Intro
Discover the normal body temperature range, including average temperatures, variations, and factors influencing basal body temperature, core temperature, and oral temperature readings for adults and children.
The human body is a complex and fascinating system, and one of its most essential aspects is its ability to regulate its internal temperature. Maintaining a normal body temperature is crucial for the proper functioning of various bodily processes, including metabolic rate, enzyme activity, and nerve function. In this article, we will delve into the world of body temperature, exploring its importance, the factors that influence it, and the consequences of abnormal temperature fluctuations.
Understanding the concept of normal body temperature is vital, as it serves as a benchmark for diagnosing and treating various medical conditions. The average body temperature is around 98.6°F (37°C), but it can vary slightly from person to person. This variation is due to factors such as age, sex, and overall health. For instance, infants and young children tend to have a higher body temperature than adults, while older adults may have a lower body temperature.
The importance of maintaining a normal body temperature cannot be overstated. Even slight deviations from the normal range can have significant effects on the body's functioning. For example, a body temperature that is too high can lead to heat-related illnesses, such as heat exhaustion or heatstroke, while a body temperature that is too low can cause hypothermia. Furthermore, abnormal body temperature can be a symptom of underlying medical conditions, such as infections, inflammation, or hormonal imbalances. Therefore, it is essential to understand the factors that influence body temperature and to recognize the signs and symptoms of abnormal temperature fluctuations.
What is Normal Body Temperature Range?
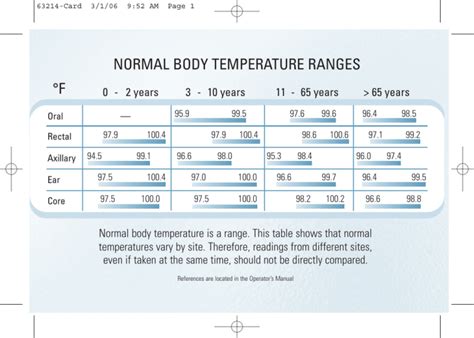
The normal body temperature range is typically considered to be between 97.7°F (36.5°C) and 99.5°F (37.7°C). However, this range can vary slightly depending on the individual and the method used to measure body temperature. For example, oral temperature measurements tend to be slightly lower than rectal or tympanic (ear) temperature measurements. It is also important to note that body temperature can fluctuate throughout the day, with temperatures tend to be higher in the late afternoon and evening.
Factors that Influence Body Temperature
Several factors can influence body temperature, including: * Age: As mentioned earlier, infants and young children tend to have a higher body temperature than adults, while older adults may have a lower body temperature. * Sex: Women tend to have a slightly higher body temperature than men, especially during the menstrual cycle. * Time of day: Body temperature tends to be higher in the late afternoon and evening. * Activity level: Engaging in physical activity can increase body temperature. * Environmental factors: Exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity, or altitude can affect body temperature. * Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as infections, inflammation, or hormonal imbalances, can cause abnormal body temperature fluctuations.How is Body Temperature Regulated?
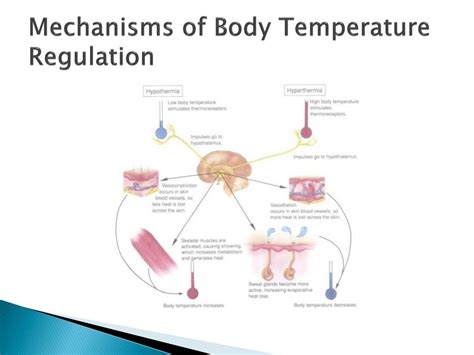
The body has a complex system for regulating its internal temperature. The hypothalamus, a small region in the brain, acts as the body's thermostat, receiving input from various sensors throughout the body and sending signals to effectors that help to maintain a stable temperature. The hypothalamus uses several mechanisms to regulate body temperature, including:
- Sweating: When the body temperature rises, the hypothalamus stimulates the sweat glands to produce sweat, which helps to cool the body.
- Shivering: When the body temperature drops, the hypothalamus stimulates the muscles to shiver, which helps to generate heat.
- Vasodilation and vasoconstriction: The hypothalamus can cause blood vessels to dilate (expand) or constrict (narrow) to help regulate blood flow and temperature.
Consequences of Abnormal Body Temperature
Abnormal body temperature can have significant consequences, ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions. Some of the consequences of abnormal body temperature include: * Heat-related illnesses: Heat exhaustion or heatstroke can occur when the body temperature rises too high. * Hypothermia: When the body temperature drops too low, hypothermia can occur, which can be life-threatening if left untreated. * Organ damage: Prolonged exposure to abnormal body temperature can cause damage to various organs, including the brain, heart, and kidneys. * Infections: Abnormal body temperature can be a symptom of underlying infections, such as sepsis or meningitis.Measuring Body Temperature
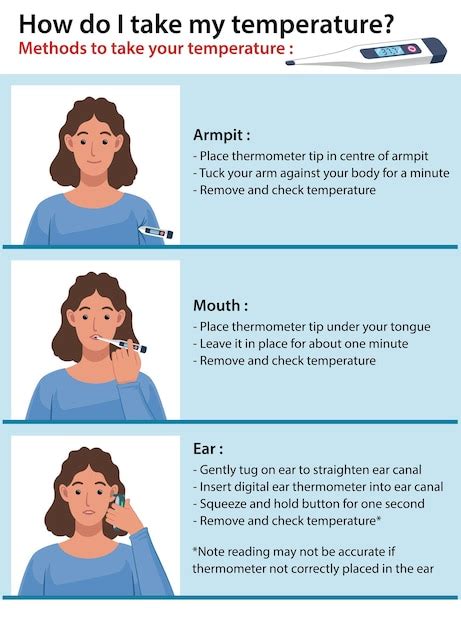
There are several methods for measuring body temperature, including:
- Oral temperature measurement: This is the most common method, which involves placing a thermometer under the tongue.
- Rectal temperature measurement: This method involves inserting a thermometer into the rectum.
- Tympanic temperature measurement: This method involves placing a thermometer in the ear canal.
- Axillary temperature measurement: This method involves placing a thermometer in the armpit.
Tips for Maintaining a Normal Body Temperature
To maintain a normal body temperature, it is essential to: * Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps to regulate body temperature. * Dress appropriately: Wearing light, loose clothing can help to keep the body cool in hot weather. * Avoid extreme temperatures: Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity, or altitude. * Engage in regular exercise: Regular physical activity can help to regulate body temperature. * Get enough sleep: Getting enough sleep helps to regulate the body's internal clock and maintain a stable body temperature.Common Medical Conditions Associated with Abnormal Body Temperature
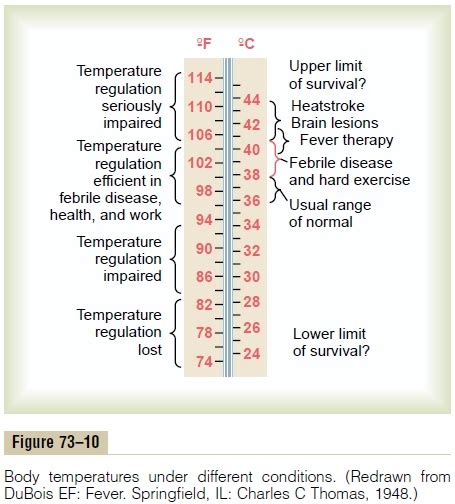
Several medical conditions are associated with abnormal body temperature, including:
- Infections: Such as sepsis, meningitis, or pneumonia.
- Inflammation: Such as appendicitis or peritonitis.
- Hormonal imbalances: Such as hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
- Neurological disorders: Such as multiple sclerosis or Parkinson's disease.
- Cancer: Certain types of cancer, such as lymphoma or leukemia, can cause abnormal body temperature.
Diagnosing and Treating Abnormal Body Temperature
Diagnosing and treating abnormal body temperature requires a comprehensive approach, including: * Medical history: A thorough medical history can help to identify underlying conditions that may be causing abnormal body temperature. * Physical examination: A physical examination can help to identify signs and symptoms of abnormal body temperature. * Laboratory tests: Laboratory tests, such as blood tests or imaging studies, can help to diagnose underlying conditions. * Treatment: Treatment for abnormal body temperature depends on the underlying cause and may include medications, surgery, or other interventions.Prevention and Management of Abnormal Body Temperature
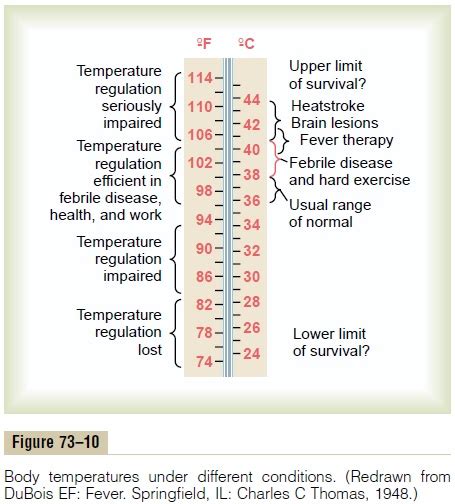
Preventing and managing abnormal body temperature requires a proactive approach, including:
- Staying informed: Staying informed about the risks and consequences of abnormal body temperature can help to prevent and manage it.
- Practicing good hygiene: Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly, can help to prevent infections.
- Getting vaccinated: Getting vaccinated against certain infections, such as flu or pneumonia, can help to prevent abnormal body temperature.
- Seeking medical attention: Seeking medical attention promptly if symptoms of abnormal body temperature occur can help to prevent complications.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, maintaining a normal body temperature is essential for the proper functioning of various bodily processes. Understanding the factors that influence body temperature, recognizing the signs and symptoms of abnormal temperature fluctuations, and taking proactive steps to prevent and manage it can help to promote overall health and well-being. Future research should focus on developing more effective methods for measuring and regulating body temperature, as well as improving our understanding of the complex mechanisms that govern it.What is the normal body temperature range?
+The normal body temperature range is typically considered to be between 97.7°F (36.5°C) and 99.5°F (37.7°C).
What factors can influence body temperature?
+Several factors can influence body temperature, including age, sex, time of day, activity level, environmental factors, and medical conditions.
How is body temperature regulated?
+The body has a complex system for regulating its internal temperature, involving the hypothalamus, sweat glands, and blood vessels.
What are the consequences of abnormal body temperature?
+Abnormal body temperature can have significant consequences, ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions, such as heat-related illnesses, hypothermia, and organ damage.
How can I maintain a normal body temperature?
+To maintain a normal body temperature, it is essential to stay hydrated, dress appropriately, avoid extreme temperatures, engage in regular exercise, and get enough sleep.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of normal body temperature range and its importance. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others. Remember to always prioritize your health and well-being by taking proactive steps to prevent and manage abnormal body temperature.
