Intro
Discover the 5 ways diabetes is diagnosed, including blood tests, urine analysis, and physical exams, to identify type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes symptoms, and learn about diagnostic criteria and screening methods.
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and its diagnosis is crucial for effective management and treatment. The importance of early diagnosis cannot be overstated, as it enables individuals to take control of their condition, make lifestyle changes, and prevent complications. With the rising prevalence of diabetes, it is essential to understand the various methods used to diagnose this condition. In this article, we will delve into the different ways diabetes is diagnosed, exploring the benefits, working mechanisms, and key information related to each method.
The diagnosis of diabetes is a complex process that involves a combination of physical examinations, medical histories, and laboratory tests. Healthcare professionals use various diagnostic tools to determine whether an individual has diabetes, prediabetes, or another condition that may be causing symptoms. The diagnostic process typically begins with a thorough medical history, during which the healthcare provider will ask questions about the individual's symptoms, family history, and lifestyle habits. This information helps the healthcare provider to identify potential risk factors and determine the best course of action for diagnosis.
The diagnosis of diabetes is a critical step in managing the condition, and it is essential to understand the different methods used to diagnose this condition. By understanding the diagnostic process, individuals can take an active role in their healthcare, make informed decisions, and work with their healthcare providers to develop effective treatment plans. In the following sections, we will explore the different ways diabetes is diagnosed, including the benefits, working mechanisms, and key information related to each method.
Introduction to Diabetes Diagnosis

Types of Diabetes
There are several types of diabetes, including type 1, type 2, gestational diabetes, and latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA). Each type of diabetes has distinct characteristics, and the diagnostic process may vary depending on the type of diabetes suspected. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition that typically develops in childhood or adolescence, while type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder that is often associated with obesity, physical inactivity, and insulin resistance. Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy, usually in the second or third trimester, and LADA is a form of type 1 diabetes that develops in adults.Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
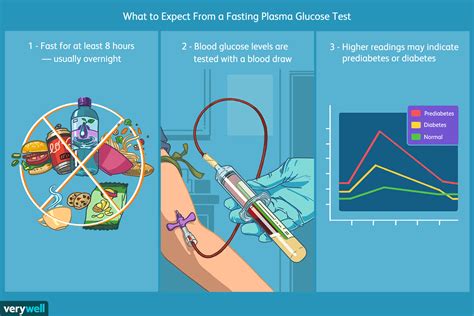
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
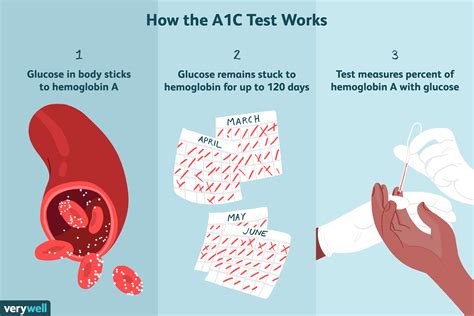
The oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is another diagnostic tool used to diagnose diabetes. This test measures the body's ability to regulate blood glucose levels after consuming a sugary drink. The healthcare provider will ask the individual to fast overnight and then consume a sugary drink containing 75 grams of glucose. Blood samples are taken at regular intervals, usually 1-2 hours after consuming the drink, to measure the level of glucose in the blood. The results are then compared to a standard reference range to determine whether the individual has diabetes, prediabetes, or normal blood glucose levels.Hemoglobin A1c Test
Random Plasma Glucose Test
The random plasma glucose test is a diagnostic tool used to diagnose diabetes in individuals who are experiencing symptoms of high blood glucose, such as increased thirst and urination, blurred vision, or fatigue. This test measures the level of glucose in the blood at any given time, regardless of when the individual last ate. The healthcare provider will take a blood sample and send it to a laboratory for analysis. The results are then compared to a standard reference range to determine whether the individual has diabetes, prediabetes, or normal blood glucose levels. A random plasma glucose level of 200 mg/dL or higher is typically diagnostic of diabetes.Urine Tests

Ketone Tests
Ketone tests are diagnostic tools used to diagnose diabetes, particularly type 1 diabetes. These tests measure the level of ketones in the blood or urine, which can indicate that the body is breaking down fat for energy instead of glucose. The healthcare provider will take a blood sample or ask the individual to provide a urine sample, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results are then compared to a standard reference range to determine whether the individual has diabetes, prediabetes, or normal blood glucose levels.Benefits of Early Diagnosis

- Improved blood glucose control
- Reduced risk of complications, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage
- Enhanced quality of life
- Increased life expectancy
- Better management of symptoms
Importance of Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring is essential for individuals with diabetes, as it enables healthcare providers to track the effectiveness of treatment and make adjustments as needed. Regular monitoring can include:- Blood glucose monitoring
- HbA1c tests
- Urine tests
- Ketone tests
- Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider
By regularly monitoring their condition, individuals with diabetes can take an active role in their healthcare, make informed decisions, and work with their healthcare providers to develop effective treatment plans.
Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with diabetes diagnosis in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. We are committed to providing you with accurate and reliable information to help you navigate the complex world of diabetes diagnosis and management.
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
+The symptoms of diabetes include increased thirst and urination, blurred vision, fatigue, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
How is diabetes diagnosed?
+Diabetes is diagnosed using a combination of physical examinations, medical histories, and laboratory tests, including fasting plasma glucose tests, oral glucose tolerance tests, and hemoglobin A1c tests.
What are the benefits of early diagnosis?
+The benefits of early diagnosis include improved blood glucose control, reduced risk of complications, enhanced quality of life, increased life expectancy, and better management of symptoms.
How often should I monitor my blood glucose levels?
+The frequency of blood glucose monitoring depends on the individual's treatment plan and healthcare provider's recommendations. Typically, individuals with diabetes should monitor their blood glucose levels at least 2-3 times per day.
What are the different types of diabetes?
+The different types of diabetes include type 1, type 2, gestational diabetes, and latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA). Each type of diabetes has distinct characteristics, and the diagnostic process may vary depending on the type of diabetes suspected.
