Intro
Discover key facts about heart fluid, including its role in cardiac health, symptoms of excess fluid, and treatments for conditions like pericardial effusion, affecting heart function and overall wellbeing.
The human body is a complex and fascinating system, with various components working together to maintain overall health and function. One often-overlooked aspect of cardiovascular health is the fluid that surrounds the heart, known as pericardial fluid. This fluid plays a crucial role in reducing friction between the heart and surrounding tissues, allowing for smooth movement and efficient pumping of blood. In this article, we will delve into the importance of heart fluid, its functions, and what can happen when it becomes imbalanced.
Heart fluid, or pericardial fluid, is a clear, colorless liquid that fills the space between the heart and the pericardium, a sac that surrounds the heart. This fluid is produced by the pericardium and helps to reduce friction between the heart and surrounding tissues, allowing for smooth movement and efficient pumping of blood. The pericardial fluid also helps to cushion the heart from shock and provides a barrier against infection. With its numerous functions, it is essential to understand the importance of maintaining a healthy balance of heart fluid.
The balance of heart fluid is crucial for maintaining overall cardiovascular health. An imbalance of pericardial fluid can lead to various health issues, including pericarditis, which is inflammation of the pericardium. This condition can cause chest pain, difficulty breathing, and fatigue. In severe cases, an imbalance of heart fluid can lead to cardiac tamponade, a life-threatening condition where the heart is compressed by excess fluid, leading to reduced cardiac output and potentially fatal consequences. Understanding the causes and symptoms of heart fluid imbalances is essential for early detection and treatment.
What is Heart Fluid?

Functions of Heart Fluid
The primary functions of heart fluid include reducing friction between the heart and surrounding tissues, cushioning the heart from shock, and providing a barrier against infection. The pericardial fluid also helps to regulate cardiac function, including heart rate and blood pressure. Additionally, the fluid contains nutrients and waste products, which are essential for maintaining cardiac health. Understanding the functions of heart fluid is crucial for appreciating its importance in maintaining overall cardiovascular health.Causes of Heart Fluid Imbalance
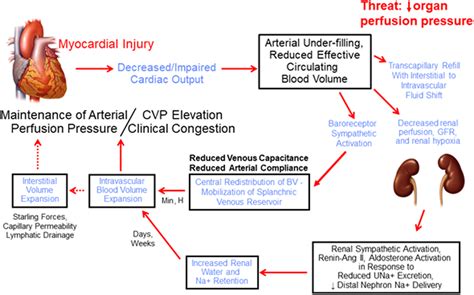
Symptoms of Heart Fluid Imbalance
The symptoms of heart fluid imbalance can vary depending on the underlying cause. Common symptoms include chest pain, difficulty breathing, and fatigue. In severe cases, an imbalance of heart fluid can lead to cardiac tamponade, which can cause symptoms such as low blood pressure, rapid heart rate, and decreased urine output. Understanding the symptoms of heart fluid imbalance is crucial for early detection and treatment.Diagnosis of Heart Fluid Imbalance
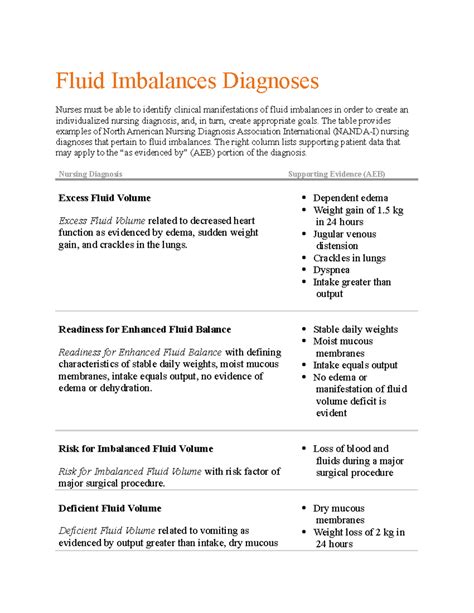
Treatment of Heart Fluid Imbalance
The treatment of heart fluid imbalance depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Mild cases may be treated with medication, such as anti-inflammatory drugs or diuretics, to reduce inflammation and fluid production. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to drain excess fluid or repair any damage to the pericardium. Understanding the treatment options is crucial for managing the condition and preventing complications.Prevention of Heart Fluid Imbalance
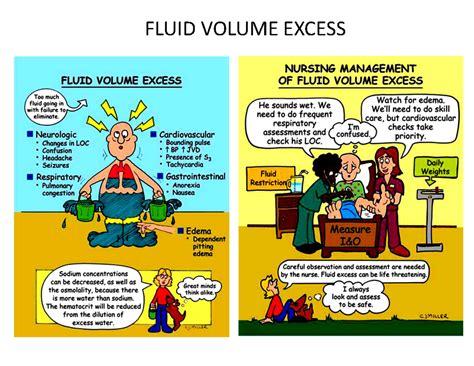
Complications of Heart Fluid Imbalance
The complications of heart fluid imbalance can be severe and potentially life-threatening. Cardiac tamponade, which is a condition where the heart is compressed by excess fluid, can lead to reduced cardiac output, low blood pressure, and decreased urine output. In severe cases, cardiac tamponade can be fatal if left untreated. Understanding the complications of heart fluid imbalance is crucial for early detection and treatment.Management of Heart Fluid Imbalance
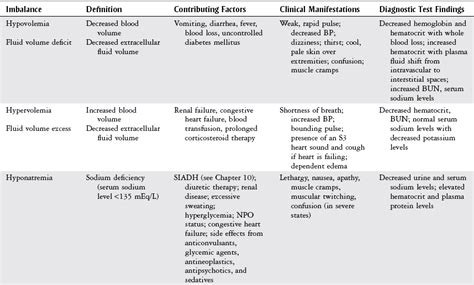
Long-term Outlook for Heart Fluid Imbalance
The long-term outlook for heart fluid imbalance depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Mild cases may have a good prognosis with treatment, while severe cases may have a poorer outlook. Understanding the long-term outlook is essential for managing the condition and preventing complications.Current Research on Heart Fluid Imbalance
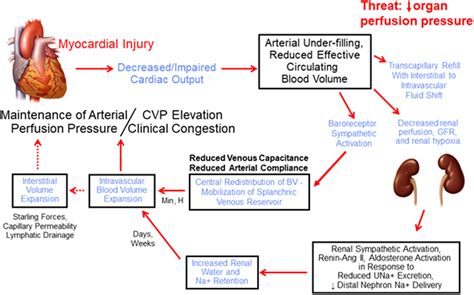
Future Directions for Heart Fluid Imbalance
The future directions for heart fluid imbalance involve continued research and development of new treatments. As our understanding of the underlying causes and mechanisms of the condition improves, new and more effective treatments can be developed. Additionally, advances in technology, such as imaging and diagnostic tests, can help to improve diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the future directions is essential for managing the condition and preventing complications.What is heart fluid?
+Heart fluid, also known as pericardial fluid, is a clear, colorless liquid that surrounds the heart and helps to reduce friction between the heart and surrounding tissues.
What are the symptoms of heart fluid imbalance?
+The symptoms of heart fluid imbalance can vary depending on the underlying cause, but common symptoms include chest pain, difficulty breathing, and fatigue.
How is heart fluid imbalance diagnosed?
+The diagnosis of heart fluid imbalance typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as echocardiography or chest X-ray.
What are the treatment options for heart fluid imbalance?
+The treatment of heart fluid imbalance depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition, but may include medication, lifestyle changes, and surgical intervention.
Can heart fluid imbalance be prevented?
+Preventing heart fluid imbalance involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, as well as avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption.
In conclusion, heart fluid imbalance is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of heart fluid imbalance, individuals can take steps to maintain their cardiovascular health and reduce their risk of complications. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments section below, and to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about heart fluid imbalance. Additionally, we invite readers to explore other resources and articles on our website to learn more about maintaining a healthy heart and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
