Intro
The use of beta blocker medicine has been a cornerstone in the treatment of various cardiovascular conditions for decades. Beta blockers, also known as beta-adrenergic blocking agents, are a class of medications that work by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, and reducing the heart's workload. This, in turn, lowers blood pressure and heart rate, making it easier for the heart to pump blood. The importance of beta blocker medicine cannot be overstated, as it has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events.
The history of beta blocker medicine dates back to the 1960s, when the first beta blocker, propranolol, was introduced. Since then, numerous beta blockers have been developed, each with its unique characteristics and uses. Today, beta blockers are used to treat a wide range of conditions, including high blood pressure, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias. They are also used to prevent migraines and reduce the symptoms of anxiety and tremors. The versatility of beta blocker medicine has made it a staple in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, and its benefits have been well-documented in numerous clinical trials.
The benefits of beta blocker medicine are numerous and well-documented. By reducing the heart's workload, beta blockers can help to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes. They can also help to improve symptoms of heart failure, such as shortness of breath and fatigue. Additionally, beta blockers have been shown to reduce the risk of sudden cardiac death, which is a major concern for individuals with heart conditions. With so many benefits, it's no wonder that beta blocker medicine has become a mainstay in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
How Beta Blocker Medicine Works
Beta blocker medicine works by blocking the effects of epinephrine on the heart and blood vessels. Epinephrine is a hormone that is released by the adrenal glands in response to stress, excitement, or other stimuli. It causes the heart to beat faster and stronger, which can increase blood pressure and cardiac output. By blocking the effects of epinephrine, beta blockers reduce the heart's workload and lower blood pressure. This can help to improve symptoms of heart failure, reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes, and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Mechanisms of Action
The mechanisms of action of beta blocker medicine are complex and involve multiple pathways. Beta blockers work by blocking the beta-1 and beta-2 adrenergic receptors, which are found in the heart and blood vessels. By blocking these receptors, beta blockers reduce the effects of epinephrine and other catecholamines, which can help to lower blood pressure and reduce cardiac output. Additionally, beta blockers can also reduce the release of renin, an enzyme that is involved in the regulation of blood pressure.Types of Beta Blocker Medicine
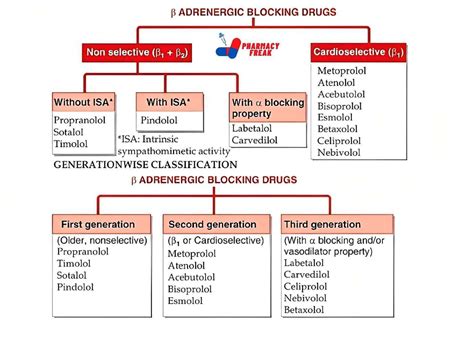
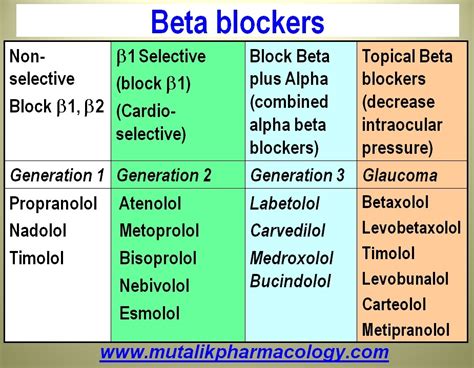
There are several types of beta blocker medicine, each with its unique characteristics and uses. Some of the most common types of beta blockers include:
- Non-selective beta blockers, which block both beta-1 and beta-2 adrenergic receptors
- Selective beta blockers, which block only beta-1 adrenergic receptors
- Beta blockers with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA), which have a mild stimulating effect on the heart
- Beta blockers with alpha-1 adrenergic blocking activity, which can help to lower blood pressure by reducing vascular resistance
Some examples of beta blocker medicine include:
- Propranolol (Inderal)
- Metoprolol (Lopressor)
- Atenolol (Tenormin)
- Carvedilol (Coreg)
- Bisoprolol (Zebeta)
Benefits and Drawbacks of Each Type
Each type of beta blocker medicine has its benefits and drawbacks. Non-selective beta blockers, for example, can be effective in reducing blood pressure and cardiac output, but they can also cause bronchospasm and other respiratory problems. Selective beta blockers, on the other hand, are less likely to cause respiratory problems, but they may be less effective in reducing blood pressure. Beta blockers with ISA can help to improve symptoms of heart failure, but they may also increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias.Uses of Beta Blocker Medicine
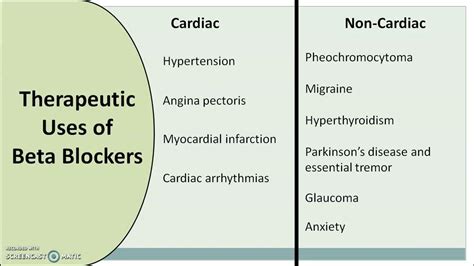
Beta blocker medicine has a wide range of uses, including:
- High blood pressure: Beta blockers can help to lower blood pressure by reducing cardiac output and vascular resistance.
- Angina: Beta blockers can help to reduce the frequency and severity of angina attacks by reducing cardiac workload and improving blood flow to the heart.
- Heart failure: Beta blockers can help to improve symptoms of heart failure, such as shortness of breath and fatigue, by reducing cardiac workload and improving cardiac function.
- Arrhythmias: Beta blockers can help to reduce the risk of cardiac arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia.
- Migraines: Beta blockers can help to reduce the frequency and severity of migraines by reducing blood flow to the brain.
Off-Label Uses
Beta blocker medicine also has several off-label uses, including: * Anxiety disorders: Beta blockers can help to reduce the symptoms of anxiety, such as tremors and palpitations. * Performance anxiety: Beta blockers can help to reduce the symptoms of performance anxiety, such as stage fright and public speaking anxiety. * Essential tremor: Beta blockers can help to reduce the symptoms of essential tremor, such as tremors and shaking.Side Effects of Beta Blocker Medicine

Beta blocker medicine can cause several side effects, including:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Shortness of breath and wheezing
- Cold hands and feet
- Insomnia and vivid dreams
- Nausea and vomiting
Common and Rare Side Effects
Some common side effects of beta blocker medicine include fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath. Rare side effects include: * Cardiac arrhythmias * Heart block * Bronchospasm * Anaphylaxis * Stevens-Johnson syndromeInteractions with Other Medications
Beta blocker medicine can interact with several other medications, including:
- Calcium channel blockers
- Anti-arrhythmic medications
- Antihypertensive medications
- Anti-diabetic medications
- Anti-depressant medications
Types of Interactions
There are several types of interactions between beta blocker medicine and other medications, including: * Pharmacokinetic interactions: Beta blockers can affect the levels of other medications in the blood. * Pharmacodynamic interactions: Beta blockers can affect the effects of other medications on the body. * Additive interactions: Beta blockers can increase the effects of other medications. * Antagonistic interactions: Beta blockers can reduce the effects of other medications.Contraindications and Precautions

Beta blocker medicine is contraindicated in several conditions, including:
- Cardiogenic shock
- Heart block
- Bronchial asthma
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Diabetes mellitus
Precautions and Warnings
Beta blocker medicine should be used with caution in several conditions, including: * Pregnancy and lactation * Pediatric patients * Geriatric patients * Patients with renal or hepatic impairment * Patients with a history of allergic reactionsWhat is beta blocker medicine used for?
+Beta blocker medicine is used to treat several conditions, including high blood pressure, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
What are the side effects of beta blocker medicine?
+Beta blocker medicine can cause several side effects, including fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
Can beta blocker medicine be used in pregnancy?
+Beta blocker medicine should be used with caution in pregnancy, as it can affect fetal development and increase the risk of complications.
What are the interactions between beta blocker medicine and other medications?
+Beta blocker medicine can interact with several other medications, including calcium channel blockers, anti-arrhythmic medications, and anti-hypertensive medications.
Can beta blocker medicine be used in patients with diabetes?
+Beta blocker medicine should be used with caution in patients with diabetes, as it can affect blood sugar levels and increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
In conclusion, beta blocker medicine is a valuable treatment option for several cardiovascular conditions. By understanding how beta blocker medicine works, its benefits and drawbacks, and its uses and side effects, patients and healthcare providers can make informed decisions about its use. With its wide range of uses and benefits, beta blocker medicine is an essential medication in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with beta blocker medicine in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to ask.
