Intro
Learn West Nile Virus symptoms, including fever, headache, and rash, and discover prevention methods to reduce risk of infection from mosquito bites, neurological diseases, and encephalitis complications.
The West Nile Virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne disease that has become a significant public health concern in recent years. With its rapid spread across the globe, it is essential to understand the symptoms, causes, and prevention methods of this disease. As we delve into the world of WNV, it becomes clear that knowledge is power, and being informed can save lives. The importance of recognizing the symptoms of WNV cannot be overstated, as prompt medical attention can greatly improve treatment outcomes. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of WNV, including its symptoms, transmission, diagnosis, and prevention methods.
The WNV is a flavivirus that is primarily transmitted through the bite of an infected mosquito. The virus can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and can even be fatal in some cases. As the disease continues to spread, it is crucial to be aware of the symptoms and take necessary precautions to prevent infection. The symptoms of WNV can be divided into two main categories: mild and severe. Mild symptoms include fever, headache, and body aches, while severe symptoms can include encephalitis, meningitis, and acute flaccid paralysis. Understanding these symptoms is vital in seeking medical attention promptly and preventing long-term damage.
As we explore the world of WNV, it becomes clear that prevention is key. By understanding the causes and transmission methods of the disease, we can take necessary precautions to prevent infection. The WNV is primarily transmitted through the bite of an infected mosquito, and preventing mosquito bites is essential in preventing the disease. This can be achieved through the use of insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, and eliminating standing water around the home. By taking these simple steps, we can reduce the risk of infection and prevent the spread of the disease.
Understanding West Nile Virus Symptoms
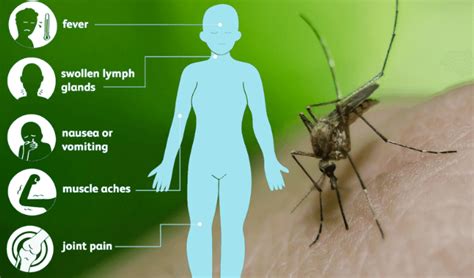
Mild Symptoms of West Nile Virus
Mild symptoms of WNV can include: * Fever * Headache * Body aches * Joint pain * Rash * Swollen lymph glands These symptoms can last for several days and can be treated with over-the-counter medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen. However, it is essential to seek medical attention if the symptoms worsen or last for an extended period.Severe Symptoms of West Nile Virus

Transmission of West Nile Virus
The WNV is primarily transmitted through the bite of an infected mosquito. Mosquitoes become infected with the virus by feeding on birds that carry the virus. The virus is then transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected mosquito. Other modes of transmission include: * Blood transfusions * Organ transplants * Breast milk * Intrauterine transmission (from mother to child during pregnancy)Diagnosis of West Nile Virus
Prevention of West Nile Virus
Preventing WNV is essential in reducing the risk of infection. Some ways to prevent WNV include: * Using insect repellents that contain DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus * Wearing protective clothing such as long-sleeved shirts and pants * Eliminating standing water around the home to reduce mosquito breeding sites * Installing or repairing screens on windows and doors to keep mosquitoes out * Avoiding outdoor activities during peak mosquito hours (dawn and dusk)Treatment of West Nile Virus

Complications of West Nile Virus
Complications of WNV can include: * Encephalitis (inflammation of the brain) * Meningitis (inflammation of the lining around the brain and spinal cord) * Acute flaccid paralysis (a condition that causes muscle weakness or paralysis) * DeathConclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with WNV in the comments section below. Have you or someone you know been affected by WNV? What steps do you take to prevent mosquito bites and reduce the risk of infection? Share your stories and tips with us, and let's work together to raise awareness about this important public health issue.
What are the symptoms of West Nile Virus?
+The symptoms of WNV can range from mild to severe and include fever, headache, body aches, joint pain, rash, and swollen lymph glands. Severe symptoms can include encephalitis, meningitis, and acute flaccid paralysis.
How is West Nile Virus transmitted?
+WNV is primarily transmitted through the bite of an infected mosquito. Other modes of transmission include blood transfusions, organ transplants, breast milk, and intrauterine transmission.
Can West Nile Virus be prevented?
+Yes, WNV can be prevented by taking simple steps such as using insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, eliminating standing water around the home, and installing or repairing screens on windows and doors.
What is the treatment for West Nile Virus?
+There is no specific treatment for WNV, and treatment is typically focused on relieving symptoms and supporting the body's immune system. Mild symptoms can be treated with over-the-counter medications, while severe symptoms may require hospitalization and supportive care.
Can West Nile Virus be fatal?
+Yes, WNV can be fatal, especially in people with weakened immune systems or underlying medical conditions. It is essential to seek medical attention promptly if symptoms occur.
