Intro
Identify bacterial genital infection symptoms, including discharge, itching, and burning. Learn about causes, treatments, and prevention of STIs like gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis.
The importance of understanding bacterial genital infection symptoms cannot be overstated, as these infections can have serious consequences if left untreated. Bacterial genital infections, also known as sexually transmitted infections (STIs), are a significant public health concern worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 1 million people acquire an STI every day, with many of these infections going undiagnosed and untreated. The lack of awareness and education about STIs and their symptoms can lead to delayed diagnosis, increased transmission, and long-term health complications.
Bacterial genital infections can be caused by various types of bacteria, including Chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. These infections can be spread through vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected partner. The symptoms of bacterial genital infections can vary depending on the type of infection, but common symptoms include abnormal discharge, pain or burning during urination, and genital itching or irritation. If left untreated, bacterial genital infections can lead to serious health complications, such as infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, and increased risk of HIV transmission.
The need for education and awareness about bacterial genital infection symptoms is critical, especially among young people and those who are sexually active. By understanding the symptoms and risks associated with bacterial genital infections, individuals can take steps to protect themselves and their partners from infection. This includes practicing safe sex, getting regular STI testing, and seeking medical attention if symptoms occur. In this article, we will delve into the world of bacterial genital infections, exploring the different types of infections, their symptoms, and the importance of prevention and treatment.
Bacterial Genital Infection Types
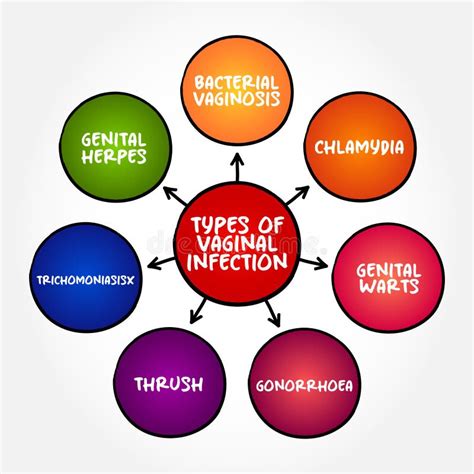
Chlamydia Symptoms
Chlamydia is often referred to as a "silent" infection, as many people do not experience symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they can include: * Abnormal vaginal discharge * Pain or burning during urination * Genital itching or irritation * Abnormal bleeding or spotting * Painful sexDiagnosis and Treatment

Antibiotic Treatment
Antibiotic treatment for bacterial genital infections typically involves a course of medication, which may be taken orally or injected. The type and duration of treatment depend on the type of infection and the individual's overall health. It is essential to complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms disappear, to ensure the infection is fully cleared.Prevention and Education

STI Testing
Regular STI testing is crucial for detecting and treating bacterial genital infections. Individuals who are sexually active should get tested at least once a year, or more frequently if they have multiple partners or engage in high-risk behaviors. STI testing can be done at healthcare providers' offices, clinics, or community health centers.Complications and Long-term Effects
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
PID is a serious health complication that can occur when bacteria from a genital infection spread to the reproductive organs. Symptoms of PID include: * Severe abdominal pain * Fever * Vaginal discharge * Abnormal bleeding * Painful sexConclusion and Next Steps

What are the common symptoms of bacterial genital infections?
+Common symptoms of bacterial genital infections include abnormal discharge, pain or burning during urination, and genital itching or irritation.
How can I prevent bacterial genital infections?
+Preventing bacterial genital infections requires a combination of education, awareness, and safe sex practices, such as practicing safe sex, getting regular STI testing, and avoiding sharing sex toys or personal items.
What are the long-term effects of untreated bacterial genital infections?
+Untreated bacterial genital infections can lead to serious health complications, such as infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, and increased risk of HIV transmission.
