Intro
Unlock the secrets of a CBC blood test with our comprehensive guide, covering complete blood count, blood cell analysis, and hematocrit testing for accurate diagnosis and treatment of blood disorders.
The complete blood count (CBC) test is a fundamental diagnostic tool used by healthcare professionals to assess a patient's overall health and detect various medical conditions. It is a common blood test that provides valuable information about the different components of blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. In this article, we will delve into the world of CBC blood tests, exploring their importance, components, and interpretation.
A CBC test is usually performed as part of a routine medical examination or when a patient presents with symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, or infection. The test is also used to monitor patients with underlying medical conditions, such as anemia, leukemia, or blood clotting disorders. By analyzing the different components of blood, healthcare professionals can gain insights into a patient's health and make informed decisions about diagnosis, treatment, and management.
The importance of CBC tests cannot be overstated, as they provide a comprehensive overview of a patient's blood profile. The test is relatively simple and non-invasive, requiring only a small blood sample from a vein in the arm. The results of a CBC test can help healthcare professionals diagnose a range of medical conditions, from mild anemia to life-threatening blood disorders. In addition, the test can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and adjust medication regimens as needed.
What is a CBC Test?

Components of a CBC Test
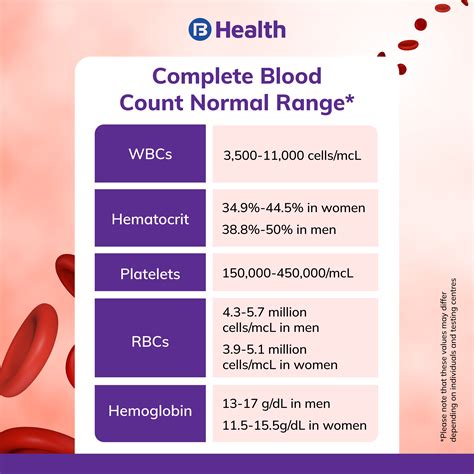
A CBC test typically includes the following components: * Red blood cell count (RBC) * Hemoglobin (Hb) * Hematocrit (Hct) * Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) * Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) * Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) * White blood cell count (WBC) * Differential count (Diff) * Platelet count (Plt)Each of these components provides valuable information about the patient's blood profile and can help healthcare professionals diagnose and manage various medical conditions.
How is a CBC Test Performed?
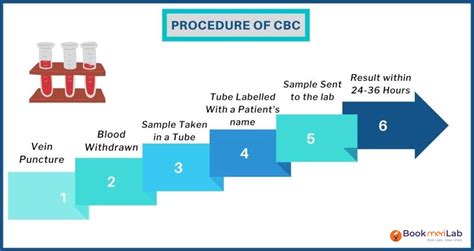
The laboratory analysis typically involves the following steps:
- Blood collection: A small blood sample is drawn from a vein in the arm.
- Blood preparation: The blood sample is prepared for analysis by adding anticoagulants and other chemicals to prevent clotting and preserve the cells.
- Cell counting: The different components of blood are counted using specialized equipment, such as automated analyzers.
- Cell sizing: The size and shape of the cells are measured using specialized equipment, such as flow cytometers.
- Data analysis: The results of the CBC test are analyzed and compared to a reference range to determine if any abnormalities are present.
Interpretation of CBC Test Results
The interpretation of CBC test results requires a thorough understanding of the different components of blood and their reference ranges. The results of a CBC test are usually reported in a standardized format, with each component measured and compared to a reference range.Here are some general guidelines for interpreting CBC test results:
- Red blood cell count (RBC): A low RBC count may indicate anemia, while a high RBC count may indicate dehydration or polycythemia.
- White blood cell count (WBC): A low WBC count may indicate immunosuppression or bone marrow failure, while a high WBC count may indicate infection or inflammation.
- Platelet count (Plt): A low platelet count may indicate thrombocytopenia or bleeding disorders, while a high platelet count may indicate thrombocytosis or blood clotting disorders.
Common Abnormalities Detected by CBC Tests
Limitations of CBC Tests
While CBC tests are a valuable diagnostic tool, they have several limitations. For example: * CBC tests may not detect all types of anemia or blood disorders. * CBC tests may not provide information about the underlying cause of a medical condition. * CBC tests may be affected by various factors, such as medication, diet, or lifestyle.Special Considerations for CBC Tests

Preparing for a CBC Test
To prepare for a CBC test, patients should: * Fast for at least 8 hours before the test. * Avoid taking certain medications, such as anticoagulants or antibiotics. * Inform their healthcare provider about any medical conditions or allergies. * Wear comfortable clothing and avoid tight clothing that may interfere with the blood draw.Conclusion and Next Steps
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with CBC tests in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns about CBC tests, please do not hesitate to ask. You can also share this article with friends and family members who may be interested in learning more about CBC tests.
What is a CBC test?
+A CBC test is a blood test that measures the different components of blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
What are the components of a CBC test?
+The components of a CBC test include red blood cell count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, mean corpuscular volume, mean corpuscular hemoglobin, mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration, white blood cell count, differential count, and platelet count.
How is a CBC test performed?
+A CBC test is performed by drawing a small blood sample from a vein in the arm and analyzing it in a laboratory using specialized equipment and techniques.
