Intro
Master diabetic blood levels with our comprehensive guide, covering normal blood sugar levels, glucose monitoring, and management tips to control diabetes and prevent complications, ensuring a healthy lifestyle.
Managing blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes. Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects how the body turns food into energy, and it can lead to a range of complications if not properly managed. High blood sugar levels can damage organs and tissues over time, while low blood sugar levels can cause immediate health problems. Therefore, understanding diabetic blood levels is essential for maintaining good health and preventing long-term damage.
The importance of monitoring blood sugar levels cannot be overstated. By keeping track of their blood glucose levels, individuals with diabetes can identify patterns and make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication. This can help them maintain a healthy balance and reduce the risk of complications. Moreover, regular monitoring can also help individuals with diabetes recognize the early warning signs of high or low blood sugar levels, allowing them to take prompt action to prevent serious health problems.
For individuals with diabetes, managing blood sugar levels is an ongoing process that requires attention to detail and a commitment to healthy habits. This includes eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and taking medication as prescribed. Additionally, individuals with diabetes should work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan for managing their condition. By taking a proactive approach to managing their blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of complications and maintain a high quality of life.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels

Blood sugar levels refer to the amount of glucose present in the blood. Glucose is a type of sugar that serves as the body's primary source of energy. In individuals with diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin (a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels) or is unable to effectively use the insulin it produces. As a result, glucose builds up in the blood, leading to high blood sugar levels. The goal of diabetes management is to maintain blood sugar levels within a target range, which can help prevent complications and maintain overall health.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Normal blood sugar levels vary throughout the day, but they are typically within the following ranges: * Fasting blood sugar levels: 70-99 mg/dL * After meals: Less than 140 mg/dL * At bedtime: 100-140 mg/dL It is essential to note that these ranges may vary depending on individual factors, such as age, medication, and overall health.Factors That Affect Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can affect blood sugar levels, including:
- Diet: Consuming high-carbohydrate or high-sugar foods can cause blood sugar levels to rise.
- Physical activity: Regular exercise can help lower blood sugar levels, while a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to high blood sugar levels.
- Medication: Certain medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can raise blood sugar levels.
- Stress: Stress can cause blood sugar levels to rise, as the body produces stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline.
- Sleep: Poor sleep quality or duration can disrupt blood sugar regulation, leading to high blood sugar levels.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can affect blood sugar levels.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
To manage blood sugar levels effectively, individuals with diabetes should: * Monitor their blood sugar levels regularly * Eat a balanced diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium * Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking or other aerobic exercises * Take medication as prescribed by their healthcare provider * Get enough sleep and practice stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or deep breathingComplications of High Blood Sugar Levels

High blood sugar levels can lead to a range of complications, including:
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
- Kidney damage (nephropathy)
- Eye damage (retinopathy)
- Foot damage (ulcers, infections)
- Heart disease and stroke
- Cognitive impairment and dementia
Preventing Complications
To prevent complications, individuals with diabetes should: * Maintain good blood sugar control * Monitor their blood pressure and cholesterol levels * Get regular check-ups with their healthcare provider * Stay up-to-date on recommended vaccinations and screenings * Practice good foot care and eye careLow Blood Sugar Levels
Low blood sugar levels, also known as hypoglycemia, occur when the body's blood sugar levels drop below 70 mg/dL. This can happen when:
- Taking too much insulin or oral diabetes medication
- Skipping meals or snacks
- Engaging in intense physical activity without adjusting food or medication
- Drinking too much alcohol
Symptoms of Low Blood Sugar Levels
Symptoms of low blood sugar levels may include: * Shaking or trembling * Sweating * Dizziness or lightheadedness * Confusion or disorientation * Nausea or vomiting * Headache * Hunger or cravings for sweetsTreating Low Blood Sugar Levels
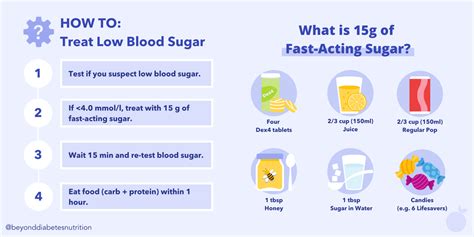
To treat low blood sugar levels, individuals should:
- Consume 15-20 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets, juice, or candy
- Wait 15-20 minutes and recheck blood sugar levels
- If symptoms persist, repeat the treatment
- If symptoms are severe or do not improve, seek medical attention
Preventing Low Blood Sugar Levels
To prevent low blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes should: * Eat regular meals and snacks * Monitor their blood sugar levels regularly * Adjust their medication and food intake based on their blood sugar levels * Avoid skipping meals or snacks * Avoid drinking too much alcoholConclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, managing blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes. By understanding the factors that affect blood sugar levels, monitoring their levels regularly, and taking steps to maintain good blood sugar control, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of complications and maintain a high quality of life. If you or someone you know is living with diabetes, it is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan for managing the condition.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with managing blood sugar levels in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information.
What are the normal blood sugar levels for individuals with diabetes?
+Normal blood sugar levels for individuals with diabetes vary, but they are typically within the following ranges: fasting blood sugar levels: 70-99 mg/dL, after meals: less than 140 mg/dL, and at bedtime: 100-140 mg/dL.
What are the symptoms of low blood sugar levels?
+Symptoms of low blood sugar levels may include shaking or trembling, sweating, dizziness or lightheadedness, confusion or disorientation, nausea or vomiting, headache, and hunger or cravings for sweets.
How can individuals with diabetes prevent complications?
+To prevent complications, individuals with diabetes should maintain good blood sugar control, monitor their blood pressure and cholesterol levels, get regular check-ups with their healthcare provider, stay up-to-date on recommended vaccinations and screenings, and practice good foot care and eye care.
