Intro
Find fast relief with Loratadine allergy medicine, offering 24-hour symptom relief from hay fever, congestion, and itchiness, with anti-inflammatory properties for effective allergic reaction treatment.
Allergies can be a significant nuisance, affecting millions of people worldwide. The constant sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes can be debilitating, interfering with daily life and overall well-being. Fortunately, there are various treatments available to alleviate these symptoms, and one of the most popular and effective options is loratadine allergy medicine. In this article, we will delve into the world of loratadine, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and practical applications.
Loratadine is a non-sedating antihistamine, which means it can provide relief from allergy symptoms without causing drowsiness. This is a significant advantage, as many people need to maintain their daily routines and activities without feeling lethargic or disoriented. Loratadine works by blocking the action of histamine, a chemical released by the body's immune system in response to an allergic reaction. By preventing histamine from binding to its receptors, loratadine reduces the symptoms associated with allergies, such as itching, sneezing, and congestion.
The importance of effective allergy relief cannot be overstated. Allergies can significantly impact a person's quality of life, affecting their ability to work, socialize, and enjoy outdoor activities. Moreover, untreated allergies can lead to more severe complications, such as sinus infections, asthma, and other respiratory problems. Therefore, it is essential to find a reliable and efficient treatment option, and loratadine has proven to be a valuable solution for many individuals.
Loratadine Mechanism of Action
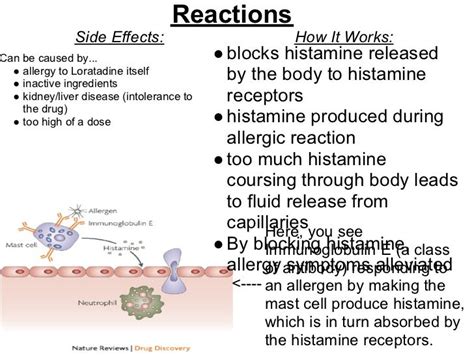
Benefits of Loratadine
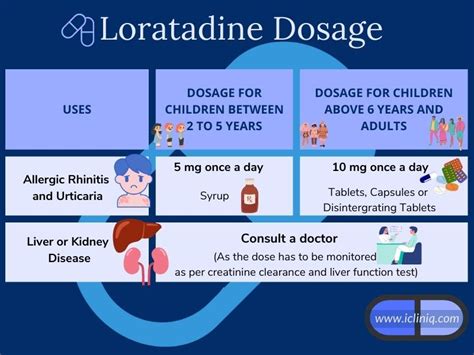
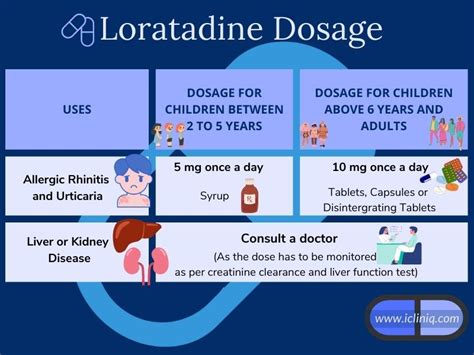
The benefits of loratadine are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant advantages of using loratadine include: * Fast and effective relief from allergy symptoms * Non-sedating, allowing users to maintain their daily routines and activities * Long-lasting effects, providing relief for up to 24 hours * Available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and liquid solutions * Suitable for use in adults and children aged 2 and aboveLoratadine Dosage and Administration
Common Uses of Loratadine
Loratadine is commonly used to treat a variety of allergic conditions, including: * Hay fever (allergic rhinitis) * Itchy eyes and skin * Hives (urticaria) * Insect bites and stings * Food allergies * Pet allergiesLoratadine Side Effects and Interactions
Loratadine Precautions and Warnings
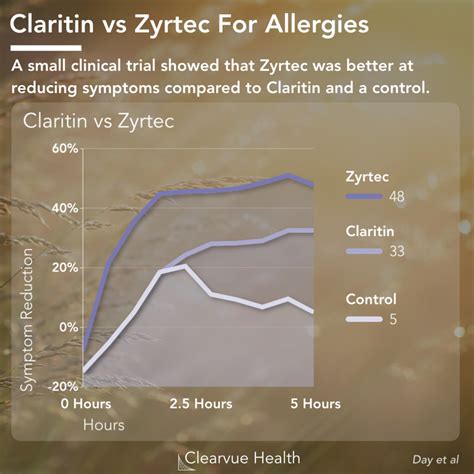
Loratadine is generally well-tolerated, but there are certain precautions and warnings to be aware of: * Loratadine is not recommended for use in children under 2 years of age * Loratadine may interact with other medications, such as sedatives and tranquilizers * Loratadine may cause drowsiness in some individuals, especially when taken with other sedating medications * Loratadine may not be suitable for use in individuals with certain medical conditions, such as liver or kidney diseaseLoratadine vs. Other Allergy Medications
Loratadine and Pregnancy
Loratadine is generally considered safe for use during pregnancy, but it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any medication. The FDA has classified loratadine as a category B medication, which means that animal studies have shown no risk to the fetus, but there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women.Loratadine Overdose and Toxicity
Loratadine and Breastfeeding
Loratadine is generally considered safe for use during breastfeeding, but it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any medication. The FDA has classified loratadine as a category B medication, which means that animal studies have shown no risk to the infant, but there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in breastfeeding women.Loratadine Storage and Disposal
Loratadine Expiration Date
Loratadine has a shelf life of 2-3 years from the date of manufacture. The expiration date should be checked before taking the medication, and any expired medication should be disposed of properly.What is loratadine used for?
+Loratadine is used to treat a variety of allergic conditions, including hay fever, itchy eyes and skin, hives, and insect bites and stings.
Is loratadine safe for use during pregnancy?
+Loratadine is generally considered safe for use during pregnancy, but it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any medication.
Can loratadine be used in children?
+Loratadine is suitable for use in children aged 2 and above, but the dosage and administration guidelines should be followed carefully.
In conclusion, loratadine is a highly effective and reliable allergy medication that provides fast and long-lasting relief from symptoms. Its non-sedating properties make it an ideal choice for individuals who need to maintain their daily routines and activities. By understanding the benefits, working mechanisms, and practical applications of loratadine, individuals can make informed decisions about their allergy treatment and take control of their symptoms. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with loratadine in the comments below, and to explore our other articles on allergy relief and management.
