Intro
The importance of understanding C diff stool cannot be overstated, as Clostridioides difficile (C diff) is a bacterium that can cause symptoms ranging from diarrhea to life-threatening inflammation of the colon. C diff is a common cause of healthcare-associated infections, and its spores can be found in the environment, making it a significant concern for individuals with weakened immune systems. The impact of C diff on public health is substantial, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimating that C diff causes almost half a million infections in the United States each year. As a result, it is crucial to educate oneself about the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for C diff, as well as the importance of prevention and proper hygiene practices.
C diff is often associated with the use of antibiotics, which can disrupt the normal balance of gut bacteria, allowing C diff to overgrow and cause infection. The bacteria produce toxins that can cause a range of symptoms, from mild diarrhea to severe abdominal pain and bloody stools. In severe cases, C diff can lead to pseudomembranous colitis, a condition characterized by inflammation of the colon and the formation of pseudomembranes, which are visible as white or yellowish patches on the colon wall. The severity of C diff symptoms can vary widely, and it is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Understanding the causes and symptoms of C diff is critical for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. C diff spores can survive on surfaces for extended periods, making it essential to practice good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and proper cleaning of surfaces and equipment. Healthcare providers play a critical role in preventing the spread of C diff, as they can take steps to minimize the use of antibiotics and implement infection control measures. By working together, we can reduce the incidence of C diff and improve outcomes for individuals affected by this debilitating infection.
C Diff Stool Testing

C diff stool testing is a critical component of diagnosing and managing C diff infections. There are several types of tests available, including enzyme immunoassays (EIAs), polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests, and stool culture tests. EIAs detect the presence of C diff toxins in stool samples, while PCR tests detect the genetic material of the bacteria. Stool culture tests involve growing the bacteria in a laboratory to confirm the presence of C diff. Each test has its advantages and disadvantages, and healthcare providers may use a combination of tests to confirm a diagnosis.
Types of C Diff Stool Tests
The choice of C diff stool test depends on several factors, including the severity of symptoms, the presence of risk factors, and the clinical setting. Some common types of C diff stool tests include: * Enzyme immunoassays (EIAs): These tests detect the presence of C diff toxins in stool samples and are often used as a screening tool. * Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests: These tests detect the genetic material of the bacteria and are highly sensitive and specific. * Stool culture tests: These tests involve growing the bacteria in a laboratory to confirm the presence of C diff.C Diff Treatment Options
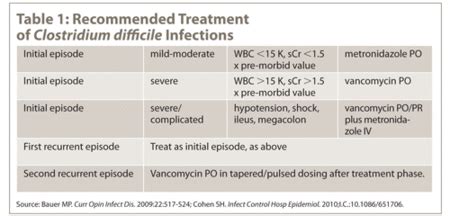
C diff treatment options vary depending on the severity of symptoms and the presence of underlying medical conditions. Mild cases of C diff may be treated with supportive care, such as fluid replacement and rest, while more severe cases may require antibiotic therapy. The most commonly used antibiotics for C diff are vancomycin and fidaxomicin, which are effective against the bacteria and can help reduce the severity of symptoms. In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend a stool transplant, also known as fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), which involves transferring stool from a healthy donor into the colon of the affected individual.
Antibiotic Treatment for C Diff
Antibiotic treatment for C diff is often necessary to manage symptoms and prevent complications. Some common antibiotics used to treat C diff include: * Vancomycin: This antibiotic is effective against C diff and is often used as a first-line treatment. * Fidaxomicin: This antibiotic is also effective against C diff and may be used in cases where vancomycin is not tolerated. * Metronidazole: This antibiotic may be used in cases where vancomycin and fidaxomicin are not effective.C Diff Prevention Strategies

C diff prevention strategies are critical for reducing the incidence of C diff infections. One of the most effective ways to prevent C diff is to practice good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and proper cleaning of surfaces and equipment. Healthcare providers can also take steps to minimize the use of antibiotics and implement infection control measures, such as isolating patients with C diff and using personal protective equipment (PPE) when interacting with them.
Importance of Hand Hygiene
Hand hygiene is essential for preventing the spread of C diff. Some key tips for practicing good hand hygiene include: * Washing hands frequently with soap and water, especially after using the bathroom and before eating. * Using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer when soap and water are not available. * Avoiding touching surfaces and equipment that may be contaminated with C diff spores.C Diff Complications
C diff complications can be severe and life-threatening. Some common complications of C diff include:
- Pseudomembranous colitis: This condition is characterized by inflammation of the colon and the formation of pseudomembranes, which are visible as white or yellowish patches on the colon wall.
- Toxic megacolon: This condition is characterized by a severely inflamed colon that can rupture, leading to life-threatening complications.
- Sepsis: This condition occurs when the infection spreads to the bloodstream, leading to a systemic inflammatory response.
Managing C Diff Complications
Managing C diff complications requires prompt medical attention and aggressive treatment. Some key strategies for managing C diff complications include: * Administering antibiotics and other medications to manage symptoms and prevent further complications. * Providing supportive care, such as fluid replacement and rest. * Implementing infection control measures, such as isolating patients and using PPE.C Diff and Antibiotic Use
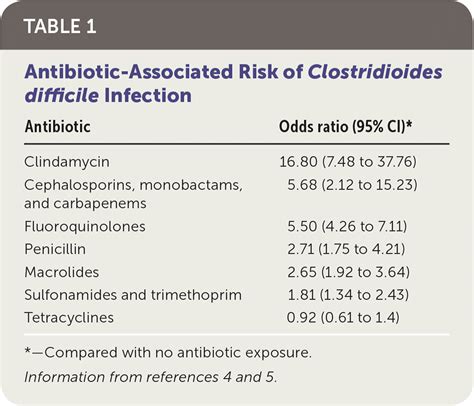
C diff and antibiotic use are closely linked, as the use of antibiotics can disrupt the normal balance of gut bacteria, allowing C diff to overgrow and cause infection. The overuse and misuse of antibiotics are significant contributors to the development of antibiotic-resistant C diff strains, making it essential to use antibiotics judiciously and only when necessary.
Antibiotic Stewardship Programs
Antibiotic stewardship programs are critical for reducing the incidence of C diff and promoting the responsible use of antibiotics. Some key strategies for promoting antibiotic stewardship include: * Implementing antibiotic use guidelines and protocols. * Monitoring antibiotic use and resistance patterns. * Providing education and training for healthcare providers on the responsible use of antibiotics.C Diff and Infection Control

C diff and infection control are closely linked, as the spread of C diff can be prevented through the implementation of effective infection control measures. Some key strategies for preventing the spread of C diff include:
- Isolating patients with C diff.
- Using PPE when interacting with patients.
- Implementing proper cleaning and disinfection protocols.
Importance of Environmental Cleaning
Environmental cleaning is essential for preventing the spread of C diff. Some key tips for environmental cleaning include: * Cleaning and disinfecting surfaces and equipment regularly. * Using a sporicidal disinfectant to kill C diff spores. * Ensuring that cleaning and disinfection protocols are followed consistently.What are the symptoms of C diff?
+The symptoms of C diff can range from mild diarrhea to severe abdominal pain and bloody stools. In severe cases, C diff can lead to pseudomembranous colitis, a condition characterized by inflammation of the colon and the formation of pseudomembranes.
How is C diff diagnosed?
+C diff is diagnosed through a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory testing, and medical history. Laboratory tests may include enzyme immunoassays (EIAs), polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests, and stool culture tests.
What are the treatment options for C diff?
+The treatment options for C diff depend on the severity of symptoms and the presence of underlying medical conditions. Mild cases of C diff may be treated with supportive care, while more severe cases may require antibiotic therapy. In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend a stool transplant, also known as fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT).
How can I prevent C diff?
+C diff can be prevented through the practice of good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and proper cleaning of surfaces and equipment. Healthcare providers can also take steps to minimize the use of antibiotics and implement infection control measures, such as isolating patients with C diff and using PPE.
What are the complications of C diff?
+The complications of C diff can be severe and life-threatening. Some common complications of C diff include pseudomembranous colitis, toxic megacolon, and sepsis. Prompt medical attention and aggressive treatment are essential for managing C diff complications.
In summary, C diff is a significant public health concern that requires prompt attention and aggressive treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for C diff, as well as the importance of prevention and proper hygiene practices, we can reduce the incidence of C diff and improve outcomes for individuals affected by this debilitating infection. If you have any questions or concerns about C diff, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider or comment below. Sharing this article with others can also help raise awareness about the importance of C diff prevention and treatment.
