Intro
Bladder infections, also known as urinary tract infections (UTIs), are a common health issue affecting millions of people worldwide. These infections occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract, causing symptoms such as painful urination, frequent urination, and abdominal discomfort. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for bladder infections is essential for effective management and prevention. In this article, we will delve into the world of bladder infections, exploring the importance of prompt treatment, prevention strategies, and lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of recurrence.
Bladder infections can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender, although they are more common in women due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria to enter the bladder more easily. If left untreated, bladder infections can lead to more severe complications, such as kidney damage or sepsis. Therefore, it is crucial to recognize the signs and symptoms of a bladder infection and seek medical attention promptly. By doing so, individuals can prevent long-term damage and alleviate the discomfort associated with these infections.
The prevalence of bladder infections has significant implications for public health, highlighting the need for education and awareness about prevention and treatment strategies. By adopting healthy habits and being mindful of the risk factors, individuals can reduce their likelihood of developing a bladder infection. Furthermore, understanding the different types of bladder infections, including acute and chronic infections, can help individuals better navigate their treatment options and make informed decisions about their health. With the right knowledge and approach, it is possible to manage and prevent bladder infections, improving overall quality of life.
Understanding Bladder Infections
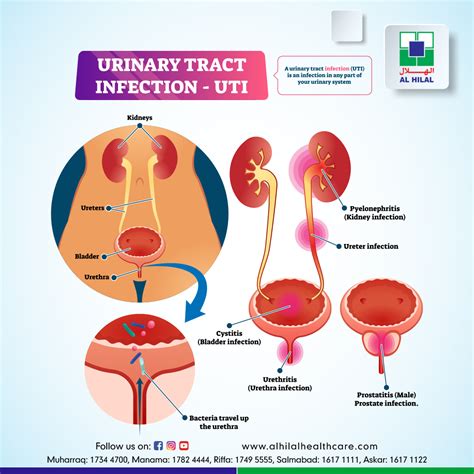
Symptoms of Bladder Infections
The symptoms of a bladder infection can vary depending on the severity of the infection and the individual's overall health. Common symptoms include: * Painful urination (dysuria) * Frequent urination (urinary frequency) * Abdominal discomfort or pain * Cloudy or strong-smelling urine * Blood in the urine (hematuria) * Fever and chillsDiagnosis and Treatment
Treatment Options
Treatment options for bladder infections depend on the severity of the infection and the individual's overall health. Common treatment options include: * Antibiotics: to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection * Pain relievers: to alleviate painful urination and abdominal discomfort * Urinary tract analgesics: to help relieve symptoms such as frequent urination and burning sensations * Drinking plenty of fluids: to help flush out bacteria and reduce the risk of recurrencePrevention Strategies

Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of developing a bladder infection. Some beneficial changes include: * Increasing fluid intake: to help flush out bacteria and reduce the risk of recurrence * Avoiding tight clothing: that can irritate the urethra and increase the risk of bacterial growth * Managing stress: to reduce the risk of urinary tract problems * Getting enough sleep: to help regulate the immune system and reduce the risk of infectionComplications and Risks
Risk Factors
Certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing a bladder infection. These include: * Female gender: due to the shorter urethra, which allows bacteria to enter the bladder more easily * Age: older adults may be more susceptible to bladder infections due to age-related changes in the urinary tract * Underlying medical conditions: such as diabetes or kidney disease, which can increase the risk of urinary tract problems * Weakened immune system: which can reduce the body's ability to fight off infectionsManaging Recurring Infections

Self-Care Strategies
Self-care strategies can help individuals manage recurring bladder infections and reduce the risk of future infections. Some effective self-care strategies include: * Keeping a bladder diary: to track symptoms and identify patterns * Practicing relaxation techniques: such as deep breathing or meditation to reduce stress * Engaging in regular exercise: to help regulate the immune system and reduce the risk of infectionConclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with bladder infections in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may be affected by bladder infections, helping to raise awareness and promote education about this common health issue.
What are the most common symptoms of a bladder infection?
+The most common symptoms of a bladder infection include painful urination, frequent urination, abdominal discomfort or pain, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and blood in the urine.
How can I prevent bladder infections?
+To prevent bladder infections, it is essential to practice good hygiene, drink plenty of fluids, urinate when needed, and avoid certain foods that can irritate the bladder.
What are the complications of untreated bladder infections?
+If left untreated, bladder infections can lead to more severe complications, such as kidney damage or sepsis, which can be life-threatening.
Can bladder infections be treated with antibiotics?
+Yes, bladder infections are typically treated with antibiotics, which can help eliminate the bacteria causing the infection.
How can I manage recurring bladder infections?
+To manage recurring bladder infections, it is essential to work with a healthcare provider, make lifestyle changes, and consider preventive measures, such as taking antibiotics or using urinary tract analgesics.
