Intro
Discover causes and effects of high bloodwork chloride levels, including symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, to understand electrolyte imbalance and its impact on overall health, addressing hyperchloremia and related conditions.
The human body is a complex system that relies on a delicate balance of various substances to function properly. One such substance is chloride, an essential electrolyte that plays a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contraction. However, when chloride levels in the blood become elevated, it can indicate an underlying health issue. In this article, we will delve into the world of high bloodwork chloride levels, exploring their causes, symptoms, and implications for overall health.
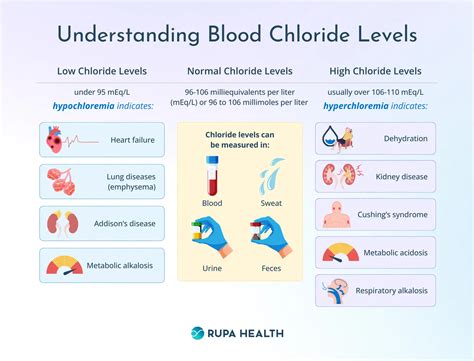
Chloride is an electrolyte that is naturally found in the body, with the majority of it being located in the blood and other bodily fluids. It helps to regulate the balance of fluids within the body, maintain proper blood pressure, and facilitate the transmission of nerve impulses. The normal range for chloride levels in the blood is typically between 96 and 106 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L). However, when chloride levels exceed this range, it can be a sign of an underlying health issue that requires attention.
High bloodwork chloride levels can be caused by a variety of factors, including dehydration, kidney disease, and certain medications. Dehydration, for example, can cause a concentration of chloride in the blood, leading to elevated levels. Kidney disease, on the other hand, can impair the kidneys' ability to filter and remove excess chloride from the blood, resulting in a buildup of the electrolyte. Certain medications, such as diuretics, can also increase chloride levels by causing the body to lose potassium and retain chloride.
Understanding Chloride Imbalance

To understand the implications of high bloodwork chloride levels, it is essential to recognize the importance of maintaining a balance of electrolytes in the body. Electrolytes, including chloride, potassium, and sodium, play a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, such as nerve function, muscle contraction, and fluid balance. When the balance of these electrolytes is disrupted, it can lead to a range of health problems, from mild to severe. In the case of high bloodwork chloride levels, an imbalance can occur when the body has an excess of chloride and a deficiency of other essential electrolytes, such as potassium.
Causes of High Chloride Levels
The causes of high bloodwork chloride levels can be diverse and complex. Some of the most common causes include: * Dehydration: Dehydration can cause a concentration of chloride in the blood, leading to elevated levels. * Kidney disease: Kidney disease can impair the kidneys' ability to filter and remove excess chloride from the blood, resulting in a buildup of the electrolyte. * Certain medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics, can increase chloride levels by causing the body to lose potassium and retain chloride. * Cushing's syndrome: Cushing's syndrome is a rare endocrine disorder that can cause an overproduction of cortisol, leading to elevated chloride levels. * Hyperparathyroidism: Hyperparathyroidism is a condition in which the parathyroid glands produce excess parathyroid hormone, leading to elevated calcium and chloride levels.Symptoms of High Chloride Levels

The symptoms of high bloodwork chloride levels can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Some common symptoms include:
- Fatigue: Elevated chloride levels can cause fatigue, weakness, and a general feeling of being unwell.
- Muscle weakness: High chloride levels can impair muscle function, leading to weakness, cramps, and spasms.
- Numbness or tingling: Elevated chloride levels can cause numbness or tingling sensations in the hands and feet.
- Abnormal heart rhythms: High chloride levels can disrupt normal heart function, leading to abnormal heart rhythms and palpitations.
- Seizures: In severe cases, high chloride levels can cause seizures, particularly in individuals with a history of seizure disorders.
Treatment and Management
Treatment and management of high bloodwork chloride levels depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Some common treatment approaches include: * Fluid replacement: In cases of dehydration, fluid replacement is essential to help restore normal chloride levels. * Medication adjustment: If certain medications are causing high chloride levels, adjusting or discontinuing these medications may be necessary. * Dietary changes: Making dietary changes, such as reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium-rich foods, can help to restore normal electrolyte balance. * Dialysis: In severe cases of kidney disease, dialysis may be necessary to help remove excess chloride and other waste products from the blood.Complications of Untreated High Chloride Levels
Untreated high bloodwork chloride levels can lead to a range of complications, including:
- Kidney damage: Elevated chloride levels can cause damage to the kidneys, particularly in individuals with pre-existing kidney disease.
- Heart problems: High chloride levels can increase the risk of heart problems, including abnormal heart rhythms, cardiac arrest, and heart failure.
- Muscle weakness: Untreated high chloride levels can cause persistent muscle weakness, leading to decreased mobility and increased risk of falls.
- Seizures: In severe cases, untreated high chloride levels can cause seizures, which can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Prevention and Early Detection
Preventing and detecting high bloodwork chloride levels early on is crucial to minimizing the risk of complications and promoting overall health. Some strategies for prevention and early detection include: * Regular health check-ups: Regular health check-ups can help to identify underlying health issues, such as kidney disease or hormonal imbalances, which can contribute to high chloride levels. * Balanced diet: Eating a balanced diet that is rich in potassium and low in sodium can help to maintain normal electrolyte balance. * Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water and staying hydrated can help to prevent dehydration, which can contribute to high chloride levels. * Monitoring medication side effects: If taking medications that can cause high chloride levels, monitoring side effects and adjusting medication as needed can help to prevent complications.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, high bloodwork chloride levels can be a sign of an underlying health issue that requires attention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and implications of high chloride levels, individuals can take steps to prevent and manage this condition. If you are concerned about your chloride levels or are experiencing symptoms of high chloride levels, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with high bloodwork chloride levels in the comments section below. Have you or someone you know been affected by this condition? What steps have you taken to manage and prevent high chloride levels? By sharing your stories and insights, you can help to raise awareness and promote education about this important health topic.
What are the normal ranges for chloride levels in the blood?
+The normal range for chloride levels in the blood is typically between 96 and 106 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L).
What are the symptoms of high bloodwork chloride levels?
+The symptoms of high bloodwork chloride levels can include fatigue, muscle weakness, numbness or tingling, abnormal heart rhythms, and seizures.
How can high bloodwork chloride levels be treated and managed?
+Treatment and management of high bloodwork chloride levels depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition, but may include fluid replacement, medication adjustment, dietary changes, and dialysis.
