Intro
Monitor your health with a Blood Sugar Level Chart, tracking glucose levels, diabetes management, and healthy ranges to maintain normal blood sugar control and prevent hyperglycemia.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, as it directly impacts energy levels, weight management, and the risk of developing chronic diseases like diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Understanding blood sugar levels and how they fluctuate throughout the day can help individuals make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and lifestyle. A blood sugar level chart is a valuable tool for tracking and managing blood glucose levels, providing insights into the body's response to different foods, activities, and medications.
Blood sugar levels can vary significantly from person to person, depending on factors such as age, weight, physical activity level, and overall health. For individuals with diabetes, monitoring blood sugar levels is essential to prevent complications and manage the condition effectively. Even for those without diabetes, being aware of blood sugar levels can help identify potential health issues early on, allowing for timely interventions and preventive measures. The importance of blood sugar management extends beyond personal health, as it also has implications for public health and healthcare systems, highlighting the need for education, awareness, and proactive strategies to promote healthy blood sugar levels.
The concept of blood sugar levels is closely linked to the body's metabolic processes, particularly the regulation of glucose, a simple sugar that serves as the primary source of energy for cells. When we consume carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. The pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that facilitates the entry of glucose into cells, thereby lowering blood sugar levels. In individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance, the body either fails to produce enough insulin or becomes less responsive to its effects, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Understanding this complex interplay between glucose, insulin, and the body's cells is essential for appreciating the significance of blood sugar level charts and their role in health management.
Blood Sugar Level Chart: Understanding the Basics
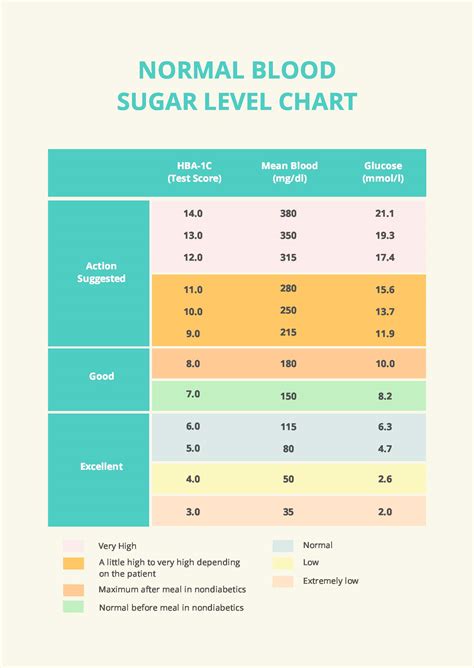
A blood sugar level chart, also known as a blood glucose chart, is a graphical representation of an individual's blood sugar levels over a specific period. It typically includes columns for recording the date, time, blood glucose level, and any relevant notes, such as food consumed, physical activity, or medications taken. By tracking blood sugar levels at different times of the day, individuals can identify patterns and trends, gaining valuable insights into how their body responds to various factors. This information can be used to adjust diet, exercise, and medication regimens, aiming to maintain blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
Key Components of a Blood Sugar Level Chart
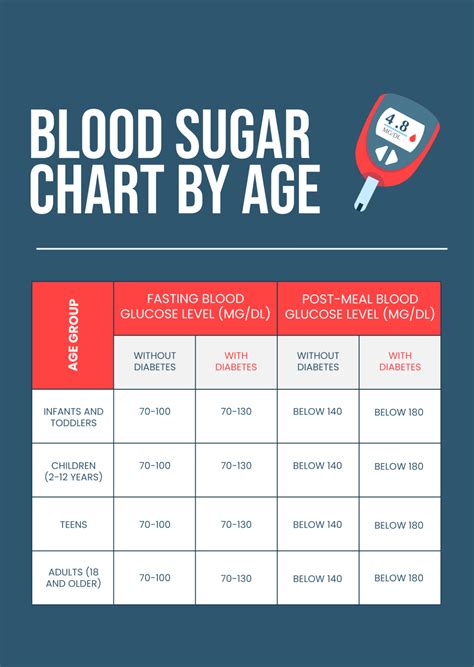
A comprehensive blood sugar level chart should include the following components:
- Date and Time: Recording the date and time of each blood glucose measurement allows for the identification of daily and weekly patterns.
- Blood Glucose Level: The actual measurement of blood sugar, usually expressed in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L).
- Food and Drink: Noting the types and amounts of food and drink consumed can help identify how different nutrients affect blood sugar levels.
- Physical Activity: Recording physical activity, including type, duration, and intensity, can provide insights into how exercise impacts blood glucose levels.
- Medications and Supplements: Listing any medications, supplements, or insulin doses taken can help track their effects on blood sugar levels.
Interpreting Blood Sugar Level Charts
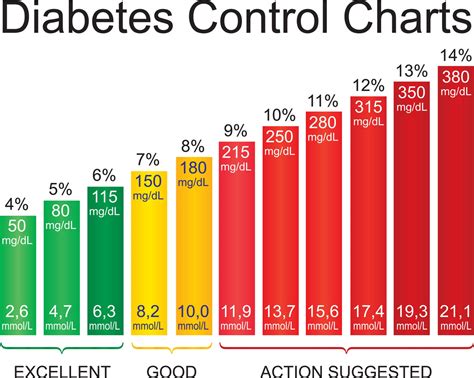
Interpreting a blood sugar level chart requires understanding the normal ranges for blood glucose levels and how they vary throughout the day. For individuals without diabetes, normal blood sugar levels are typically between 70 mg/dL and 140 mg/dL. For those with diabetes, the target range may vary depending on the individual's health goals, age, and other factors, but generally falls between 80 mg/dL and 180 mg/dL before meals and less than 140 mg/dL after meals.
Target Blood Sugar Levels
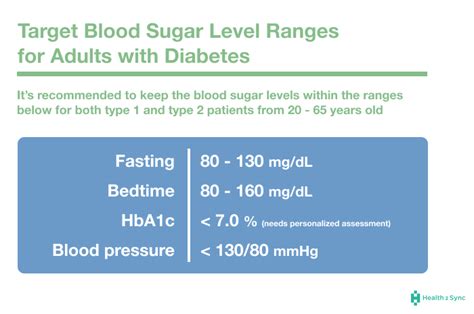
Understanding target blood sugar levels is crucial for effective management:
- Fasting Blood Sugar: Levels should be less than 100 mg/dL for individuals without diabetes and less than 130 mg/dL for those with diabetes.
- Before Meals: Target levels are less than 110 mg/dL for non-diabetics and less than 130 mg/dL for diabetics.
- After Meals: Levels should be less than 140 mg/dL for non-diabetics and less than 180 mg/dL for diabetics.
- At Bedtime: Target levels are less than 100 mg/dL for non-diabetics and less than 140 mg/dL for diabetics.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels

Effective management of blood sugar levels involves a combination of dietary changes, regular physical activity, and, for individuals with diabetes, medication or insulin therapy. A balanced diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium, and high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals can help regulate blood glucose levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, not only helps lower blood sugar levels but also improves insulin sensitivity.
Dietary Recommendations

Key dietary recommendations for managing blood sugar levels include:
- Choose Whole Grains: Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread provide fiber, vitamins, and minerals that help regulate blood sugar.
- Include Lean Protein: Lean protein sources like poultry, fish, and legumes can help stabilize blood glucose levels.
- Eat a Variety of Vegetables: Vegetables are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, and low in calories, making them an ideal component of a blood sugar management diet.
- Healthy Fats: Nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil are rich in healthy fats that support heart health and can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, managing blood sugar levels is a multifaceted process that requires awareness, commitment, and the right strategies. By understanding how to use a blood sugar level chart, interpreting the results, and making informed lifestyle choices, individuals can take significant steps towards maintaining healthy blood glucose levels. Whether you're looking to prevent diabetes, manage the condition, or simply improve your overall health, the insights and recommendations provided here can serve as a valuable starting point.
We invite you to share your experiences, ask questions, or provide feedback on this article. Your engagement can help us better understand your needs and provide more tailored information in the future. Additionally, consider sharing this article with friends, family, or social networks to spread awareness about the importance of blood sugar management and the role of blood sugar level charts in achieving healthier lives.
What is a normal blood sugar level?
+Normal blood sugar levels are typically between 70 mg/dL and 140 mg/dL for individuals without diabetes, but can vary depending on the time of day and other factors.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on your health status and the advice of your healthcare provider, but generally, it's recommended to check levels at least 4 times a day for individuals with diabetes.
What foods can help lower blood sugar levels?
+Foods rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, such as whole grains, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can help regulate and lower blood sugar levels.
