Intro
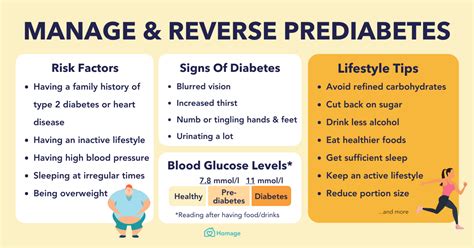
Identify prediabetes range signs, including insulin resistance, blood sugar spikes, and metabolic changes, to prevent type 2 diabetes and promote healthy glucose levels through early detection and management of borderline diabetes symptoms.
Prediabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. It is a warning sign that you are at risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other health problems. Recognizing the signs of prediabetes is crucial, as it allows for early intervention and prevention of more severe health issues. In this article, we will explore the 5 prediabetes range signs that you should be aware of.
The importance of recognizing prediabetes cannot be overstated. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 88 million adults in the United States have prediabetes, and 90% of them are unaware of their condition. If left untreated, prediabetes can lead to type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and other health complications. Therefore, it is essential to understand the signs and symptoms of prediabetes and take action to prevent its progression.
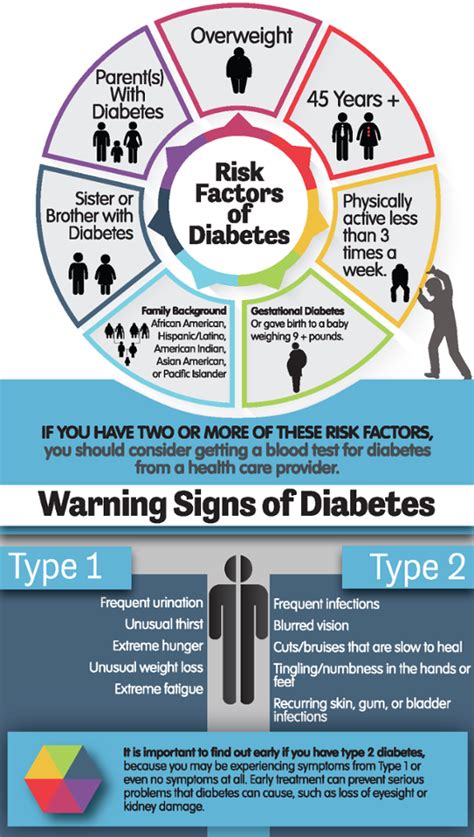
Prediabetes is often referred to as a "silent" condition, as it may not exhibit noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, there are certain signs and risk factors that can indicate an increased risk of developing prediabetes. These include being overweight or obese, having a family history of diabetes, being physically inactive, and having a history of gestational diabetes or delivering a baby over 4 kg. By understanding these risk factors and recognizing the signs of prediabetes, you can take proactive steps to prevent or manage the condition.
Prediabetes Range Signs
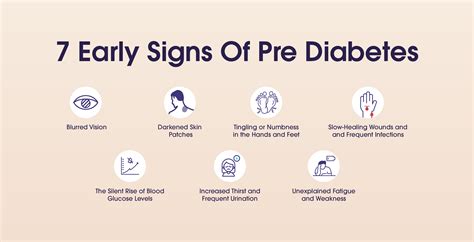
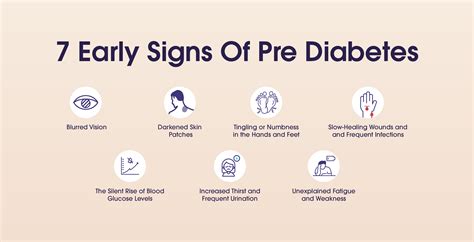
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) defines prediabetes as a condition where blood glucose levels are between 100 mg/dL and 125 mg/dL during an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) or between 5.7% and 6.4% during a hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test. There are several signs that may indicate you are in the prediabetes range, including:
Increased Thirst and Urination
One of the primary signs of prediabetes is increased thirst and urination. When there is excess glucose in the blood, the body tries to eliminate it through the urine, leading to frequent urination. This can cause dehydration, which in turn increases thirst. If you find yourself drinking more water than usual and urinating more frequently, it may be a sign that your blood sugar levels are higher than normal.Prediabetes Risk Factors
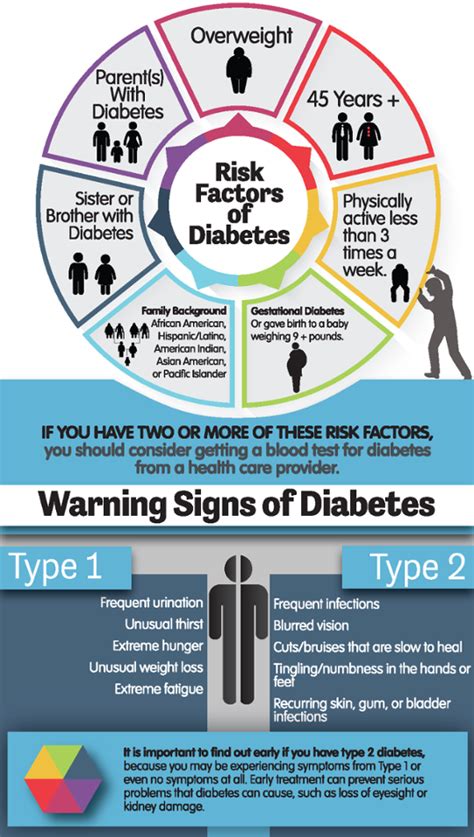
In addition to increased thirst and urination, there are several other risk factors that can increase your likelihood of developing prediabetes. These include:
- Being overweight or obese
- Having a family history of diabetes
- Being physically inactive
- Having a history of gestational diabetes or delivering a baby over 4 kg
- Having polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Having acanthosis nigricans (a skin condition characterized by dark, velvety skin patches)
Blurred Vision
Blurred vision is another sign that may indicate prediabetes. High blood sugar levels can cause the lens in the eye to swell, leading to changes in vision. If you experience blurred vision, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to rule out other potential causes.Prediabetes Diagnosis
Diagnosing prediabetes typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. The most common tests used to diagnose prediabetes include:
- Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test: This test measures blood glucose levels after an overnight fast.
- Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT): This test measures blood glucose levels after consuming a sugary drink.
- Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test: This test measures average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months.
Slow Healing of Cuts and Wounds
Slow healing of cuts and wounds is another sign that may indicate prediabetes. High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves and blood vessels, leading to impaired wound healing. If you notice that your cuts and wounds are taking longer to heal than usual, it may be a sign that your blood sugar levels are higher than normal.Prediabetes Treatment
Treating prediabetes typically involves lifestyle modifications and, in some cases, medication. The primary goals of treatment are to:
- Lose weight, if necessary
- Increase physical activity
- Improve diet and nutrition
- Manage stress
- Monitor blood glucose levels regularly
Tingling or Numbness in Hands and Feet
Tingling or numbness in hands and feet is another sign that may indicate prediabetes. High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to rule out other potential causes.Prediabetes Prevention
Preventing prediabetes involves adopting a healthy lifestyle, including:
- Eating a balanced diet that is low in sugar and saturated fats
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or jogging
- Losing weight, if necessary
- Managing stress through techniques such as meditation or yoga
- Getting enough sleep and maintaining a healthy sleep schedule
Fluctuations in Blood Pressure
Fluctuations in blood pressure are another sign that may indicate prediabetes. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels, leading to high blood pressure. If you experience fluctuations in blood pressure, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to rule out other potential causes.Prediabetes Management
Managing prediabetes involves working with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan. This may include:
- Monitoring blood glucose levels regularly
- Adjusting diet and nutrition to manage blood sugar levels
- Increasing physical activity to improve insulin sensitivity
- Managing stress through techniques such as meditation or yoga
- Getting enough sleep and maintaining a healthy sleep schedule
What is prediabetes, and how is it diagnosed?
+Prediabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. It is diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, including fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test, oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test.
What are the risk factors for developing prediabetes?
+The risk factors for developing prediabetes include being overweight or obese, having a family history of diabetes, being physically inactive, having a history of gestational diabetes or delivering a baby over 4 kg, having polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and having acanthosis nigricans (a skin condition characterized by dark, velvety skin patches).
How can prediabetes be treated and managed?
+Prediabetes can be treated and managed through lifestyle modifications, including losing weight, increasing physical activity, improving diet and nutrition, managing stress, and monitoring blood glucose levels regularly. In some cases, medication may also be prescribed to help manage blood sugar levels.
Can prediabetes be prevented?
+Yes, prediabetes can be prevented by adopting a healthy lifestyle, including eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, losing weight if necessary, managing stress, and getting enough sleep. Early detection and treatment can also help prevent the progression of prediabetes to type 2 diabetes.
What are the complications of untreated prediabetes?
+Untreated prediabetes can lead to complications such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and blindness. It is essential to work with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan and prevent these complications.
In conclusion, recognizing the signs of prediabetes is crucial for early intervention and prevention of more severe health issues. By understanding the risk factors and signs of prediabetes, you can take proactive steps to prevent or manage the condition. If you are concerned about your risk of developing prediabetes or have questions about diagnosis, treatment, or management, consult with a healthcare professional. Share this article with friends and family to raise awareness about prediabetes and encourage others to take control of their health. Take the first step towards a healthier lifestyle today!
