Intro
Learn about NMS Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome symptoms, causes, and treatment. Identify key signs like fever, rigidity, and confusion, and understand related conditions like serotonin syndrome and dystonic reactions.
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) is a rare but life-threatening neurological disorder that can occur in response to the use of neuroleptic or antipsychotic medications. NMS is characterized by a distinctive set of symptoms, including fever, muscle rigidity, and altered mental status. The condition is often associated with the use of typical antipsychotics, such as haloperidol, but can also occur with the use of atypical antipsychotics, such as olanzapine and risperidone.
The symptoms of NMS can develop rapidly, often within hours or days of starting or increasing the dose of a neuroleptic medication. In some cases, the symptoms may develop more slowly, over several weeks or months. The condition is often preceded by a prodromal phase, during which the individual may experience symptoms such as anxiety, agitation, and insomnia. As the condition progresses, the individual may develop more severe symptoms, including fever, muscle rigidity, and altered mental status.
The diagnosis of NMS is often challenging, as the symptoms can be nonspecific and may resemble those of other conditions, such as infection or heat stroke. A high index of suspicion is necessary to diagnose NMS, particularly in individuals who are taking neuroleptic medications. The diagnosis is typically made based on a combination of clinical findings, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
NMS Symptoms
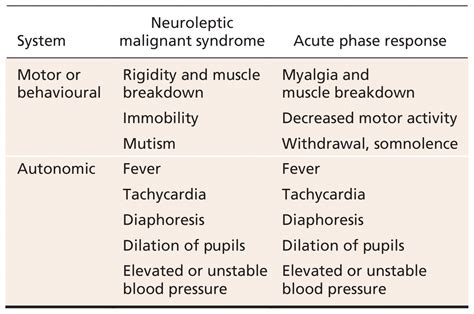
Muscular Symptoms
Muscular symptoms are a hallmark of NMS, and can range from mild to severe. Muscle rigidity is the most common muscular symptom, and can affect any muscle group, including the face, neck, and limbs. In some cases, the muscle rigidity can be so severe that it leads to immobility and an inability to speak or swallow. Muscle weakness is another common muscular symptom, and can range from mild to severe.Causes and Risk Factors

Risk Factors
Several risk factors have been identified for NMS, including the use of high-potency neuroleptic medications, the use of multiple neuroleptic medications, and the presence of underlying medical conditions, such as dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. Individuals who are taking neuroleptic medications for the first time, or who are increasing the dose of a neuroleptic medication, are also at increased risk of developing NMS.Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnostic Criteria
The diagnostic criteria for NMS include the presence of three or more of the following symptoms: fever, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, autonomic dysfunction, and changes in white blood cell count and liver enzymes. The symptoms must be severe enough to require hospitalization, and must not be explained by another medical condition.Prevention and Management

Management Strategies
Several management strategies are available for NMS, including the discontinuation of neuroleptic medications, the use of supportive care, such as hydration and cooling, and the administration of medications, such as dantrolene and bromocriptine. Dantrolene is a muscle relaxant that can help to reduce muscle rigidity, while bromocriptine is a dopamine agonist that can help to restore normal dopamine function.Complications and Prognosis
Prognostic Factors
Several prognostic factors have been identified for NMS, including the severity of symptoms, the presence of underlying medical conditions, and the response to treatment. Individuals who experience severe symptoms, such as respiratory failure or cardiac arrest, are at increased risk of complications and death.Future Directions

Research Priorities
Several research priorities have been identified for NMS, including the development of more effective treatments, the identification of risk factors and prognostic factors, and the use of advanced imaging techniques to understand the mechanisms of the condition.What is Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)?
+NMS is a rare but life-threatening neurological disorder that can occur in response to the use of neuroleptic or antipsychotic medications.
What are the symptoms of NMS?
+The symptoms of NMS include fever, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, autonomic dysfunction, and changes in white blood cell count and liver enzymes.
How is NMS diagnosed?
+The diagnosis of NMS is typically made based on a combination of clinical findings, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
What is the treatment for NMS?
+The treatment for NMS includes the discontinuation of neuroleptic medications, the use of supportive care, such as hydration and cooling, and the administration of medications, such as dantrolene and bromocriptine.
What is the prognosis for NMS?
+The prognosis for NMS is generally good, particularly if the condition is recognized and treated promptly.
In conclusion, NMS is a rare but life-threatening neurological disorder that can occur in response to the use of neuroleptic or antipsychotic medications. The symptoms of NMS can be severe and include fever, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, autonomic dysfunction, and changes in white blood cell count and liver enzymes. Prompt recognition and treatment are critical to preventing complications and improving outcomes. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions about NMS in the comments section below. Additionally, we invite readers to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about this important topic.
