Intro
Discover how bone scans aid in cancer detection, utilizing nuclear medicine to identify metastatic cancer cells, osteoblastic activity, and skeletal abnormalities, enhancing diagnosis and treatment of bone cancer and metastatic disease.
The diagnosis and treatment of cancer have become more sophisticated over the years, with various tests and procedures being developed to detect and manage the disease. One such diagnostic tool is the bone scan, which plays a crucial role in detecting cancer that has spread to the bones. Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, and early detection is key to effective treatment and management. In this article, we will delve into the world of bone scans for cancer detection, exploring the importance of this diagnostic tool, how it works, and its benefits.
Cancer can spread to any part of the body, but it commonly metastasizes to the bones, lungs, liver, and brain. When cancer cells break away from the primary tumor site, they can travel through the bloodstream or lymphatic system and settle in other parts of the body. Bone metastasis is a common occurrence in various types of cancer, including breast, prostate, lung, and kidney cancer. A bone scan is a diagnostic test that helps doctors detect cancer that has spread to the bones, allowing for early intervention and treatment.
The bone scan is a non-invasive test that uses small amounts of radioactive material to highlight areas of abnormal bone activity. This test is particularly useful in detecting bone metastasis, as it can show areas of increased bone activity, which may indicate the presence of cancer cells. The bone scan is also used to monitor the effectiveness of cancer treatment, as it can help doctors track changes in bone activity over time. With the help of a bone scan, doctors can diagnose and treat bone metastasis early, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Bone Scan Procedure
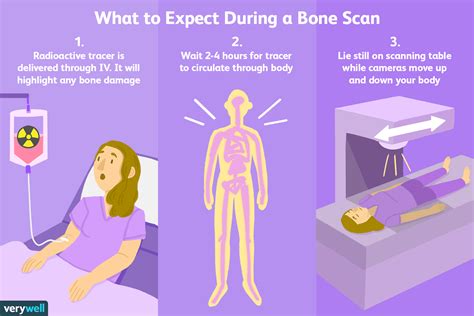
How Bone Scans Work
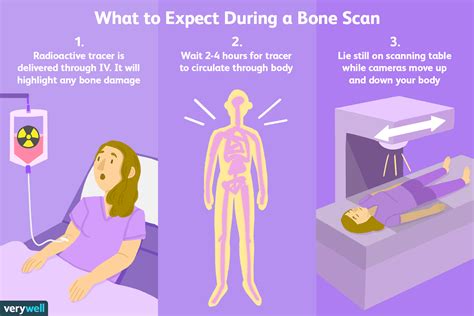
Benefits of Bone Scans
Types of Bone Scans
There are several types of bone scans, including: * Whole-body bone scans: This type of scan shows the entire skeleton and is used to detect bone metastasis. * Regional bone scans: This type of scan focuses on a specific area of the body, such as the spine or pelvis. * Bone marrow scans: This type of scan shows the bone marrow and is used to detect bone marrow disorders. * PET-CT bone scans: This type of scan combines a bone scan with a PET-CT scan, which provides more detailed images of the body.Preparing for a Bone Scan
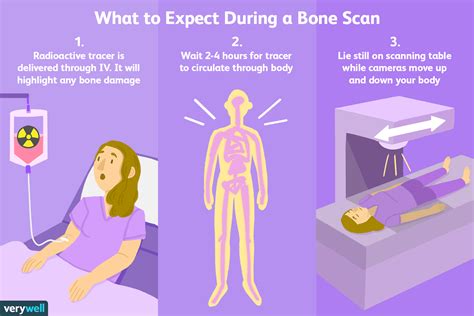
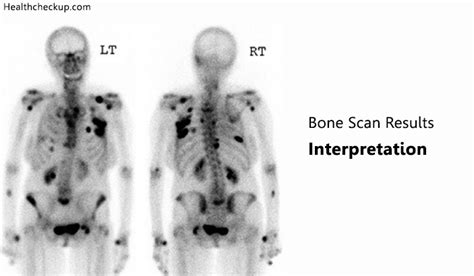
Interpreting Bone Scan Results
Risks and Side Effects

Common Questions About Bone Scans
Some common questions about bone scans include: * What is a bone scan? * How does a bone scan work? * What are the benefits of a bone scan? * What are the risks and side effects of a bone scan? * How do I prepare for a bone scan?Conclusion and Next Steps

What is a bone scan?
+A bone scan is a diagnostic test that uses small amounts of radioactive material to highlight areas of abnormal bone activity.
How does a bone scan work?
+A bone scan works by detecting areas of high bone activity, which is typically indicated by an increased uptake of the radiotracer.
What are the benefits of a bone scan?
+The benefits of a bone scan include early detection of bone metastasis, monitoring the effectiveness of cancer treatment, and non-invasive and relatively painless procedure.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of bone scans for cancer detection. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to your doctor or healthcare provider. Remember, early detection and treatment are key to improving outcomes and quality of life for patients with cancer. Share this article with your loved ones and friends to raise awareness about the importance of bone scans in cancer detection.
