Intro
Discover the physical symptoms of stress, including anxiety, fatigue, headaches, and digestive issues, and learn how to manage stress-related disorders, tension, and emotional overwhelm for overall well-being.
Stress is a natural response of the body to a perceived threat or pressure, and it can manifest in various ways, affecting not only our mental health but also our physical well-being. The physical symptoms of stress can be subtle at first, but if left unchecked, they can escalate into more severe health issues. Understanding the physical symptoms of stress is crucial for taking proactive steps to manage stress and prevent its detrimental effects on our overall health.
The human body is equipped with a complex stress response system, often referred to as the "fight or flight" response. When we perceive a threat, our body releases stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol, preparing us to either confront the threat or flee from it. While this response is vital for survival, chronic activation of the stress response can lead to a myriad of physical symptoms. These symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe pain and can affect various systems of the body, including the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and musculoskeletal systems.
The impact of stress on our physical health is multifaceted and can be observed in our daily lives. For instance, stress can affect our sleep patterns, leading to insomnia or excessive sleepiness, which in turn can affect our mood, energy levels, and ability to concentrate. Furthermore, chronic stress can weaken our immune system, making us more susceptible to illnesses and infections. It is essential to recognize the physical symptoms of stress to take appropriate measures to mitigate its effects and maintain a healthy balance between our mental and physical well-being.
Common Physical Symptoms Of Stress

The physical symptoms of stress can vary widely among individuals, but there are several common symptoms that many people experience. These include headaches, muscle tension, and gastrointestinal problems such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Stress can also lead to changes in appetite, with some people experiencing weight loss due to decreased appetite, while others may gain weight due to increased cravings for comfort foods. Moreover, stress can affect our cardiovascular health, leading to high blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, and an increased risk of heart disease.
Cardiovascular Symptoms
Stress has a significant impact on our cardiovascular system. When we are under stress, our body releases stress hormones that prepare our body for the "fight or flight" response. This leads to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure, which can be beneficial in the short term but detrimental if experienced chronically. Chronic stress can lead to the development of hypertension (high blood pressure), which is a significant risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. Furthermore, stress can also lead to the release of inflammatory markers, which can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis (the buildup of plaque in the arteries), further increasing the risk of cardiovascular events.Impact Of Stress On The Gastrointestinal System
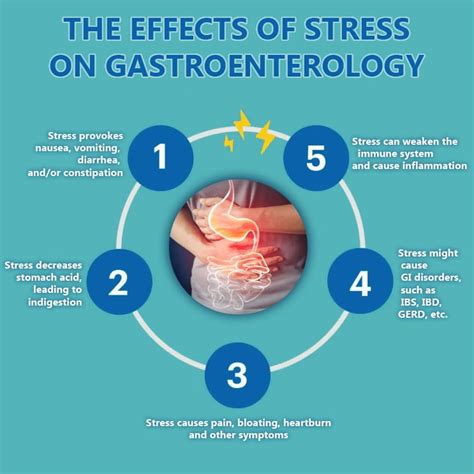
The gastrointestinal (GI) system is another area of the body that is significantly affected by stress. Stress can lead to a range of GI symptoms, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), acid reflux, and stomach ulcers. The exact mechanism by which stress affects the GI system is not fully understood, but it is believed that stress can alter the functioning of the gut-brain axis, leading to changes in gut motility, inflammation, and the composition of the gut microbiota. These changes can result in symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits.
Musculoskeletal Symptoms
Muscle tension is one of the most common physical symptoms of stress. When we are under stress, our muscles become tense, preparing our body for action. This muscle tension can lead to pain and stiffness in various parts of the body, including the neck, back, and shoulders. Chronic muscle tension can also lead to the development of musculoskeletal disorders such as tendinitis and bursitis. Moreover, stress can exacerbate existing musculoskeletal conditions, making them more painful and debilitating.Managing Physical Symptoms Of Stress

Managing the physical symptoms of stress requires a multifaceted approach that incorporates lifestyle changes, stress management techniques, and professional help when necessary. Regular exercise is a crucial component of stress management, as it can help reduce muscle tension, improve mood, and enhance sleep quality. Additionally, practices such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help mitigate the effects of stress on the body. Maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and getting enough sleep are also essential for managing stress and preventing its physical symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes For Stress Management
Making lifestyle changes is an effective way to manage stress and alleviate its physical symptoms. This includes adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, which can help support immune function and reduce inflammation. Limiting the intake of processed foods, sugars, and caffeine, which can exacerbate stress and its physical symptoms, is also recommended. Furthermore, engaging in regular physical activity, practicing good sleep hygiene, and taking regular breaks throughout the day can help reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being.Seeking Professional Help

While lifestyle changes and stress management techniques can be effective in managing the physical symptoms of stress, there are times when seeking professional help is necessary. If stress is impacting daily life, causing significant distress, or leading to severe physical symptoms, it may be helpful to consult with a healthcare professional. Therapists, counselors, and psychologists can provide guidance on stress management, offer support, and help individuals develop coping strategies. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage symptoms of stress and anxiety.
The Role Of Mindfulness In Stress Management
Mindfulness practices, such as mindfulness meditation and mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), have been shown to be effective in reducing stress and its physical symptoms. Mindfulness involves paying attention to the present moment in a non-judgmental way, which can help reduce worry about the future or regrets about the past. Regular mindfulness practice can lead to a decrease in stress hormones, an improvement in mood, and an enhancement in overall well-being. Additionally, mindfulness can increase self-awareness, allowing individuals to better recognize the signs of stress and take proactive steps to manage it.Conclusion And Future Directions

In conclusion, the physical symptoms of stress are a significant concern that can affect various aspects of our health and well-being. Understanding these symptoms and taking proactive steps to manage stress is essential for preventing its detrimental effects. By incorporating lifestyle changes, stress management techniques, and seeking professional help when necessary, individuals can effectively manage the physical symptoms of stress and improve their overall quality of life. Future research should continue to explore the complex relationship between stress and physical health, focusing on the development of novel stress management interventions and the promotion of stress resilience.
A Call To Action
It is crucial for individuals to take an active role in managing stress and its physical symptoms. This involves being aware of the signs of stress, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and seeking help when needed. By prioritizing stress management and overall well-being, we can reduce the risk of stress-related illnesses, improve our quality of life, and enhance our resilience to stress. Let us work together to promote stress awareness, support stress management initiatives, and foster a culture that values and prioritizes mental and physical health.What are the most common physical symptoms of stress?
+The most common physical symptoms of stress include headaches, muscle tension, gastrointestinal problems, changes in appetite, and sleep disturbances.
How does stress affect the cardiovascular system?
+Stress can lead to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure, which can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease if experienced chronically.
What lifestyle changes can help manage stress and its physical symptoms?
+Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and stress management techniques like meditation and deep breathing can help manage stress and its physical symptoms.
We invite you to share your experiences and insights on managing stress and its physical symptoms. Your comments and questions can help others who may be facing similar challenges. Let's work together to create a supportive community that prioritizes mental and physical well-being. Please feel free to share this article with others who may benefit from this information, and let's continue the conversation on social media using relevant hashtags.
