Intro
Unlock the secrets of your Blood Work CMP test results, understanding key components like electrolytes, liver function, and kidney health to diagnose conditions and monitor treatment, with expert explanations of abnormal results and more.
Blood work is a crucial diagnostic tool used by healthcare professionals to assess an individual's overall health and detect potential health issues. One of the most common blood tests is the Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP), which provides valuable insights into various aspects of a person's health. Understanding CMP test results is essential for individuals to take control of their health and make informed decisions. In this article, we will delve into the world of blood work, explore the significance of CMP test results, and provide a comprehensive guide to interpreting these results.
The CMP test is a broad screening tool that measures various components of the blood, including electrolytes, enzymes, and other substances. It is typically used to evaluate liver and kidney function, as well as to detect potential issues with blood sugar regulation, electrolyte balance, and fluid balance. The CMP test is often ordered as part of a routine health examination or when symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, or abdominal pain are present. By analyzing the results of the CMP test, healthcare professionals can identify potential health issues and develop effective treatment plans.
The importance of understanding CMP test results cannot be overstated. By being informed about their blood work, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health and prevent potential complications. Furthermore, understanding CMP test results can help individuals make informed decisions about their lifestyle, diet, and treatment options. In the following sections, we will provide a detailed explanation of the CMP test, its components, and how to interpret the results.
What is a Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)?
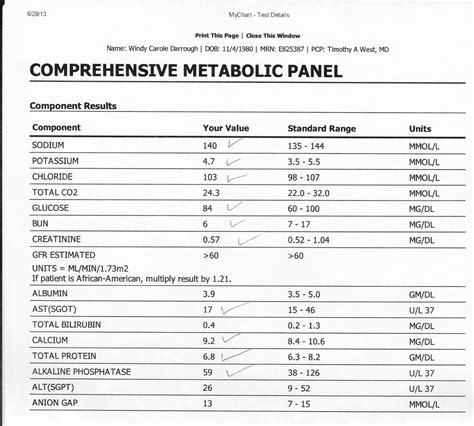
A Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP) is a blood test that measures various components of the blood to assess an individual's overall health. The CMP test is a broad screening tool that evaluates liver and kidney function, as well as blood sugar regulation, electrolyte balance, and fluid balance. The test typically includes measurements of:
- Electrolytes (sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate)
- Enzymes (alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase, and alkaline phosphatase)
- Proteins (albumin and total protein)
- Waste products (blood urea nitrogen and creatinine)
- Blood sugar (glucose)
The CMP test is usually ordered as part of a routine health examination or when symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, or abdominal pain are present. By analyzing the results of the CMP test, healthcare professionals can identify potential health issues and develop effective treatment plans.
Components of a CMP Test

The CMP test includes measurements of various components of the blood, which are categorized into several sections. These sections include:
- Electrolytes: Electrolytes are minerals that carry an electric charge and play a crucial role in maintaining various bodily functions, such as nerve and muscle function, hydration, and pH balance. The CMP test measures the levels of sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate in the blood.
- Enzymes: Enzymes are proteins that facilitate chemical reactions in the body. The CMP test measures the levels of certain enzymes, such as alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP), which are produced by the liver and other organs.
- Proteins: Proteins are essential for various bodily functions, such as building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and maintaining fluid balance. The CMP test measures the levels of albumin and total protein in the blood.
- Waste products: Waste products, such as blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine, are produced by the body's metabolic processes and are typically excreted by the kidneys. The CMP test measures the levels of these waste products in the blood.
- Blood sugar: Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is a vital source of energy for the body's cells. The CMP test measures the level of glucose in the blood.
Interpreting CMP Test Results
Interpreting CMP test results requires a comprehensive understanding of the various components measured by the test. The results are typically reported as a series of numbers, which are compared to reference ranges to determine if they are within normal limits. The following are some general guidelines for interpreting CMP test results:
- Electrolytes:
- Sodium: 135-145 mmol/L
- Potassium: 3.5-5.0 mmol/L
- Chloride: 96-106 mmol/L
- Bicarbonate: 22-28 mmol/L
- Enzymes:
- ALT: 0-40 U/L
- AST: 0-40 U/L
- ALP: 30-120 U/L
- Proteins:
- Albumin: 3.5-5.5 g/dL
- Total protein: 6.0-8.0 g/dL
- Waste products:
- BUN: 6-24 mg/dL
- Creatinine: 0.6-1.2 mg/dL
- Blood sugar:
- Fasting glucose: 70-100 mg/dL
- Postprandial glucose: <140 mg/dL
Abnormal results may indicate various health issues, such as:
- Electrolyte imbalances: Abnormal levels of sodium, potassium, chloride, or bicarbonate may indicate issues with hydration, acid-base balance, or kidney function.
- Liver damage: Elevated levels of ALT, AST, or ALP may indicate liver damage or disease.
- Kidney disease: Elevated levels of BUN or creatinine may indicate kidney disease or impaired kidney function.
- Diabetes: Elevated levels of glucose may indicate diabetes or impaired glucose regulation.
Common Abnormalities in CMP Test Results
Abnormalities in CMP test results can indicate various health issues. Some common abnormalities include:
- Elevated liver enzymes: Elevated levels of ALT, AST, or ALP may indicate liver damage or disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis.
- Electrolyte imbalances: Abnormal levels of sodium, potassium, chloride, or bicarbonate may indicate issues with hydration, acid-base balance, or kidney function.
- Kidney disease: Elevated levels of BUN or creatinine may indicate kidney disease or impaired kidney function.
- Diabetes: Elevated levels of glucose may indicate diabetes or impaired glucose regulation.
- Protein abnormalities: Abnormal levels of albumin or total protein may indicate issues with liver or kidney function, or malnutrition.
What to Do If You Have Abnormal CMP Test Results
If you have abnormal CMP test results, it is essential to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and develop an effective treatment plan. Your healthcare provider may order additional tests or examinations to confirm the diagnosis and monitor your condition. In some cases, abnormal CMP test results may indicate a need for lifestyle changes, such as:
- Dietary modifications: Changes to your diet, such as reducing salt or sugar intake, may be necessary to manage electrolyte imbalances or blood sugar regulation.
- Exercise: Regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity and glucose regulation.
- Medications: Your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to manage underlying conditions, such as diabetes or kidney disease.
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, understanding CMP test results is essential for individuals to take control of their health and make informed decisions. By being informed about their blood work, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health and prevent potential complications. If you have any questions or concerns about your CMP test results, it is essential to consult with your healthcare provider. Additionally, you can take the following next steps:
- Schedule a follow-up appointment: Schedule a follow-up appointment with your healthcare provider to discuss your test results and develop a treatment plan.
- Make lifestyle changes: Make lifestyle changes, such as dietary modifications or exercise, to manage underlying conditions.
- Stay informed: Stay informed about your health and any underlying conditions by reading reputable sources and consulting with your healthcare provider.
What is a Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP) test?
+A Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP) test is a blood test that measures various components of the blood to assess an individual's overall health.
What components are measured in a CMP test?
+A CMP test measures various components, including electrolytes, enzymes, proteins, waste products, and blood sugar.
How do I interpret my CMP test results?
+Interpreting CMP test results requires a comprehensive understanding of the various components measured by the test. The results are typically reported as a series of numbers, which are compared to reference ranges to determine if they are within normal limits.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of CMP test results and how to interpret them. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from this information. By being informed about your health, you can take proactive steps to manage your health and prevent potential complications.
