Intro
Discover the potential risks of boric acid, including vaginal irritation, yeast infections, and allergic reactions, and learn how to mitigate these side effects with proper use and precautions.
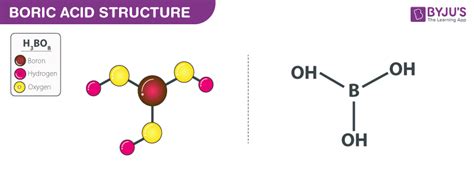
Boric acid, a naturally occurring compound, has been utilized for various purposes, including as an antiseptic, insecticide, and preservative. Its applications range from medical treatments to household pest control. Despite its effectiveness, boric acid can have adverse effects on humans and the environment. Understanding these side effects is crucial for safe and responsible use.
The importance of acknowledging boric acid side effects cannot be overstated. Whether used in pharmaceuticals, as a pesticide, or in personal care products, the potential risks associated with boric acid exposure must be considered. This is particularly true for vulnerable populations, such as children, pregnant women, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions. By delving into the specifics of boric acid side effects, individuals can make informed decisions about its use and take necessary precautions to mitigate potential harm.
Boric acid's versatility and widespread application mean that its side effects can manifest in different ways, depending on the context and extent of exposure. From skin irritation to more severe health complications, the spectrum of potential side effects is broad. Furthermore, environmental concerns related to boric acid use highlight the need for a comprehensive approach to understanding and managing its impacts. As research continues to uncover more about boric acid's effects, staying informed is key to navigating its benefits and risks effectively.
Introduction to Boric Acid
Common Uses of Boric Acid

Boric Acid Side Effects on Human Health

Severe Health Complications
In cases of prolonged or high-level exposure, boric acid can cause more severe health complications, including: - **Kidney Damage:** High doses of boric acid can affect kidney function and lead to kidney damage. - **Reproductive Issues:** There is evidence suggesting that high exposure to boric acid may affect reproductive health, although more research is needed to understand this fully. - **Neurological Effects:** Some studies indicate that boric acid exposure could be associated with neurological effects, such as headaches and dizziness, though the evidence is not conclusive.Environmental Impact of Boric Acid
Precautions and Safe Use
Given the potential side effects of boric acid, it is essential to handle it with care and follow safety guidelines. This includes wearing protective clothing, such as gloves and goggles, when applying boric acid products, and ensuring good ventilation to prevent inhalation of dust or vapors. Additionally, keeping boric acid out of reach of children and pets is crucial, as they may be more susceptible to its toxic effects.Alternatives to Boric Acid
Conclusion and Future Directions
The use of boric acid is a complex issue, with both benefits and drawbacks. As research continues to explore its effects on human health and the environment, it is crucial for users to be aware of the potential side effects and take steps to minimize risks. By adopting safe handling practices, exploring alternative solutions, and staying informed about the latest findings, individuals can navigate the use of boric acid more effectively. Ultimately, a balanced approach that considers both the advantages and the disadvantages of boric acid will be key to maximizing its benefits while protecting health and the environment.What are the common uses of boric acid?
+Boric acid is used in various applications, including as an antiseptic, preservative, and pesticide. It is found in medical treatments, personal care products, and household pest control solutions.
Can boric acid cause severe health complications?
+Yes, exposure to high levels of boric acid can lead to severe health issues, including kidney damage, reproductive problems, and neurological effects. It is essential to handle boric acid with care and follow safety guidelines.
Are there alternatives to boric acid for pest control and personal care?
+Yes, several alternatives to boric acid are available. For pest control, diatomaceous earth and certain essential oils can be effective. In personal care, ingredients like tea tree oil and coconut oil offer antimicrobial properties without the potential risks of boric acid.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with boric acid, including any questions you may have about its safe use or alternatives. Your engagement helps create a more informed community, and we look forward to your comments and feedback. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from understanding the side effects and responsible use of boric acid.
