Intro
Discover average A1c levels by age, understanding blood sugar control, diabetes management, and healthy glucose ranges for adults and seniors, to monitor and improve your HbA1c test results.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals of all ages, particularly for those living with diabetes. The average A1c levels by age can vary significantly, and understanding these variations is essential for effective diabetes management. A1c, also known as hemoglobin A1c, is a blood test that measures the average level of glucose in the blood over the past 2 to 3 months. It's a critical indicator of how well diabetes is being managed. In this article, we will delve into the average A1c levels by age, exploring the factors that influence these levels and the importance of maintaining healthy blood sugar levels across different age groups.
The importance of monitoring A1c levels cannot be overstated. For individuals with diabetes, regular A1c tests help healthcare providers assess the effectiveness of the current treatment plan and make adjustments as necessary. For those without diabetes, A1c tests can serve as an early warning system, identifying individuals at risk of developing the condition. Moreover, understanding the average A1c levels by age can help in setting realistic targets for blood sugar control, which is vital for preventing diabetes-related complications.
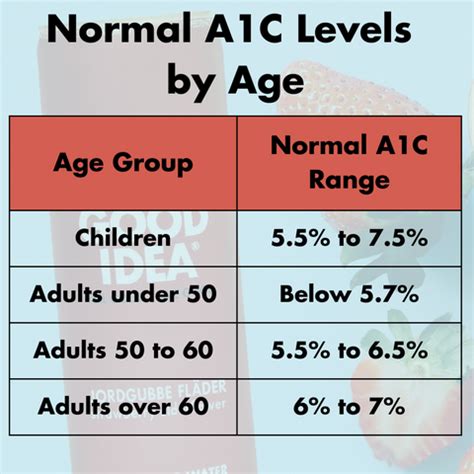
As individuals age, their risk of developing diabetes and related complications increases. Factors such as lifestyle, genetics, and the presence of other health conditions can influence A1c levels. For younger individuals, particularly those under the age of 18, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends an A1c target below 7.5% for those with diabetes. This target is slightly higher than for adults, reflecting the challenges of managing diabetes in younger populations and the importance of balancing tight blood sugar control with the need to minimize hypoglycemic events.
Average A1c Levels in Children and Adolescents
Factors Influencing A1c Levels in Younger Populations
Several factors can influence A1c levels in children and adolescents, including the type of diabetes (Type 1 vs. Type 2), the effectiveness of the current treatment plan, adherence to diet and exercise recommendations, and the presence of other health conditions. Additionally, psychological factors such as stress and anxiety can impact blood sugar control, making comprehensive care that addresses both physical and mental health essential.Average A1c Levels in Adults
Lifestyle Interventions for A1c Control
Lifestyle interventions are fundamental for managing diabetes and achieving healthy A1c levels. These interventions include: - **Dietary Changes:** Following a balanced diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium, and high in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. - **Physical Activity:** Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week. - **Weight Management:** Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, which can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and reduce A1c levels. - **Stress Management:** Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises, to minimize the impact of stress on blood sugar levels.Average A1c Levels in Older Adults
Considerations for Diabetes Management in Older Adults
Diabetes management in older adults requires careful consideration of several factors, including: - **Comorbid Conditions:** The presence of other health conditions, such as heart disease, kidney disease, or dementia, which can influence the choice of medications and the aggressiveness of A1c targets. - **Cognitive Function:** The ability to manage diabetes independently, which may decline with age, necessitating support from family members or caregivers. - **Hypoglycemia Risk:** The risk of severe hypoglycemia, which increases with age and can be life-threatening, making it essential to balance A1c targets with hypoglycemia prevention strategies.Achieving Healthy A1c Levels

Monitoring and Adjusting Treatment
Regular monitoring of A1c levels and other health indicators, such as blood pressure and lipid profiles, is crucial for managing diabetes effectively. Based on these monitoring results, the treatment plan may need to be adjusted, which could involve changes to diet and exercise, adjustments to medication, or the addition of new therapies.Conclusion and Future Directions

Emerging Trends in Diabetes Management
The future of diabetes management holds much promise, with emerging trends including the development of more sophisticated glucose monitoring technologies, the introduction of new classes of diabetes medications, and a greater emphasis on personalized medicine. These advancements will enable healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans more effectively to the individual needs of each patient, leading to better A1c control and improved health outcomes.What is the average A1c level for individuals without diabetes?
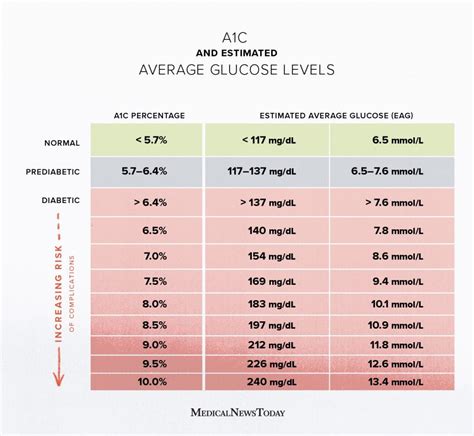
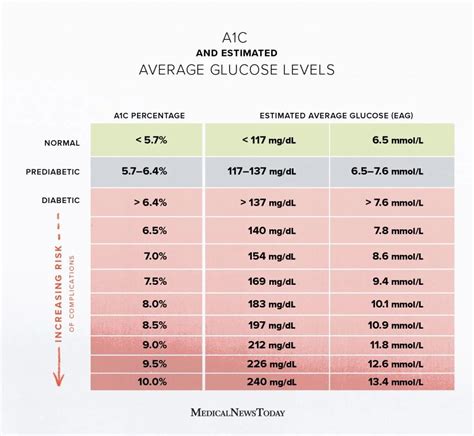
+For individuals without diabetes, the average A1c level is typically below 5.7%. Levels between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes, while levels of 6.5% or higher are diagnostic of diabetes.
How often should A1c levels be checked?
+A1c levels should be checked at least twice a year in individuals with stable diabetes and more frequently in those with newly diagnosed diabetes, those who are changing treatments, or those who are not meeting their A1c targets.
What factors can influence A1c results?
+Several factors can influence A1c results, including the presence of hemoglobinopathies, recent blood transfusions, and certain medications. It's essential to discuss any factors that might affect A1c results with a healthcare provider.
We invite readers to share their experiences with managing A1c levels and to ask questions about any aspects of diabetes care that they find challenging. By engaging in a dialogue about diabetes management, we can work together to improve health outcomes and the quality of life for individuals with diabetes. Whether you're looking for advice on achieving healthy A1c levels, managing diabetes-related complications, or navigating the complexities of diabetes care, we're here to provide support and guidance every step of the way.
