Intro
Discover common reasons for missing menstruation, including hormonal imbalance, pregnancy, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), affecting menstrual cycle and fertility, causing amenorrhea and irregular periods.
Missing menstruation, also known as amenorrhea, is a condition where a woman's menstrual period is absent or infrequent. This can be a cause for concern for many women, as it can be a sign of an underlying health issue. In this article, we will explore the reasons for missing menstruation, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Missing menstruation can be caused by a variety of factors, including hormonal imbalances, lifestyle changes, and certain medical conditions. For some women, missing menstruation may be a temporary condition that resolves on its own, while for others, it may be a persistent problem that requires medical attention. Understanding the reasons for missing menstruation is essential for women to take control of their reproductive health and seek medical help when needed.
The menstrual cycle is a complex process that involves the coordination of hormones, the brain, and the reproductive organs. Any disruption to this process can lead to missing menstruation. Some common causes of missing menstruation include polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, and pituitary tumors. Lifestyle factors such as stress, weight changes, and excessive exercise can also contribute to missing menstruation. Additionally, certain medical conditions such as premature ovarian failure and uterine abnormalities can cause missing menstruation.
Causes of Missing Menstruation

Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances are a common cause of missing menstruation. The menstrual cycle is regulated by a complex interplay of hormones, including estrogen, progesterone, and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Any disruption to this hormonal balance can lead to missing menstruation. For example, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that can cause missing menstruation. PCOS is characterized by high levels of androgens, which can disrupt the menstrual cycle and lead to missing menstruation.Medical Conditions that Cause Missing Menstruation
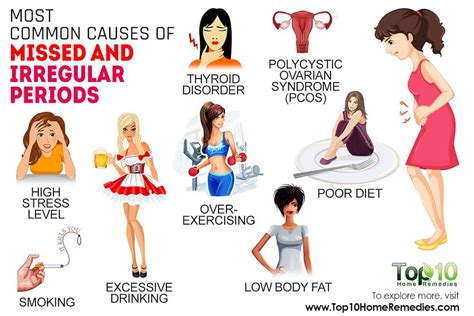
Lifestyle Factors that Contribute to Missing Menstruation
Lifestyle factors can also contribute to missing menstruation. For example, stress can disrupt the menstrual cycle and lead to missing menstruation. Stress can cause the body to produce high levels of cortisol, which can disrupt the production of hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle. Weight changes, such as significant weight gain or loss, can also contribute to missing menstruation. Excessive exercise, such as intense athletic training, can also disrupt the menstrual cycle and lead to missing menstruation.Symptoms of Missing Menstruation

Diagnosis of Missing Menstruation
The diagnosis of missing menstruation typically involves a physical exam, medical history, and laboratory tests. The doctor may perform a pelvic exam to check for any abnormalities in the reproductive organs. The doctor may also order laboratory tests, such as blood tests or imaging studies, to check for hormonal imbalances or other underlying medical conditions.Treatment Options for Missing Menstruation
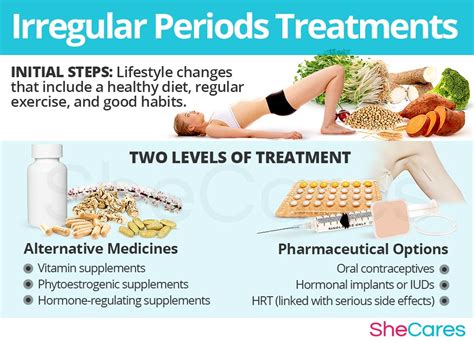
Home Remedies for Missing Menstruation
There are also some home remedies that may help regulate the menstrual cycle and prevent missing menstruation. For example: * Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as yoga or meditation * Eating a balanced diet that includes foods rich in iron and calcium * Avoiding excessive exercise or athletic training * Getting enough sleep and maintaining a regular sleep schedule * Avoiding certain medications, such as birth control pills or antidepressants, that can disrupt the menstrual cyclePrevention of Missing Menstruation
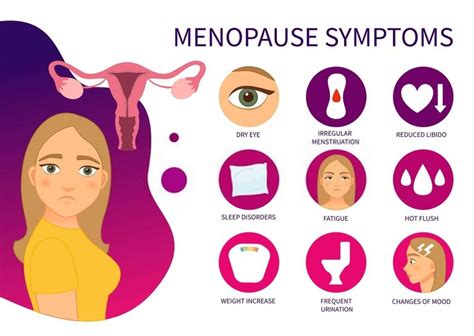
Risks and Complications of Missing Menstruation
Missing menstruation can increase the risk of certain health complications, such as infertility, osteoporosis, and heart disease. For example, women with PCOS or premature ovarian failure may experience infertility due to irregular ovulation. Missing menstruation can also increase the risk of osteoporosis, as the lack of estrogen can lead to bone loss. Additionally, missing menstruation can increase the risk of heart disease, as the lack of estrogen can lead to high blood pressure and high cholesterol.Conclusion and Next Steps

What are the common causes of missing menstruation?
+Missing menstruation can be caused by hormonal imbalances, lifestyle changes, and certain medical conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, and pituitary tumors.
How is missing menstruation diagnosed?
+The diagnosis of missing menstruation typically involves a physical exam, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as blood tests or imaging studies, to check for hormonal imbalances or other underlying medical conditions.
What are the treatment options for missing menstruation?
+The treatment options for missing menstruation depend on the underlying cause and may include hormone replacement therapy (HRT), medication to treat underlying medical conditions, and lifestyle changes, such as stress management, weight loss, or exercise modification.
Can missing menstruation increase the risk of health complications?
+Yes, missing menstruation can increase the risk of certain health complications, such as infertility, osteoporosis, and heart disease, due to the lack of estrogen and irregular ovulation.
How can I prevent missing menstruation?
+Preventing missing menstruation requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions, such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, practicing stress-reducing techniques, and avoiding certain medications.
