Intro
Understand diabetes blood work, including glucose tests, hemoglobin A1c, and lipid profiles, to manage blood sugar levels and prevent complications with regular monitoring and healthy lifestyle changes.
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and it is crucial to monitor and manage the disease to prevent complications. One of the most effective ways to monitor diabetes is through blood work, which provides valuable insights into blood sugar levels, insulin function, and overall health. In this article, we will delve into the world of diabetes blood work, exploring its importance, types, and what the results mean.
Diabetes blood work is a critical component of diabetes management, as it helps healthcare providers diagnose, monitor, and adjust treatment plans. By analyzing blood samples, healthcare providers can determine blood sugar levels, detect potential complications, and adjust medication or lifestyle recommendations accordingly. Regular blood work can also help individuals with diabetes understand their condition better, empowering them to take control of their health and make informed decisions.
The importance of diabetes blood work cannot be overstated, as it plays a vital role in preventing complications and improving overall health outcomes. For instance, high blood sugar levels can damage organs and tissues over time, leading to conditions such as kidney disease, nerve damage, and blindness. By monitoring blood sugar levels through regular blood work, individuals with diabetes can identify potential issues early on and take corrective action to prevent long-term damage. Moreover, diabetes blood work can help healthcare providers identify other health issues that may be related to diabetes, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or thyroid problems.
Types of Diabetes Blood Work
There are several types of diabetes blood work, each with its unique purpose and benefits. The most common types of diabetes blood work include:
- Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test: This test measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast, typically 8-12 hours.
- Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT): This test measures blood sugar levels after consuming a sugary drink, usually 2 hours after ingestion.
- Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test: This test measures average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
- Insulin level test: This test measures insulin levels in the blood, which can help diagnose insulin resistance or deficiency.
- Lipid profile test: This test measures cholesterol and triglyceride levels in the blood, which can help identify cardiovascular risk factors.
Understanding Diabetes Blood Work Results
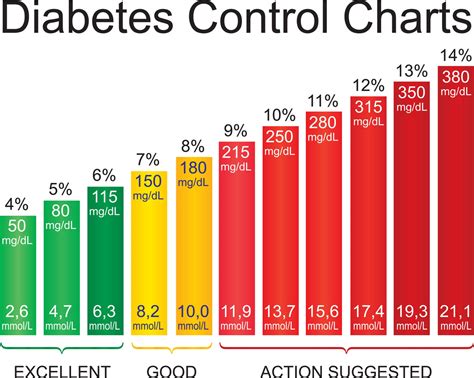
The results of diabetes blood work can be complex and confusing, but understanding what they mean is essential for effective diabetes management. Here are some key things to know: * FPG test results: Normal results are typically below 100 mg/dL, while results between 100-125 mg/dL indicate impaired fasting glucose. Results above 126 mg/dL indicate diabetes. * OGTT test results: Normal results are typically below 140 mg/dL, while results between 140-199 mg/dL indicate impaired glucose tolerance. Results above 200 mg/dL indicate diabetes. * HbA1c test results: Normal results are typically below 5.7%, while results between 5.7-6.4% indicate prediabetes. Results above 6.5% indicate diabetes. * Insulin level test results: Normal results vary depending on the laboratory and testing method, but generally, results above 10-20 uU/mL indicate insulin resistance.Benefits of Regular Diabetes Blood Work

Regular diabetes blood work offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved blood sugar control: Regular monitoring helps individuals with diabetes adjust their treatment plans and lifestyle habits to achieve better blood sugar control.
- Early detection of complications: Regular blood work can detect potential complications, such as kidney disease or nerve damage, early on, allowing for prompt treatment and prevention.
- Enhanced medication management: Regular blood work helps healthcare providers adjust medication dosages and types to optimize treatment outcomes.
- Increased patient empowerment: Regular blood work provides individuals with diabetes with valuable insights into their condition, empowering them to take control of their health and make informed decisions.
Preparing for Diabetes Blood Work
Preparing for diabetes blood work is essential to ensure accurate and reliable results. Here are some tips: * Fast for the recommended amount of time before the test, usually 8-12 hours. * Avoid consuming sugary drinks or foods before the test. * Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water before and during the test. * Avoid strenuous exercise or physical activity before the test. * Inform your healthcare provider about any medications or supplements you are taking, as they may affect test results.Common Diabetes Blood Work Tests

There are several common diabetes blood work tests, each with its unique purpose and benefits. Some of the most common tests include:
- Complete blood count (CBC): This test measures various components of the blood, including red and white blood cell counts, hemoglobin, and platelet count.
- Basic metabolic panel (BMP): This test measures electrolyte levels, blood sugar, and kidney function.
- Comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP): This test measures a broader range of components, including liver function, electrolyte levels, and blood sugar.
- Lipid profile test: This test measures cholesterol and triglyceride levels in the blood.
Diabetes Blood Work and Lifestyle Changes
Diabetes blood work is not just about monitoring blood sugar levels; it's also about making lifestyle changes to improve overall health. Here are some tips: * Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. * Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day, aiming for at least 8 cups (64 ounces) daily. * Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week. * Manage stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.Diabetes Blood Work and Technology

Technology has revolutionized diabetes blood work, making it easier and more convenient to monitor blood sugar levels. Some of the latest technologies include:
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems: These devices track blood sugar levels throughout the day, providing real-time data and insights.
- Flash glucose monitoring (FGM) systems: These devices measure blood sugar levels at regular intervals, providing a snapshot of glucose levels.
- Mobile apps: Many mobile apps allow individuals with diabetes to track their blood sugar levels, medication, and lifestyle habits, making it easier to manage their condition.
Diabetes Blood Work and Mental Health
Diabetes blood work is not just about physical health; it's also about mental health. Living with diabetes can be stressful and overwhelming, and regular blood work can help individuals with diabetes cope with their condition. Here are some tips: * Seek support: Connect with friends, family, or a support group to share experiences and emotions. * Practice self-care: Engage in activities that bring joy and relaxation, such as reading, listening to music, or taking a warm bath. * Stay positive: Focus on the positive aspects of life, and celebrate small victories and achievements.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, diabetes blood work is a critical component of diabetes management, providing valuable insights into blood sugar levels, insulin function, and overall health. By understanding the different types of diabetes blood work, preparing for tests, and making lifestyle changes, individuals with diabetes can take control of their health and improve their overall well-being. If you have diabetes or are at risk of developing the condition, consult with your healthcare provider to discuss the best approach to diabetes blood work and management.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with diabetes blood work in the comments section below. Have you had any challenges or successes with managing your diabetes through blood work? What tips or advice would you like to share with others? Let's start a conversation and support each other in our journey to better health.
What is the purpose of diabetes blood work?
+The purpose of diabetes blood work is to monitor and manage diabetes, detect potential complications, and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
What are the different types of diabetes blood work?
+The different types of diabetes blood work include fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test, oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test, insulin level test, and lipid profile test.
How often should I get diabetes blood work done?
+The frequency of diabetes blood work depends on individual factors, such as the type of diabetes, treatment plan, and overall health. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best schedule for your needs.
Can I do diabetes blood work at home?
+Yes, there are several at-home diabetes blood work kits and devices available, such as continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems and flash glucose monitoring (FGM) systems. However, it's essential to consult with your healthcare provider before using any at-home testing device.
What are the benefits of regular diabetes blood work?
+The benefits of regular diabetes blood work include improved blood sugar control, early detection of complications, enhanced medication management, and increased patient empowerment.
