Intro
Understand average blood sugar levels, normal glucose ranges, and target HbA1c values to manage diabetes, prediabetes, and insulin resistance effectively.
Maintaining average blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When we eat, our body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. The pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose, thereby regulating blood sugar levels. In this article, we will delve into the importance of maintaining average blood sugar levels, the factors that influence them, and provide guidance on how to manage and regulate them effectively.
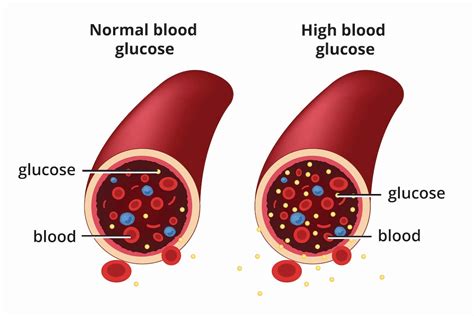
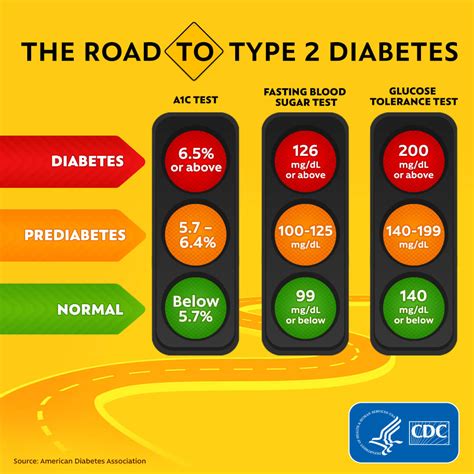
Understanding average blood sugar levels is essential for preventing complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends that people with diabetes aim for an average blood sugar level of less than 154 mg/dL (8.6 mmol/L) after eating and less than 126 mg/dL (7 mmol/L) before eating. For individuals without diabetes, the normal range for blood sugar levels is between 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L) and 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) throughout the day. It is essential to note that these values may vary depending on factors such as age, physical activity level, and overall health.
The importance of maintaining average blood sugar levels cannot be overstated. When blood sugar levels are consistently high, it can lead to a range of health problems, including increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage. On the other hand, low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia) can cause symptoms such as shakiness, dizziness, and confusion. In severe cases, hypoglycemia can lead to seizures, coma, or even death. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor and manage blood sugar levels regularly, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
Average Blood Sugar Levels: What's Normal?

Average blood sugar levels vary throughout the day, depending on factors such as meal times, physical activity, and sleep patterns. For individuals without diabetes, normal blood sugar levels are typically between 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L) and 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) after eating. For people with diabetes, the ADA recommends the following targets for average blood sugar levels:
- Before meals: less than 130 mg/dL (7.2 mmol/L)
- After meals: less than 180 mg/dL (10 mmol/L)
- At bedtime: less than 120 mg/dL (6.7 mmol/L)
It is essential to note that these targets may vary depending on individual factors, such as age, physical activity level, and overall health. It is crucial to work with a healthcare provider to determine the best targets for average blood sugar levels.
Factors That Influence Average Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence average blood sugar levels, including: * Diet: The type and amount of carbohydrates consumed can significantly impact blood sugar levels. * Physical activity: Regular exercise can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. * Sleep patterns: Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt blood sugar regulation. * Stress levels: High stress levels can raise blood sugar levels and worsen insulin resistance. * Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can raise blood sugar levels.Managing Average Blood Sugar Levels

Managing average blood sugar levels requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medication (if necessary), and regular monitoring. Here are some tips to help manage average blood sugar levels:
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Manage stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Monitoring Average Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring average blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Here are some ways to monitor blood sugar levels: * Blood glucose meters: Use a blood glucose meter to measure blood sugar levels at different times of the day. * Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems: Use a CGM system to track blood sugar levels throughout the day and night. * Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) tests: Get regular HbA1c tests to measure average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.Average Blood Sugar Levels and Diabetes
Average blood sugar levels play a critical role in the management of diabetes. For individuals with diabetes, maintaining average blood sugar levels within the target range can help prevent complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Here are some tips for managing average blood sugar levels with diabetes:
- Work with a healthcare provider: Develop a personalized plan to manage average blood sugar levels.
- Take medication as prescribed: If medication is necessary, take it as prescribed to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly: Use a blood glucose meter or CGM system to track blood sugar levels throughout the day.
- Make lifestyle modifications: Focus on a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management to help regulate blood sugar levels.
Complications of High Average Blood Sugar Levels
High average blood sugar levels can lead to a range of complications, including: * Heart disease: High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. * Kidney damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys and increase the risk of kidney failure. * Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves and cause numbness, tingling, and pain. * Blindness: High blood sugar levels can damage the eyes and increase the risk of blindness.Average Blood Sugar Levels and Prediabetes
Average blood sugar levels play a critical role in the management of prediabetes. For individuals with prediabetes, maintaining average blood sugar levels within the target range can help prevent the development of type 2 diabetes. Here are some tips for managing average blood sugar levels with prediabetes:
- Work with a healthcare provider: Develop a personalized plan to manage average blood sugar levels.
- Make lifestyle modifications: Focus on a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly: Use a blood glucose meter or CGM system to track blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Preventing Average Blood Sugar Levels from Rising
Preventing average blood sugar levels from rising requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications and regular monitoring. Here are some tips to help prevent average blood sugar levels from rising: * Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. * Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help regulate blood sugar levels. * Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week. * Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate blood sugar levels. * Manage stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.Average Blood Sugar Levels and Pregnancy

Average blood sugar levels play a critical role in pregnancy, particularly for women with gestational diabetes. For women with gestational diabetes, maintaining average blood sugar levels within the target range can help prevent complications such as high birth weight, premature birth, and stillbirth. Here are some tips for managing average blood sugar levels during pregnancy:
- Work with a healthcare provider: Develop a personalized plan to manage average blood sugar levels.
- Make lifestyle modifications: Focus on a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly: Use a blood glucose meter or CGM system to track blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Managing Average Blood Sugar Levels with Medication
For some individuals, medication may be necessary to manage average blood sugar levels. Here are some common medications used to manage blood sugar levels: * Metformin: A medication that helps regulate blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity. * Sulfonylureas: A medication that stimulates the pancreas to produce more insulin. * Meglitinides: A medication that stimulates the pancreas to produce more insulin.What is the normal range for average blood sugar levels?
+The normal range for average blood sugar levels is between 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L) and 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) throughout the day.
What are the risks of high average blood sugar levels?
+High average blood sugar levels can increase the risk of heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
How can I manage average blood sugar levels?
+Managing average blood sugar levels requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medication (if necessary), and regular monitoring.
In summary, maintaining average blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. By understanding the factors that influence average blood sugar levels and taking steps to manage them, individuals can reduce their risk of complications and improve their overall health. We encourage readers to share their experiences and tips for managing average blood sugar levels in the comments below. Additionally, we invite readers to share this article with others who may benefit from this information, and to take the first step towards managing their average blood sugar levels by consulting with a healthcare provider. By working together, we can promote healthy blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of related complications.
