Intro
Learn about Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) tests, kidney function, and creatinine levels, understanding BUNs role in diagnosing kidney disease, dehydration, and urea cycle disorders, with insights into normal ranges and elevated BUN levels.
The importance of understanding Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) levels cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in assessing kidney function and overall health. Elevated BUN levels can indicate a range of health issues, from mild dehydration to severe kidney disease. In this article, we will delve into the world of BUN, exploring its significance, causes of elevation, and the measures that can be taken to maintain healthy BUN levels.
BUN is a waste product that is produced by the body's metabolic processes and is typically removed by the kidneys. When the kidneys are functioning properly, they filter out excess BUN from the blood, and it is excreted in the urine. However, when the kidneys are not functioning correctly, BUN can build up in the blood, leading to a range of health problems. Understanding the causes and consequences of elevated BUN levels is essential for maintaining good health and preventing long-term damage to the kidneys.
The measurement of BUN levels is a common medical test that is used to assess kidney function and diagnose a range of health conditions. The test is typically performed on a blood sample, and the results are usually available within a few hours. BUN levels are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), and the normal range for adults is between 6 and 24 mg/dL. However, it is essential to note that BUN levels can be influenced by a range of factors, including age, sex, and overall health.
What is Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
Causes of Elevated BUN Levels
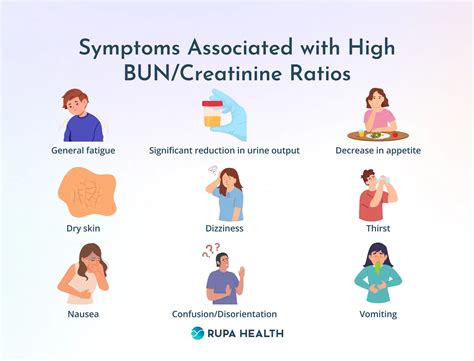
There are several causes of elevated BUN levels, including: * Dehydration: When the body is dehydrated, the kidneys produce more concentrated urine, which can lead to an increase in BUN levels. * Kidney disease: Kidney disease can cause a decrease in kidney function, leading to an increase in BUN levels. * Heart failure: Heart failure can cause a decrease in blood flow to the kidneys, leading to an increase in BUN levels. * High-protein diet: A high-protein diet can increase the amount of BUN produced by the body, leading to elevated BUN levels. * Certain medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics and antibiotics, can increase BUN levels.Symptoms of Elevated BUN Levels
Diagnosis of Elevated BUN Levels
The diagnosis of elevated BUN levels typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. The laboratory tests may include: * BUN test: This test measures the level of BUN in the blood. * Creatinine test: This test measures the level of creatinine in the blood, which can help to assess kidney function. * Urinalysis: This test measures the level of protein, blood, and other substances in the urine.Treatment of Elevated BUN Levels
Prevention of Elevated BUN Levels
Preventing elevated BUN levels involves maintaining good kidney health and managing underlying conditions that can cause elevated BUN levels. This can include: * Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help to prevent dehydration and reduce BUN levels. * Eating a balanced diet: Eating a balanced diet that is low in protein can help to reduce BUN levels. * Managing underlying conditions: Managing underlying conditions, such as kidney disease and heart failure, can help to prevent elevated BUN levels. * Avoiding certain medications: Avoiding certain medications, such as diuretics and antibiotics, can help to prevent elevated BUN levels.Complications of Elevated BUN Levels
Prognosis of Elevated BUN Levels
The prognosis of elevated BUN levels depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. In general, the prognosis is good if the underlying cause is treated promptly and effectively. However, if the underlying cause is not treated, the prognosis can be poor, and the condition can lead to long-term damage to the kidneys and other organs.Conclusion and Recommendations

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with elevated BUN levels in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to ask. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please share it with your friends and family on social media.
What is the normal range for BUN levels in adults?
+The normal range for BUN levels in adults is between 6 and 24 mg/dL.
What are the symptoms of elevated BUN levels?
+The symptoms of elevated BUN levels can include fatigue, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, and shortness of breath.
How can I prevent elevated BUN levels?
+To prevent elevated BUN levels, you can stay hydrated, eat a balanced diet, manage underlying conditions, and avoid certain medications.
