Intro
Learn about checking stool samples, including stool test procedures, fecal analysis, and gut health diagnostics to identify digestive issues and diseases like gastrointestinal infections.
The analysis of stool samples is a crucial diagnostic tool in the field of gastroenterology and healthcare. Stool tests can help identify a range of health issues, from infections and inflammatory conditions to digestive disorders and even certain types of cancer. The importance of checking stool samples lies in their ability to provide valuable insights into the body's digestive health, enabling healthcare professionals to make accurate diagnoses and develop effective treatment plans.
The process of analyzing a stool sample involves a series of tests designed to detect various substances, organisms, or abnormalities that may indicate a health problem. These tests can include microscopic examinations, cultural tests, and chemical analyses, among others. By examining the physical characteristics, consistency, and composition of a stool sample, healthcare professionals can gather significant information about a patient's digestive health and overall well-being.
In recent years, advances in medical technology have led to the development of more sophisticated and non-invasive methods for analyzing stool samples. These advancements have improved the accuracy and efficiency of stool testing, making it a more valuable tool in the diagnosis and management of various health conditions. As research continues to uncover the complexities of the human gut microbiome, the importance of stool analysis is likely to grow, offering new insights into the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases.
Introduction to Stool Analysis
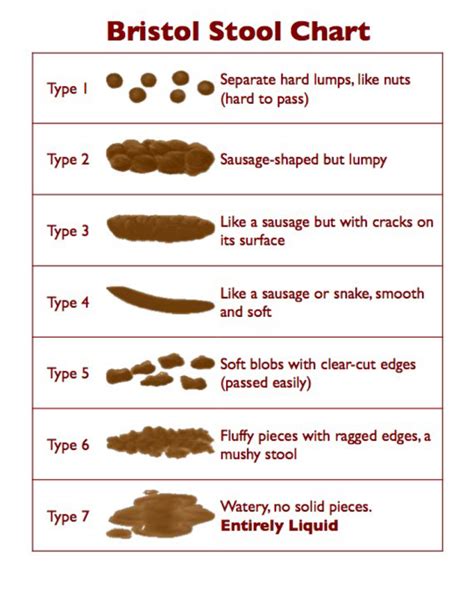
Types of Stool Tests
There are several types of stool tests, each designed to detect specific substances, organisms, or conditions. Some of the most common types of stool tests include: * Fecal occult blood test (FOBT): This test detects hidden blood in the stool, which can be a sign of colorectal cancer or other gastrointestinal disorders. * Stool culture: This test involves culturing a stool sample to identify the presence of bacteria, viruses, or other microorganisms that may cause infections. * Ova and parasite exam: This test is used to detect the presence of parasites, such as worms or protozoa, in the stool. * Fecal fat test: This test measures the amount of fat in the stool, which can help diagnose conditions such as malabsorption or pancreatic insufficiency.The Benefits of Stool Analysis

How Stool Analysis Works
The process of stool analysis typically involves the following steps: 1. Collection of the stool sample: The patient is typically asked to collect a stool sample at home, using a special container or kit provided by the healthcare provider. 2. Preparation of the sample: The stool sample is then prepared for testing, which may involve mixing it with a preservative or other substances to help preserve the sample. 3. Laboratory testing: The prepared sample is then sent to a laboratory for testing, where it is examined using various techniques, such as microscopy or culturing. 4. Interpretation of results: The results of the stool test are then interpreted by a healthcare professional, who uses the information to make a diagnosis or develop a treatment plan.Common Conditions Diagnosed with Stool Analysis
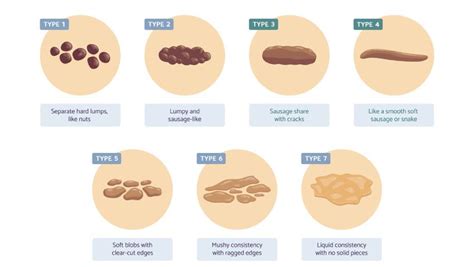
Limitations and Risks of Stool Analysis
While stool analysis is a valuable diagnostic tool, it is not without limitations and risks. Some of the potential limitations and risks of stool analysis include: * False negatives: Stool tests may not always detect the presence of a particular substance or organism, even if it is present. * False positives: Stool tests may also produce false positive results, which can lead to unnecessary treatment or further testing. * Contamination: Stool samples can become contaminated with bacteria or other substances, which can affect the accuracy of the test results. * Discomfort: Collecting a stool sample can be uncomfortable or embarrassing for some patients.Advances in Stool Analysis Technology

Future Directions for Stool Analysis
The future of stool analysis is likely to involve the continued development of more advanced and non-invasive testing methods. Some potential future directions for stool analysis include: * Personalized medicine: Stool analysis may be used to develop personalized treatment plans that take into account an individual's unique genetic profile and gut microbiome. * Prevention: Stool analysis may be used to identify individuals who are at risk of developing certain health conditions, allowing for early intervention and prevention. * Point-of-care testing: The development of point-of-care stool testing devices may allow healthcare professionals to perform stool tests in the clinic or office, providing faster and more convenient results for patients.Conclusion and Recommendations

We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with stool analysis in the comments section below. Have you undergone a stool test? What were your experiences? Do you have any questions or concerns about stool analysis? Share your stories and help us raise awareness about the importance of stool testing in maintaining good digestive health.
What is stool analysis?
+Stool analysis, also known as stool testing or fecal testing, is a diagnostic procedure used to examine the contents of a patient's stool.
What are the benefits of stool analysis?
+Stool analysis offers several benefits, including early detection and diagnosis of health issues, accurate diagnosis, monitoring of treatment, and prevention of complications.
What are the common conditions diagnosed with stool analysis?
+Stool analysis can be used to diagnose a range of health conditions, including infections, inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, and colorectal cancer.
