Intro
Unlock the secrets of blood glucose numbers, understanding normal ranges, glycemic control, and diabetes management with insightful tips on monitoring and regulating blood sugar levels for a healthier life.
Blood glucose numbers are a crucial aspect of managing diabetes and maintaining overall health. For individuals living with diabetes, understanding these numbers is vital to making informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication. In this article, we will delve into the world of blood glucose numbers, exploring their importance, how they are measured, and what they mean for individuals with diabetes.
The importance of blood glucose numbers cannot be overstated. They provide a snapshot of an individual's blood sugar levels at a given moment, allowing them to adjust their treatment plan accordingly. By monitoring blood glucose numbers, individuals with diabetes can identify patterns and trends, making it easier to manage their condition. Moreover, understanding blood glucose numbers can help prevent complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
For individuals without diabetes, understanding blood glucose numbers is also essential. It can help them make informed decisions about their diet and lifestyle, reducing the risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. By being aware of their blood glucose numbers, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain healthy blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Whether you have diabetes or not, understanding blood glucose numbers is crucial for maintaining optimal health and well-being.
What are Blood Glucose Numbers?
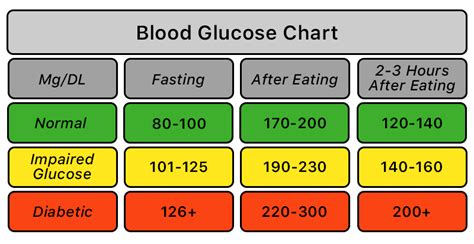
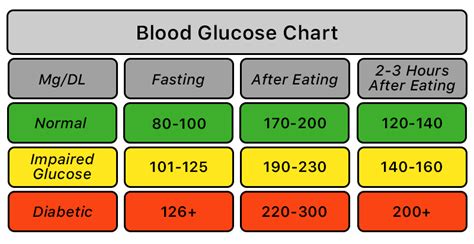
Blood glucose numbers are typically measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). The American Diabetes Association recommends the following blood glucose targets for individuals with diabetes: less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) two hours after eating and less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) when fasting. Understanding these targets is crucial for managing diabetes and preventing complications.
How are Blood Glucose Numbers Measured?
Blood glucose numbers can be measured using a variety of methods, including fingerstick tests, continuous glucose monitoring systems, and laboratory tests. Fingerstick tests involve pricking the finger with a lancet to collect a small blood sample, which is then placed on a test strip and inserted into a glucose meter. Continuous glucose monitoring systems use a small sensor inserted under the skin to track glucose levels throughout the day. Laboratory tests, such as the oral glucose tolerance test, measure blood glucose levels after consuming a sugary drink.Understanding Blood Glucose Targets
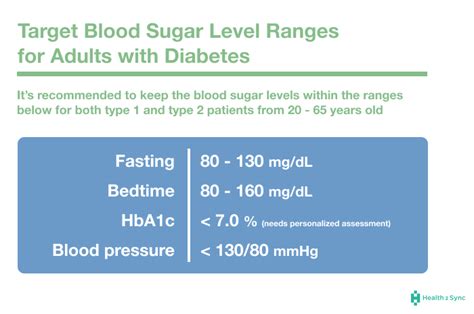
It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to determine individualized blood glucose targets. By understanding these targets, individuals with diabetes can make informed decisions about their treatment plan, including diet, exercise, and medication. Moreover, understanding blood glucose targets can help individuals with diabetes identify patterns and trends, making it easier to manage their condition.
Factors that Affect Blood Glucose Numbers
Several factors can affect blood glucose numbers, including diet, exercise, medication, and stress. A healthy diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and refined carbohydrates can help regulate blood glucose levels. Regular exercise, such as walking or jogging, can also help lower blood glucose levels by increasing insulin sensitivity. Medications, such as metformin, can help regulate blood glucose levels by increasing insulin sensitivity and reducing glucose production in the liver. Stress can also affect blood glucose levels by releasing hormones that raise blood glucose levels.Managing Blood Glucose Numbers
Stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can also help regulate blood glucose levels by reducing stress hormones. By working with a healthcare provider, individuals with diabetes can develop a personalized treatment plan that takes into account their lifestyle, health status, and medication regimen. Moreover, understanding blood glucose numbers can help individuals with diabetes make informed decisions about their treatment plan, reducing the risk of complications and improving overall health and well-being.
Practical Tips for Managing Blood Glucose Numbers
Here are some practical tips for managing blood glucose numbers: * Eat a healthy diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and refined carbohydrates * Engage in regular exercise, such as walking or jogging, to increase insulin sensitivity * Take medication as prescribed by a healthcare provider * Practice stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, to reduce stress hormones * Monitor blood glucose levels regularly to identify patterns and trends * Work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment planCommon Complications of Uncontrolled Blood Glucose Numbers
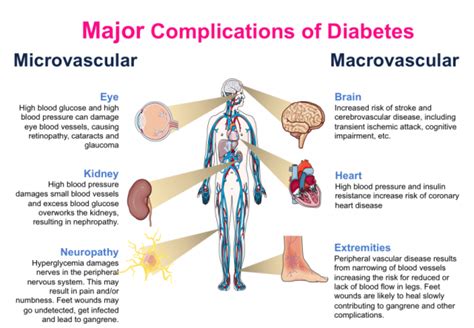
Other complications of uncontrolled blood glucose numbers include blindness, amputations, and increased risk of infections. Blindness can occur when high blood glucose levels damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision loss. Amputations can occur when high blood glucose levels damage the nerves and blood vessels in the feet, leading to poor wound healing and infection. Increased risk of infections can occur when high blood glucose levels weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections.
Preventing Complications of Uncontrolled Blood Glucose Numbers
Preventing complications of uncontrolled blood glucose numbers requires a comprehensive approach that includes diet, exercise, medication, and stress management. A healthy diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and refined carbohydrates can help regulate blood glucose levels. Regular exercise, such as walking or jogging, can also help lower blood glucose levels by increasing insulin sensitivity. Medications, such as metformin, can help regulate blood glucose levels by increasing insulin sensitivity and reducing glucose production in the liver.Stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can also help regulate blood glucose levels by reducing stress hormones. By working with a healthcare provider, individuals with diabetes can develop a personalized treatment plan that takes into account their lifestyle, health status, and medication regimen. Moreover, understanding blood glucose numbers can help individuals with diabetes make informed decisions about their treatment plan, reducing the risk of complications and improving overall health and well-being.
Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with managing blood glucose numbers in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider. By working together, we can improve our understanding of blood glucose numbers and develop effective strategies for managing diabetes and maintaining overall health and well-being.
What is the normal range for blood glucose numbers?
+The normal range for blood glucose numbers is less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) two hours after eating and less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) when fasting.
How often should I check my blood glucose numbers?
+The frequency of checking blood glucose numbers depends on individual factors, such as medication regimen and lifestyle. It is recommended to work with a healthcare provider to determine the best schedule for checking blood glucose numbers.
What are the complications of uncontrolled blood glucose numbers?
+Uncontrolled blood glucose numbers can lead to several complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Other complications include blindness, amputations, and increased risk of infections.
