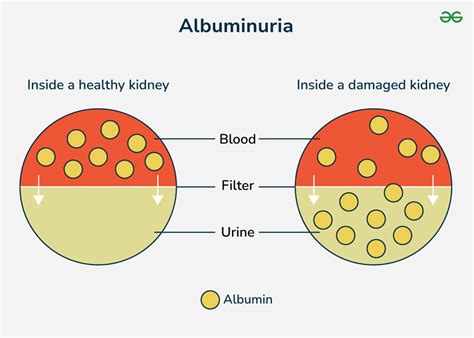
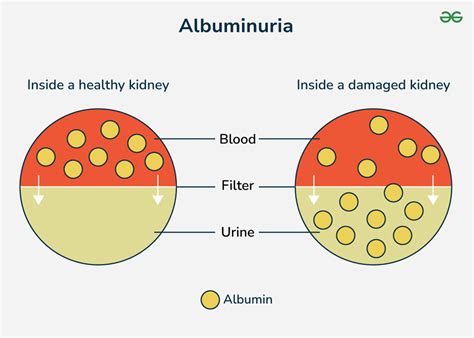
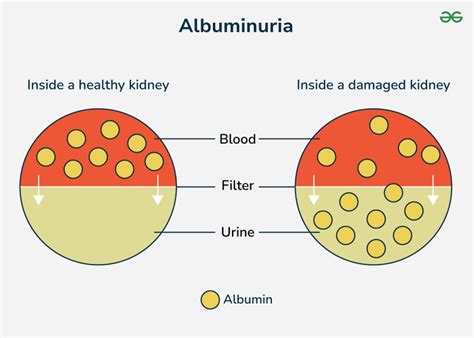
The kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste and excess fluids from the blood, and they also help regulate blood pressure, electrolyte balance, and red blood cell production. When the kidneys are healthy, they are able to filter out small molecules like glucose and amino acids, while keeping larger molecules like proteins and blood cells in the bloodstream. However, when the kidneys are damaged, they may become permeable, allowing proteins like albumin to leak into the urine. This is why albuminuria is often used as a marker of kidney damage or disease.
What are Normal Albumin Urine Levels?
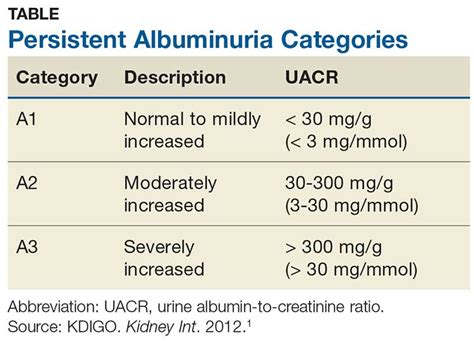
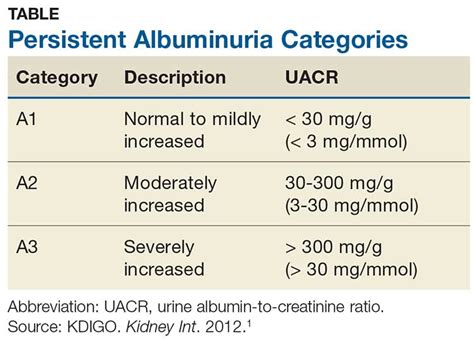
Normal albumin urine levels are typically defined as less than 30 milligrams per gram of creatinine (mg/g Cr) in a random urine sample. Creatinine is a waste product that is filtered by the kidneys, and it is used as a reference point to standardize albumin measurements. In healthy individuals, the kidneys are able to filter out almost all of the albumin from the blood, resulting in very low levels of albumin in the urine. However, in people with kidney disease or damage, albumin levels may be elevated, indicating that the kidneys are not functioning properly.
How are Albumin Urine Levels Measured?
Albumin urine levels can be measured using a variety of methods, including dipstick tests, laboratory tests, and home testing kits. Dipstick tests are a quick and convenient way to detect albumin in urine, but they may not be as accurate as laboratory tests. Laboratory tests, on the other hand, involve sending a urine sample to a laboratory for analysis, where the albumin levels can be measured using specialized equipment. Home testing kits are also available, which allow individuals to measure their albumin levels in the comfort of their own homes.
What do Elevated Albumin Urine Levels Mean?
Elevated albumin urine levels can indicate a range of health problems, from mild kidney damage to more severe kidney disease. In some cases, elevated albumin levels may be a sign of an underlying condition, such as diabetes or hypertension, which can increase the risk of kidney damage. In other cases, elevated albumin levels may be a sign of kidney disease itself, such as nephrotic syndrome or chronic kidney disease. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider if albumin levels are elevated, as early detection and treatment can help prevent further kidney damage and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Causes of Elevated Albumin Urine Levels
There are several causes of elevated albumin urine levels, including:
* Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys and increase the risk of albuminuria.
* Hypertension: High blood pressure can damage the kidneys and increase the risk of albuminuria.
* Kidney disease: Conditions such as nephrotic syndrome and chronic kidney disease can cause albuminuria.
* Family history: Individuals with a family history of kidney disease may be more likely to develop albuminuria.
* Age: Older adults are more likely to develop albuminuria due to age-related decline in kidney function.
Symptoms of Elevated Albumin Urine Levels
In many cases, elevated albumin urine levels may not cause any noticeable symptoms, especially in the early stages of kidney damage. However, as kidney disease progresses, individuals may experience a range of symptoms, including:
* Foamy or bubbly urine
* Swelling in the legs, feet, or hands
* Fatigue or weakness
* Loss of appetite
* Nausea or vomiting
Treatment and Management of Elevated Albumin Urine Levels
Treatment and management of elevated albumin urine levels depend on the underlying cause of the condition. In some cases, lifestyle changes such as losing weight, exercising regularly, and following a healthy diet may be enough to reduce albumin levels. In other cases, medication or other interventions may be necessary to manage underlying conditions such as diabetes or hypertension. In severe cases of kidney disease, dialysis or kidney transplantation may be necessary.
Prevention of Elevated Albumin Urine Levels
Prevention of elevated albumin urine levels involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing underlying conditions that can increase the risk of kidney damage. Some ways to prevent elevated albumin urine levels include:
* Maintaining a healthy weight
* Exercising regularly
* Following a healthy diet
* Managing blood sugar levels
* Managing blood pressure
* Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, albumin urine levels are an important indicator of kidney health, and elevated levels can indicate a range of health problems. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for elevated albumin urine levels, individuals can take steps to maintain healthy kidneys and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Future research should focus on developing new and innovative ways to detect and manage kidney disease, as well as improving our understanding of the underlying mechanisms that contribute to albuminuria.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with albumin urine levels in the comments section below. Have you or a loved one been diagnosed with elevated albumin urine levels? What steps have you taken to manage the condition? By sharing our knowledge and experiences, we can work together to promote kidney health and reduce the burden of kidney disease.
What is the normal range for albumin urine levels?
+
Normal albumin urine levels are typically defined as less than 30 milligrams per gram of creatinine (mg/g Cr) in a random urine sample.
What are the symptoms of elevated albumin urine levels?
+
In many cases, elevated albumin urine levels may not cause any noticeable symptoms, especially in the early stages of kidney damage. However, as kidney disease progresses, individuals may experience a range of symptoms, including foamy or bubbly urine, swelling in the legs, feet, or hands, fatigue or weakness, loss of appetite, and nausea or vomiting.
How can I prevent elevated albumin urine levels?
+
Prevention of elevated albumin urine levels involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing underlying conditions that can increase the risk of kidney damage. Some ways to prevent elevated albumin urine levels include maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, following a healthy diet, managing blood sugar levels, managing blood pressure, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.