Intro
Discover how Clonidine is used to treat anxiety, reducing symptoms of stress and panic attacks, while also exploring its effects on blood pressure and ADHD management.
Anxiety is a prevalent mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can manifest in various forms, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder, among others. While there are several treatments available for anxiety, including therapy and medication, one medication that has gained attention for its potential in managing anxiety symptoms is clonidine. Clonidine is primarily known as a blood pressure medication, but its use has expanded to include the treatment of anxiety disorders, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and certain pain conditions. Understanding how clonidine works and its potential benefits and side effects can provide valuable insights into its role in managing anxiety.
The use of clonidine for anxiety is based on its mechanism of action, which involves stimulating certain receptors in the brain that help to reduce symptoms of anxiety and stress. By activating these receptors, clonidine can produce a calming effect, which can be particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing anxiety. Moreover, clonidine's ability to reduce blood pressure and heart rate can also contribute to its anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) effects, as these physical symptoms are often associated with anxiety attacks. The versatility of clonidine in treating various conditions, including anxiety, underscores its potential as a valuable therapeutic agent.
Given the complexity of anxiety disorders and the varied responses individuals may have to different treatments, it is essential to explore all available options, including medications like clonidine. The effectiveness of clonidine in reducing anxiety symptoms, coupled with its relatively favorable side effect profile compared to some other anxiolytic medications, makes it a worthwhile consideration for those seeking relief from anxiety. Furthermore, the fact that clonidine is not classified as a controlled substance reduces the risk of dependence, a significant concern with some anti-anxiety medications. This aspect of clonidine's pharmacological profile can provide reassurance to patients and healthcare providers alike, making it a more appealing option for long-term management of anxiety.
Introduction to Clonidine

Clonidine is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs known as centrally acting alpha-2 adrenergic agonists. It was initially developed and is primarily used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). By stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain, clonidine decreases the sympathetic nervous system activity, which in turn lowers blood pressure and heart rate. This mechanism of action also underlies its potential in treating anxiety and other conditions. The use of clonidine for anxiety is off-label, meaning it is not approved by the FDA specifically for this purpose, but healthcare providers may prescribe it based on clinical judgment and patient response.
How Clonidine Works for Anxiety
The anxiolytic effects of clonidine are thought to result from its action on the brain's alpha-2 adrenergic receptors. These receptors play a role in regulating the body's stress response, including the release of neurotransmitters like norepinephrine, which can contribute to feelings of anxiety. By activating these receptors, clonidine can help reduce the release of norepinephrine and other stress hormones, thereby decreasing anxiety symptoms. This mechanism is distinct from that of traditional anxiolytics, such as benzodiazepines, which work by enhancing the effect of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain.Benefits of Using Clonidine for Anxiety
There are several benefits to using clonidine for anxiety, including its potential to provide rapid relief from anxiety symptoms, its relatively favorable side effect profile, and its lack of potential for dependence. Additionally, clonidine can be used in conjunction with other medications, including antidepressants, to enhance their anxiolytic effects. This flexibility in treatment regimens can be particularly useful for patients who have not responded adequately to first-line treatments or who experience significant side effects from traditional anxiolytics.
Some key benefits of clonidine for anxiety include:
- Rapid onset of action: Clonidine can start to reduce anxiety symptoms quickly, often within a few hours of administration.
- Low risk of dependence: Unlike some other anti-anxiety medications, clonidine does not carry a high risk of dependence or withdrawal symptoms.
- Versatility in dosing: Clonidine is available in various formulations, including tablets, patches, and injectable forms, allowing for flexible dosing regimens.
- Potential for use in combination therapy: Clonidine can be used alongside other medications to treat anxiety, offering a tailored approach to managing symptoms.
Potential Side Effects of Clonidine
While clonidine is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects, some of which may be dose-dependent. Common side effects include: - Drowsiness or sedation - Dry mouth - Dizziness or lightheadedness - Constipation - Fatigue - HeadacheIn rare cases, clonidine can cause more severe side effects, such as rebound hypertension (a sudden and severe increase in blood pressure) if the medication is stopped abruptly. It is essential for patients to work closely with their healthcare provider to monitor side effects and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
Clonidine Dosage for Anxiety
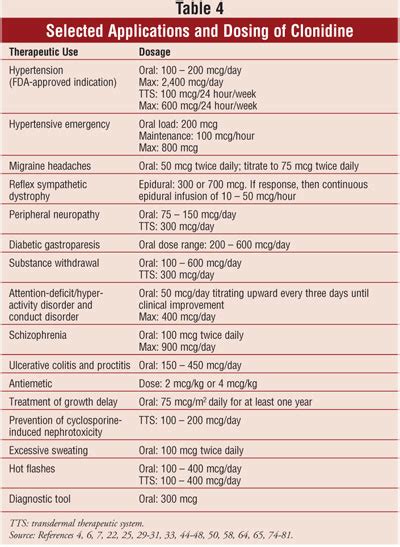
The dosage of clonidine for anxiety can vary depending on the individual patient's response and the severity of their symptoms. Typically, treatment is started with a low dose, which can be gradually increased until the desired therapeutic effect is achieved or side effects become limiting. The oral form of clonidine is usually administered two to three times a day, while the transdermal patch is applied once a week.
It is crucial for patients to follow the prescribed dosage regimen and not to adjust their dose without consulting their healthcare provider. Abrupt cessation of clonidine can lead to withdrawal symptoms, including rebound hypertension, anxiety, and insomnia, among others.
Combination Therapy with Clonidine
Clonidine is often used in combination with other medications to treat anxiety, particularly in cases where monotherapy (use of a single medication) is not sufficient to control symptoms. The choice of combination therapy depends on the patient's specific condition, the severity of their symptoms, and their response to previous treatments. Common combinations include: - Clonidine with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): SSRIs are a type of antidepressant that can also be effective in treating anxiety disorders. Adding clonidine to an SSRI regimen may enhance anxiolytic effects. - Clonidine with benzodiazepines: In some cases, clonidine may be used alongside benzodiazepines for short-term management of severe anxiety. However, this combination should be used cautiously due to the potential for increased sedation and the risk of dependence associated with benzodiazepines.Alternatives to Clonidine for Anxiety

While clonidine can be an effective treatment for anxiety, it may not be suitable or effective for everyone. Fortunately, there are several alternative treatments available, including:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): A type of psychotherapy that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors contributing to their anxiety.
- Medications: Other classes of medications, such as SSRIs, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), and benzodiazepines, can be used to treat anxiety disorders.
- Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, sufficient sleep, and stress management techniques (e.g., meditation, yoga) can help reduce anxiety symptoms.
It is essential for individuals to discuss their treatment options with a healthcare provider to determine the best approach for their specific needs and circumstances.
Future Directions in Anxiety Treatment
The landscape of anxiety treatment is continually evolving, with ongoing research into new medications, therapies, and lifestyle interventions. Some promising areas of research include the development of novel anxiolytic medications with improved efficacy and safety profiles, the use of digital therapies (e.g., online CBT platforms), and the exploration of alternative approaches such as mindfulness-based stress reduction and acupuncture.As our understanding of the neurobiological mechanisms underlying anxiety disorders grows, so too does the potential for targeted and more effective treatments. The role of clonidine in anxiety treatment highlights the importance of considering off-label uses of medications and the value of a multidisciplinary approach to managing mental health conditions.
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, clonidine represents a valuable option for the treatment of anxiety, offering a unique mechanism of action and a relatively favorable side effect profile. While it may not be suitable for everyone, its use, either alone or in combination with other therapies, can provide significant relief from anxiety symptoms. As with any medication, it is crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan and to monitor progress and side effects.
For those interested in learning more about clonidine and its use in anxiety treatment, consulting with a healthcare professional is the first step. They can provide personalized advice and guidance, helping individuals make informed decisions about their mental health care.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with anxiety treatment in the comments below. Your insights can help others who may be navigating similar challenges. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information.
What is clonidine, and how does it work for anxiety?
+Clonidine is a medication primarily used to treat high blood pressure but is also used off-label for anxiety. It works by stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain, which helps reduce the release of stress hormones and thereby decreases anxiety symptoms.
What are the common side effects of clonidine?
+Common side effects of clonidine include drowsiness, dry mouth, dizziness, constipation, fatigue, and headache. In rare cases, it can cause more severe side effects, such as rebound hypertension if stopped abruptly.
Can clonidine be used in combination with other medications for anxiety?
+Yes, clonidine can be used in combination with other medications, such as SSRIs, to enhance their anxiolytic effects. However, the decision to use combination therapy should be made under the guidance of a healthcare provider to ensure safety and efficacy.
