Intro
Understand blood glucose readings, monitoring, and management. Learn normal, high, and low blood sugar levels, and how to track glucose levels for diabetes control and healthy living.
Blood glucose readings are a crucial aspect of managing diabetes, and understanding them is essential for individuals with the condition to take control of their health. The importance of monitoring blood glucose levels cannot be overstated, as it allows individuals to make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication. In this article, we will delve into the world of blood glucose readings, exploring what they mean, how to interpret them, and why they are vital for effective diabetes management.
For individuals with diabetes, blood glucose readings are a daily reality. They provide a snapshot of the body's glucose levels at a given moment, allowing individuals to adjust their treatment plan accordingly. By understanding blood glucose readings, individuals can identify patterns and trends, making it easier to manage their condition. Moreover, blood glucose readings can help individuals with diabetes to prevent complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage, which can arise if the condition is not properly managed.
The significance of blood glucose readings extends beyond individuals with diabetes. Healthcare professionals also rely on these readings to diagnose and monitor the condition. By analyzing blood glucose readings, healthcare professionals can determine the best course of treatment, adjust medication, and provide personalized advice on diet and exercise. Furthermore, blood glucose readings can help researchers to better understand the complexities of diabetes, leading to the development of new treatments and therapies.
Understanding Blood Glucose Readings
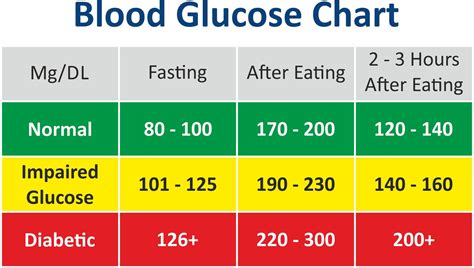
Understanding blood glucose readings is essential for individuals with diabetes. A blood glucose reading is a measure of the amount of glucose in the blood, typically expressed in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). The reading is usually taken from a finger prick blood sample, using a glucose meter or a continuous glucose monitoring system. The glucose meter provides a numerical reading, which can be interpreted as follows:
- Normal blood glucose levels: 70-99 mg/dL (3.9-5.5 mmol/L)
- Elevated blood glucose levels: 100-125 mg/dL (5.6-6.9 mmol/L)
- High blood glucose levels: 126 mg/dL or higher (7.0 mmol/L or higher)
Factors Affecting Blood Glucose Readings
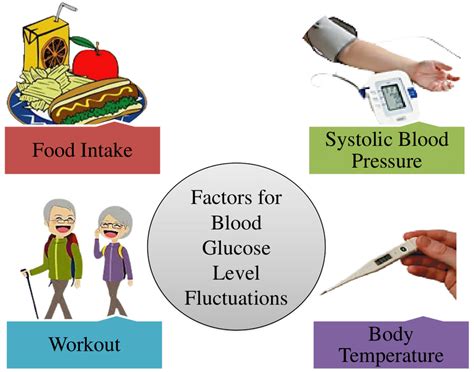
Several factors can affect blood glucose readings, including:
- Diet: Consuming high-carbohydrate or high-sugar foods can cause blood glucose levels to rise.
- Exercise: Physical activity can lower blood glucose levels.
- Medication: Certain medications, such as insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents, can affect blood glucose levels.
- Stress: Stress can cause blood glucose levels to rise.
- Sleep: Poor sleep quality or duration can affect blood glucose levels.
Interpreting Blood Glucose Readings
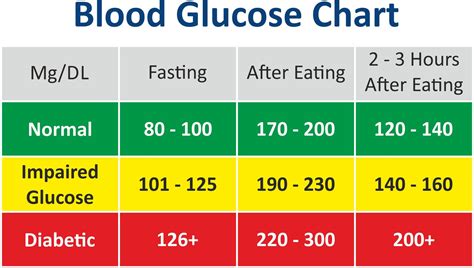
Interpreting blood glucose readings requires consideration of various factors, including the time of day, meal times, and physical activity. Here are some tips for interpreting blood glucose readings:
- Fasting blood glucose: A reading taken after an overnight fast, typically before breakfast.
- Postprandial blood glucose: A reading taken after a meal, typically 1-2 hours after eating.
- Preprandial blood glucose: A reading taken before a meal, typically before breakfast, lunch, or dinner.
Blood Glucose Targets
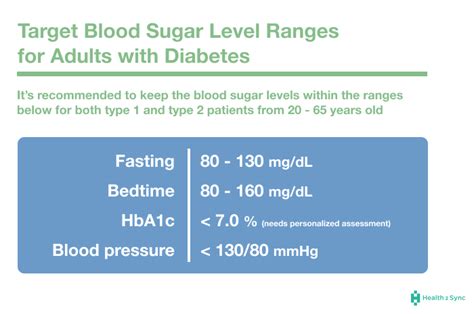
Blood glucose targets vary depending on the individual and their specific needs. Generally, the American Diabetes Association recommends the following targets:
- Fasting blood glucose: Less than 130 mg/dL (7.2 mmol/L)
- Postprandial blood glucose: Less than 180 mg/dL (10.0 mmol/L)
Tools for Monitoring Blood Glucose
Several tools are available for monitoring blood glucose, including:
- Glucose meters: Portable devices that measure blood glucose levels from a finger prick blood sample.
- Continuous glucose monitoring systems: Small devices that measure blood glucose levels continuously, typically over a 7-14 day period.
- Flash glucose monitoring systems: Small devices that measure blood glucose levels intermittently, typically over a 14-day period.
Benefits of Continuous Glucose Monitoring

Continuous glucose monitoring offers several benefits, including:
- Improved glycemic control: By providing real-time data on blood glucose levels, continuous glucose monitoring can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment plan.
- Reduced hypoglycemia: Continuous glucose monitoring can alert individuals to potential hypoglycemia, allowing them to take preventive measures.
- Enhanced quality of life: Continuous glucose monitoring can reduce the burden of frequent finger prick blood samples, making it easier to manage diabetes.
Managing Blood Glucose Levels
Managing blood glucose levels requires a comprehensive approach, including:
- Diet: Eating a balanced diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium.
- Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, or cycling.
- Medication: Taking medication as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
- Stress management: Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga.
Strategies for Reducing Blood Glucose Levels

Several strategies can help reduce blood glucose levels, including:
- Increasing physical activity: Regular exercise can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood glucose levels.
- Losing weight: If overweight or obese, losing weight can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood glucose levels.
- Getting enough sleep: Poor sleep quality or duration can affect blood glucose levels, so aiming for 7-8 hours of sleep per night is essential.
What is the normal range for blood glucose levels?
+Normal blood glucose levels are typically between 70-99 mg/dL (3.9-5.5 mmol/L). However, this range may vary depending on the individual and their specific needs.
How often should I check my blood glucose levels?
+The frequency of blood glucose monitoring depends on the individual and their specific needs. Generally, it is recommended to check blood glucose levels at least 4-6 times per day, including before meals and before bedtime.
What are the benefits of continuous glucose monitoring?
+Continuous glucose monitoring offers several benefits, including improved glycemic control, reduced hypoglycemia, and enhanced quality of life. By providing real-time data on blood glucose levels, continuous glucose monitoring can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment plan.
In conclusion, blood glucose readings are a vital aspect of managing diabetes. By understanding what blood glucose readings mean, how to interpret them, and why they are essential, individuals with diabetes can take control of their health. With the right tools and strategies, individuals can manage their blood glucose levels, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their overall quality of life. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with blood glucose readings in the comments below. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this knowledge.
